1126. Data Structure - TrieTrie and Prefix Tree
Implement trie for word search.
1. Trie
1.1 Definition of Trie
A Trie (pronounced try) or Prefix Tree is an ordered tree in which characters are stored at each node. Each path down the tree may represent a word.
1.2 Usage of Trie
Very commonly, a trie is used to store the entire (English) language for quick prefix lookups. While a hash table can quickly look up whether a string is a valid word, however it cannot tell us if a string is a prefix of any valid words. A trie can do this very quickly.
Below picture shows how words are stored in trie. This trie stores five words: dog, dot, pump, fat, fire. Each node has a hashmap and a flag to indicate whether the current node is a leaf(a complete path for a word).
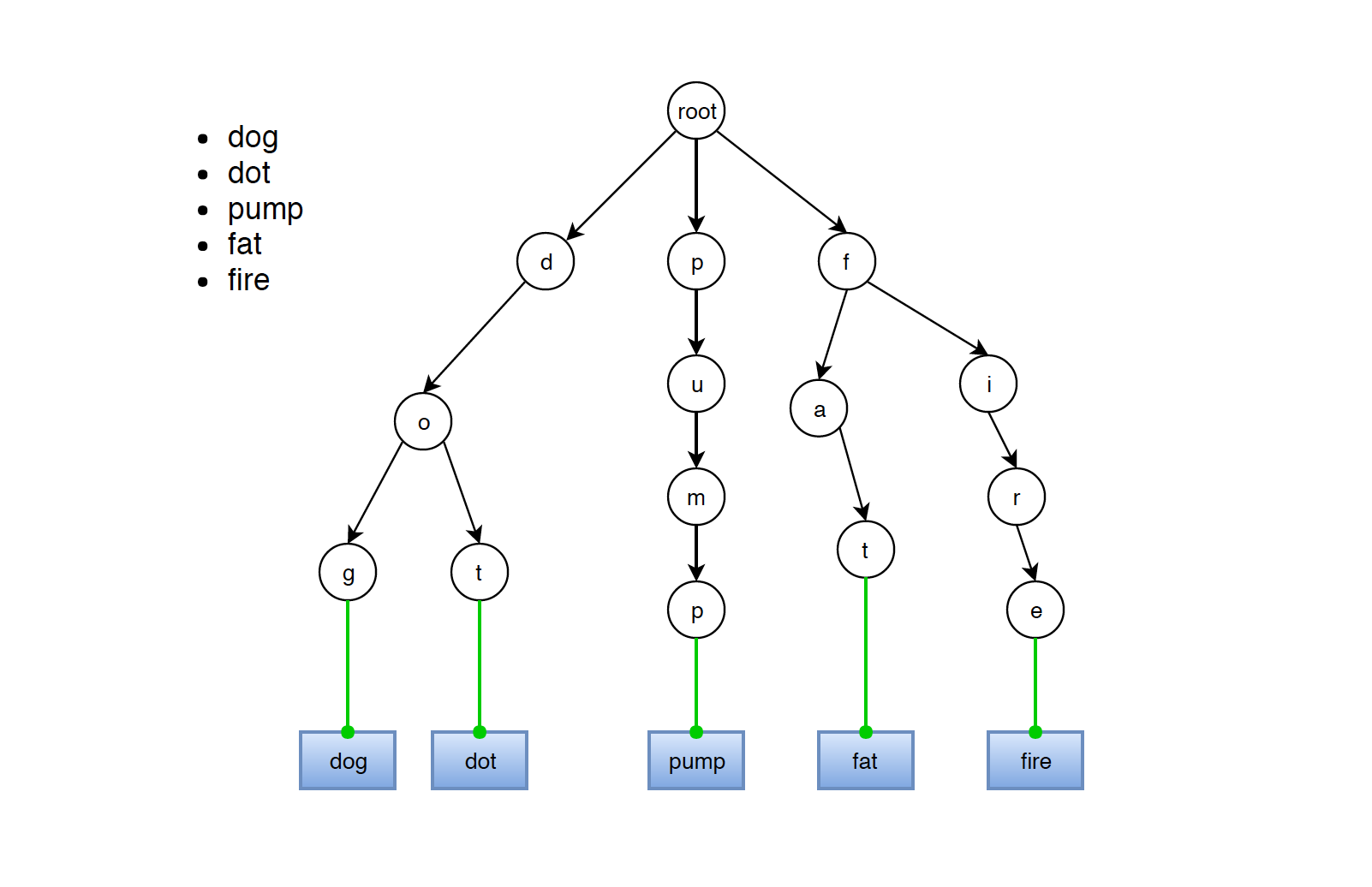
- In trie, each path from root to any node represents a word.
