1114. Data Structure - DequeDeque
Implement deque with linked list and circular array.
1. Deque
1.1 Real-life Example
Undo and Redo function in text editor.
1.2 Deque in Programming Terms
A double-ended queue (abbreviated to deque) is an abstract data type that generalizes a queue, for which elements can be added to or removed from either the front (head) or back (tail). It has four principal operations:
addFirst: add an element to the headaddLast: add an element to the tailremoveFirst: remove the first elementremoveLast: remove the last element
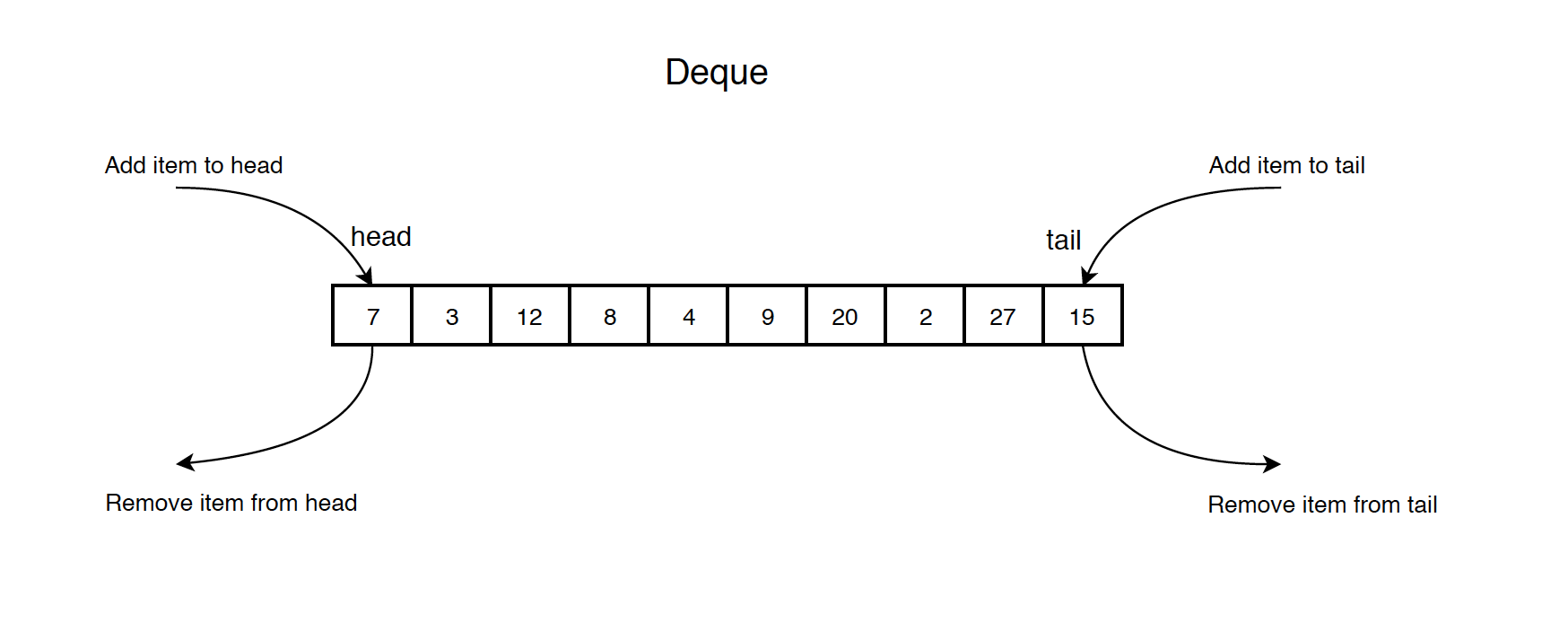
1.3 Common Operations on Queue
- addFirst(item): Add an item to the head of the list.
- addLast(item): Add an item to the tail of the list.
- removeFirst(): Pull the first item out of the list.
- removeLast(): Pull the last item out of the list.
- peekFirst(): Return the first item of the deque.
- peekLast(): Return the last item of the deque.
- isEmpty(): Return true if the deque is empty.
1.4 Time Complexity
- addFirst: $O(1)$
- addLast: $O(1)$
- removeFirst: $O(1)$
- removeLast: $O(1)$
- peekFirst: $O(1)$
- peekLast: $O(1)$
2. Implementation
2.1 Using Linked List
Define Node.
public class ListNode {
public int val;
public ListNode prev;
public ListNode next;
public ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
this.prev = null;
this.next = null;
}
}
Implement Deque.
public class LinkedListDeque {
private ListNode head; // the first node
private ListNode tail; // the last node
public LinkedListDeque() {
head = null;
tail = null;
}
// Add item to the head of the list
public void addFirst(int value) {
if (head == null) {
head = new ListNode(value);
tail = head;
} else {
head.prev = new ListNode(value);
head.prev.next = head;
head = head.prev;
}
}
// Remove the head from the list and return its value
public int removeFirst() throws Exception {
if (head == null) {
throw new Exception();
}
int value = head.val;
head = head.next;
if (head != null) {
head.prev = null;
} else {
tail = null;
}
return value;
}
// Get the value of the head
public int peekFirst() throws Exception {
if (head == null) {
throw new Exception();
}
return head.val;
}
// Add item to the tail of the list
public void addLast(int value) {
if (tail == null) {
tail = new ListNode(value);
head = tail;
} else {
tail.next = new ListNode(value);
tail.next.prev = tail;
tail = tail.next;
}
}
// Remove the tail from the list and return its value
public int removeLast() throws Exception {
if (tail == null) {
throw new Exception();
}
int value = tail.val;
tail = tail.prev;
if (tail != null) {
tail.next = null;
} else {
head = null;
}
return value;
}
// Get the value of the tail
public int peekLast() throws Exception {
if (tail == null) {
throw new Exception();
}
return tail.val;
}
// Return whether the deque is empty
public boolean isEmpty() {
return head == null || tail == null;
}
}
2.2 Using Circular Array
Use MOD to get the new position.
public class CircularArrayDeque {
private int head; // the first node in deque, not the first item in array
private int tail; // the last node in deque, not the first item in array
private int[] arr;
private int size;
public CircularArrayDeque(int capacity) {
arr = new int[capacity];
head = 0;
tail = 0;
size = 0;
}
// Add item to the head of the deque
public void addFirst(int value) {
// check if deque is full
if (isFull()) {
return;
}
head = head - 1;
if (head < 0) {
head = arr.length - 1;
}
arr[head] = value;
size += 1;
}
// Remove the first item from the deque and return its value
public int removeFirst() throws Exception {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new Exception("Circular Array Deque is empty when dequeue!");
}
int value = arr[head];
head = (head + 1) % arr.length;
size -= 1;
return value;
}
// Get the first item
public int peekFirst() throws Exception {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new Exception("Circular Array Deque is empty when peek!");
}
return arr[head];
}
// Add item to the end of the deque
public void addLast(int value) {
// check if deque is full
if (isFull()) {
return;
}
tail = (head + size) % arr.length;
arr[tail] = value;
size += 1;
}
// Remove the last item from the deque and return its value
public int removeLast() throws Exception {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new Exception("Circular Array Deque is empty when dequeue!");
}
int value = arr[tail];
tail = tail - 1;
if (tail < 0) {
tail = arr.length - 1;
}
size -= 1;
return value;
}
// Get the last item
public int peekLast() throws Exception {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new Exception("Circular Array Deque is empty when peek!");
}
return arr[tail];
}
// Return whether the queue is full
public boolean isFull() {
return size == arr.length;
}
// Return whether the queue is empty
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
}