- It is not necessary that leaf has to be the node without children. For example, suppose ‘dog’ and ‘dot’ are words in this trie. Then, node ‘g’ and node ‘t’ are obviously marked as leaves. If word ‘do’ is also in this trie, then node ‘o’ is also marked as leaf, even if it has two children, ‘g’ and ‘t’.
1.3 Common Operations on Trie
- Search
- Insertion
- Deletion
2. Search
Given a trie as follows, search word ‘dot’.
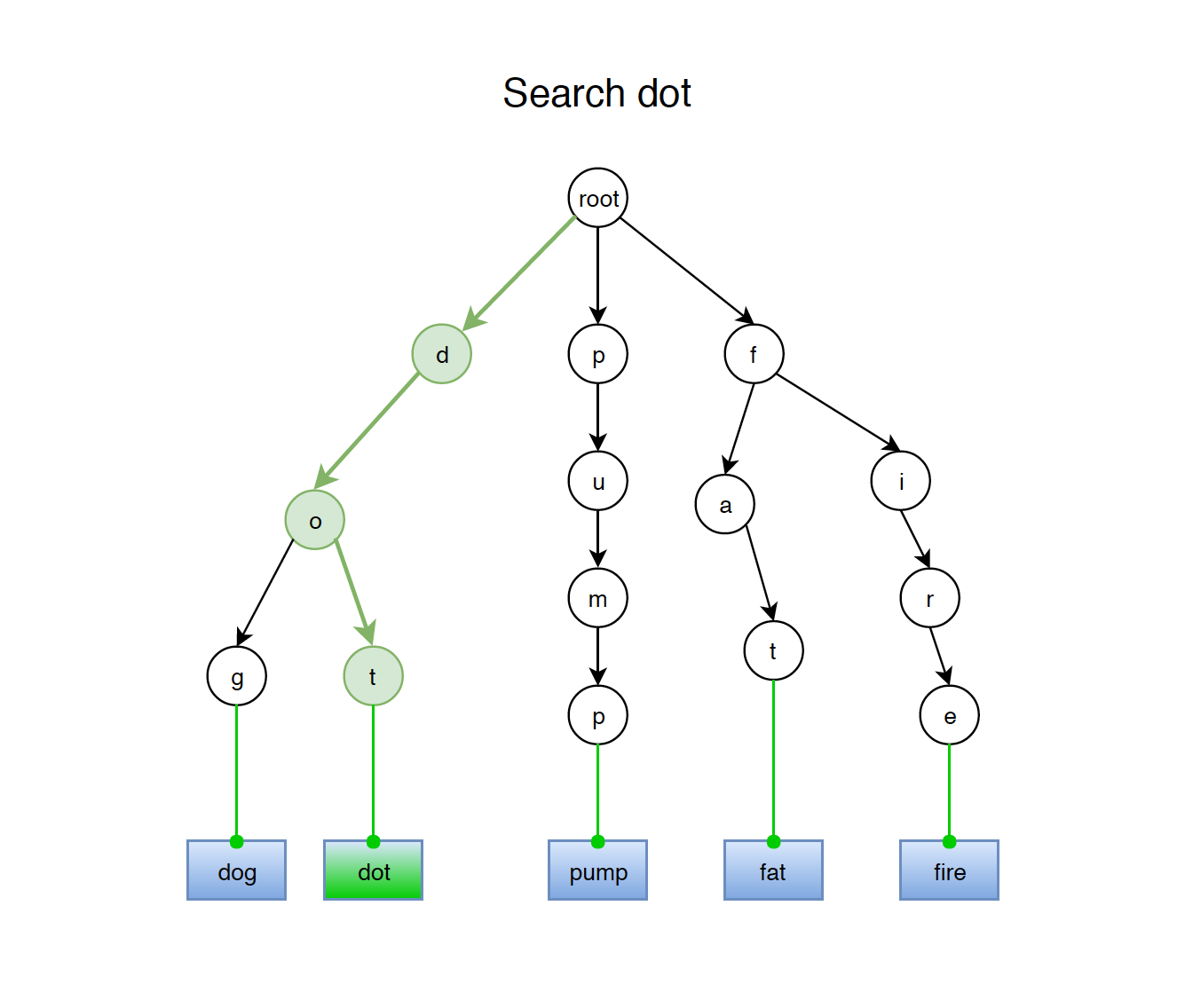 There are two search approaches in trie.
There are two search approaches in trie.
- Find whether the given word exists.
- Find whether any word starts with the given prefix exists.
Both approaches have the similar search pattern. To search a given word in Trie, we first convert the word to chars. Then start comparing each of them with trie node from root. If the current character is present in the node, move forward to its children. Recursively doing this until all of the characters are found.
Trie is constructed with nodes recursively. The following example shows how Trie node is defined.
public class TrieNode {
public Map<Character, TrieNode> children;
public boolean leaf;
public TrieNode() {
children = new HashMap<Character, TrieNode>();
leaf = false;
}
}
2.1 Searching Prefix
// Return true if there is any word in trie that starts with the given prefix
public boolean startsWith(String prefix) {
if (searchNode(prefix) == null) {
return false;
} else {
return true;
}
}
private TrieNode searchNode(String str) {
TrieNode current = root;
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
char ch = str.charAt(i);
if (current.children.containsKey(ch)) {
current = current.children.get(ch);
} else {
return null;
}
}
return current;
}
2.2 Searching Entire Word
Similar with prefix search, add additional check whether the node is leaf.
// Return true if the word is in trie
public boolean search(String word) {
TrieNode tn = searchNode(word);
if (tn != null && tn.leaf) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
2.3 Searching Words with Same Prefix
Return all words which start with the given prefix, check if the node is leaf.
// Return all words which start with the given prefix
public List<String> searchWords(String prefix) {
TrieNode current = root;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < prefix.length(); i++) {
char ch = prefix.charAt(i);
if (!current.children.containsKey(ch)) {
return null;
} else {
sb.append(ch);
current = current.children.get(ch);
}
}
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
dfs(current, sb.toString(), list);
return list;
}
private void dfs(TrieNode node, String prefix, List<String> list) {
if (node.leaf) {
list.add(prefix);
}
for (Map.Entry<Character, TrieNode> entry : node.children.entrySet()) {
dfs(entry.getValue(), prefix + entry.getKey(), list);
}
}
3. Insertion
Given a trie as follows, insert new word ‘firm’ into this trie.
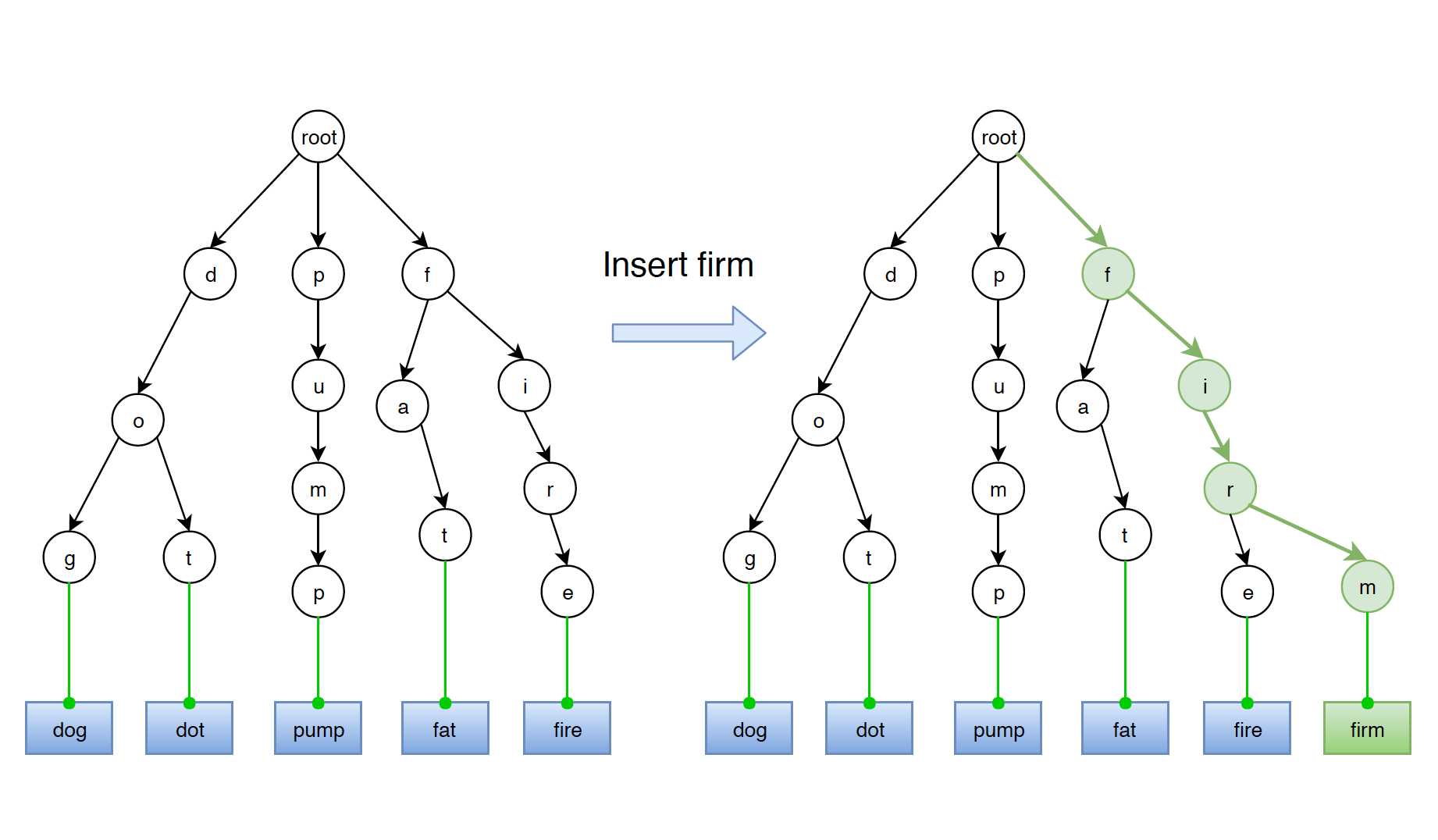 We start searching the given word from root till we cannot find one particular character. Then we construct new trie nodes recursively for the rest characters. In the end, set the leaf attribute of the last node to true.
We start searching the given word from root till we cannot find one particular character. Then we construct new trie nodes recursively for the rest characters. In the end, set the leaf attribute of the last node to true.
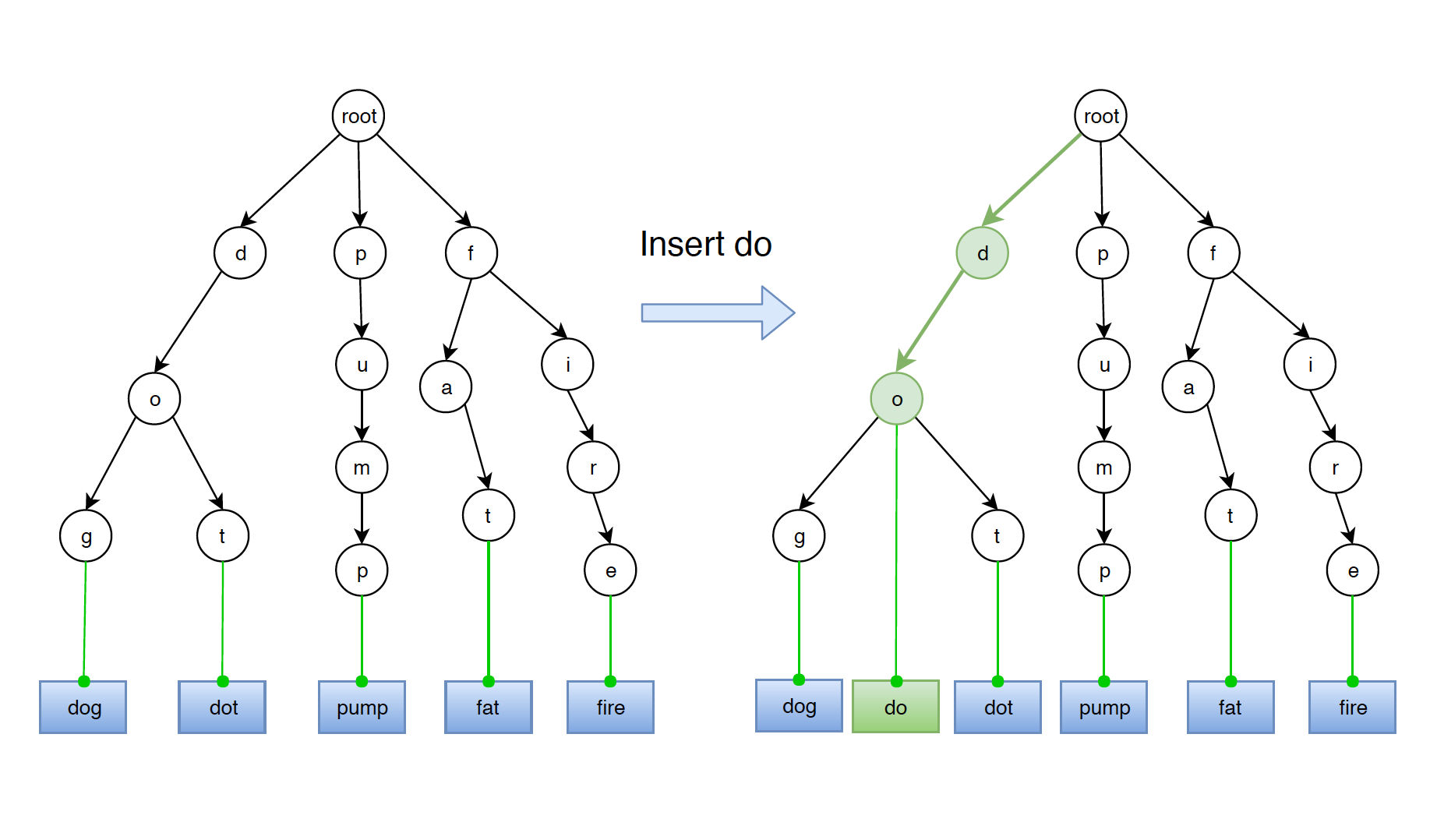
One case needs to be noticed here. If the new word(eg. ‘do’) is prefix of other words(word ‘do’ is prefix of word ‘dot’), we just need to mark the last node(eg. node ‘o’) of the new word as leaf without creating any new node. Even though node ‘o’ has children, it is marked as leaf since the path from root to node ‘o’ represents word ‘do’.
 Below is the implementation of the insert method.
Below is the implementation of the insert method.
// Insert a word into trie
public void insert(String word) {
TrieNode current = root;
for (int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++) {
char ch = word.charAt(i);
if (!current.children.containsKey(ch)) {
current.children.put(ch, new TrieNode());
}
current = current.children.get(ch);
}
current.leaf = true;
}
4. Deletion
There are three cases when deleting a word from Trie.
- Word is prefix of other words.
- Word has prefix of other words.
- Word is unique, neither it is prefix of other words, nor it has prefix of other words.
4.1 Word Is Prefix of Other Words
Word ‘do’ is the prefix of word ‘dot’ and ‘dog’.
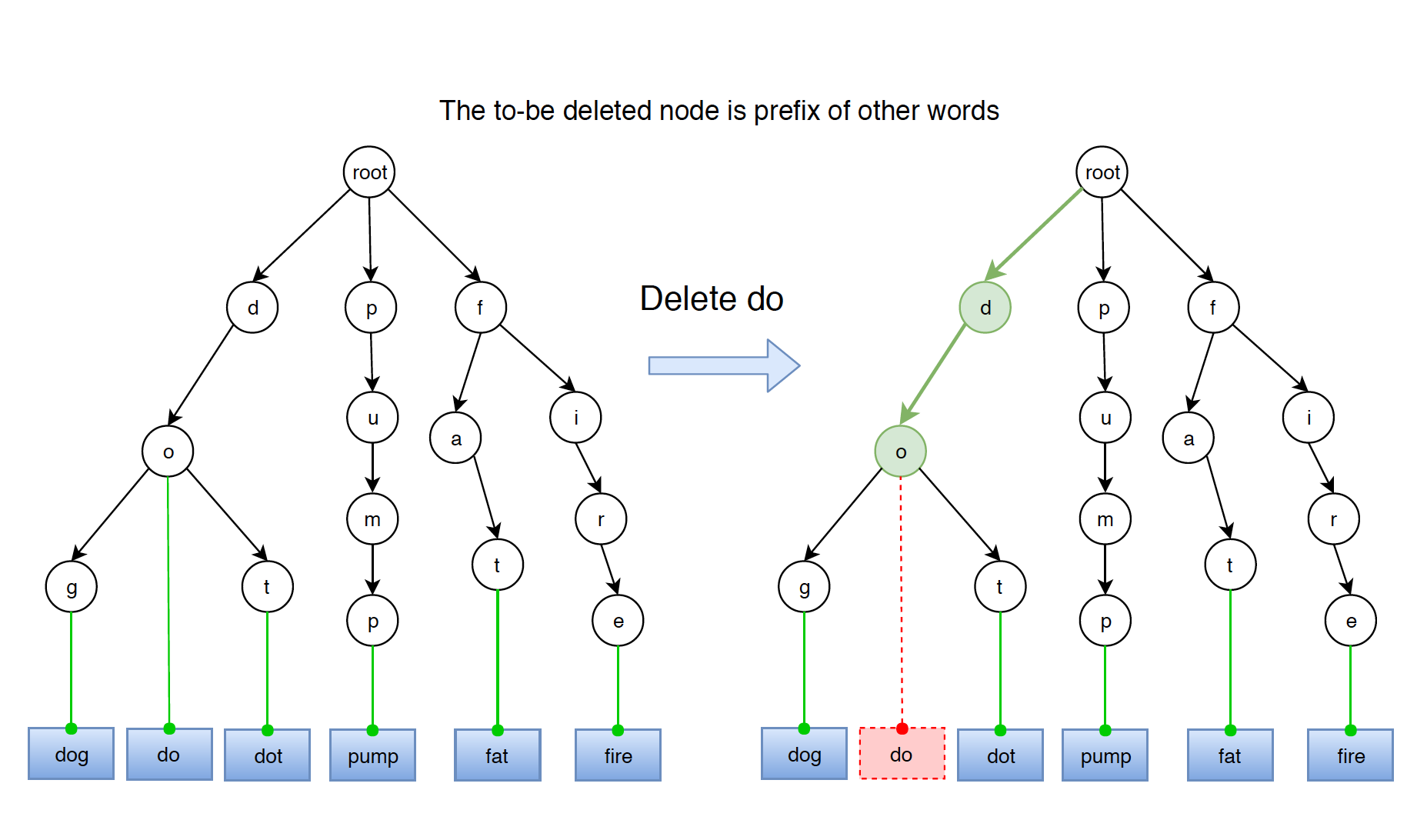 The solution is easy, just unmark the leaf node. The leaf node for word ‘do’ is node ‘o’.
The solution is easy, just unmark the leaf node. The leaf node for word ‘do’ is node ‘o’.
4.2 Word Has Prefix of Other Words
Word ‘fat’ has same prefix with word ‘fire’. They share the prefix ‘f’.
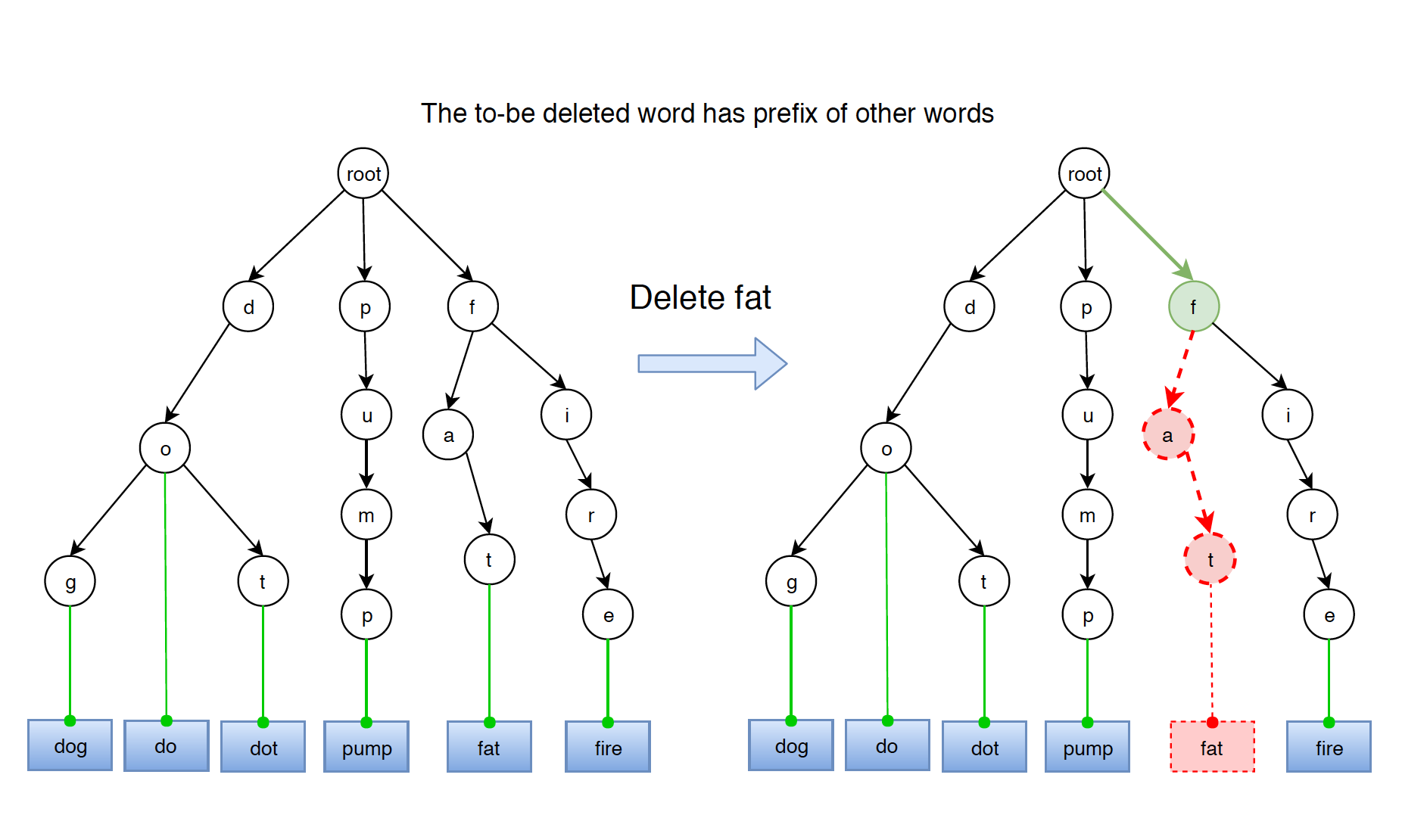 If word has prefix of other words, then delete nodes from prefix to end of the word.
If word has prefix of other words, then delete nodes from prefix to end of the word.
4.3 Word Is Unique
Word ‘pump’ is a standalone word. It doesn’t share any prefix with others.
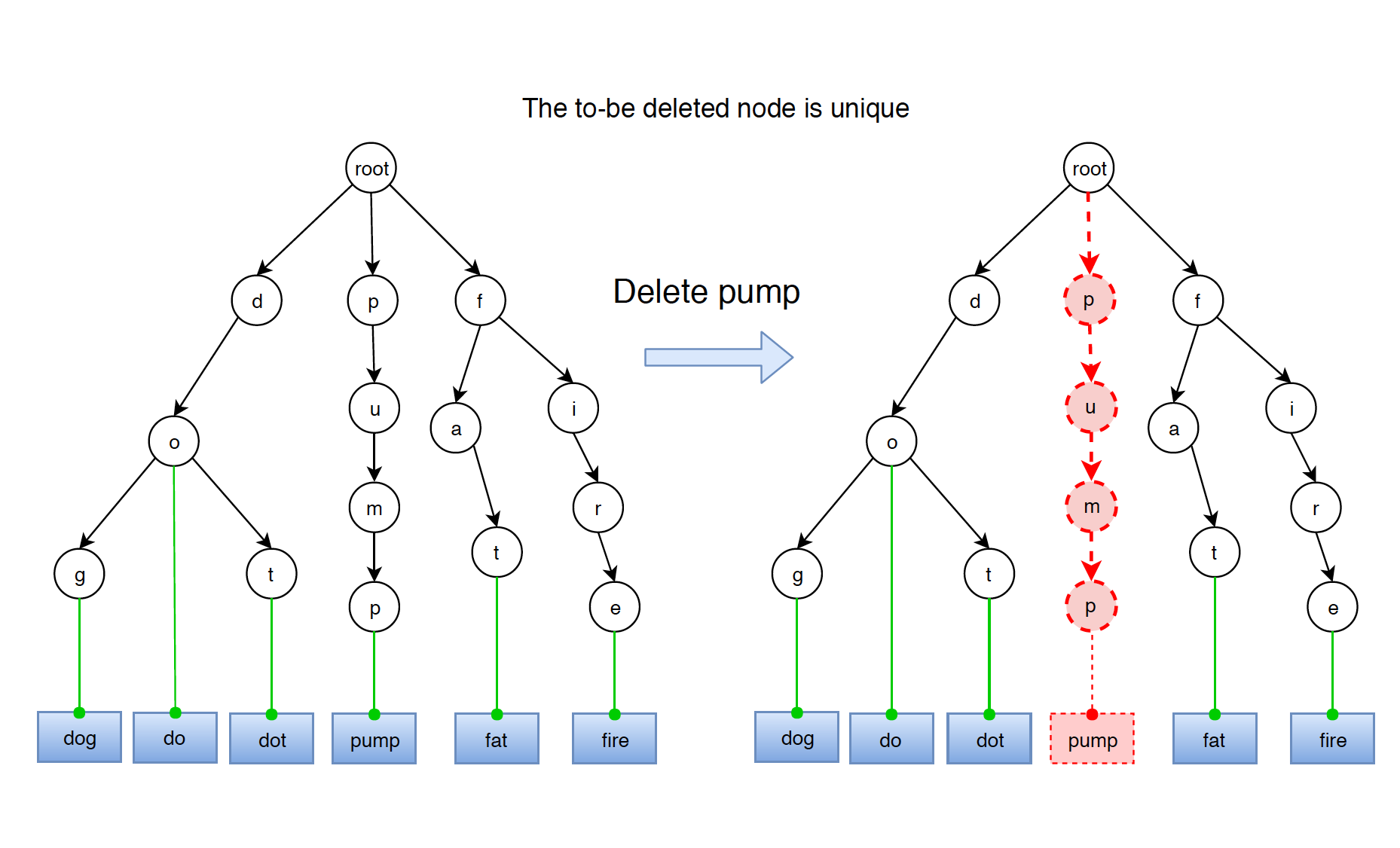 If word neither is prefix of other words, nor has prefix of other words, then just delete all the nodes.
If word neither is prefix of other words, nor has prefix of other words, then just delete all the nodes.
The following implementation covers all above scenarios.
public boolean delete(String word) {
TrieNode current = root;
TrieNode lastBranchNode = null;
Character lastBrachChar = null;
for (int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++) {
char ch = word.charAt(i);
if (current.children.containsKey(ch)) {
if (current.children.size() > 1) {
lastBranchNode = current;
lastBrachChar = ch;
}
current = current.children.get(ch);
} else {
// word not found
return false;
}
}
if (current.children.size() > 0) {
// case 1: The to-be deleted word is prefix of another long word in trie.
current.leaf = false;
return true;
}
if (lastBranchNode != null) {
// case 2: The to-be deleted word has other words as prefix
lastBranchNode.children.remove(lastBrachChar);
return true;
} else {
// case 3: The to-be deleted word present as unique word
root.children.remove(word.charAt(0));
return true;
}
}
5. Trie Variants
5.1 Trie Node
If the words contains only lower-case letters, then we can define Trie Node with array instead of hashmap.
public class TrieNode {
public TrieNode[] children;
public boolean leaf;
public TrieNode() {
children = new TrieNode[26];
leaf = false;
}
}