2402. Java Concurrency - MultiThreadingThread and Runnable
Use Thread class and Runnable interface to create thread.
1. How to Create a Thread with Java?
Java lets you create thread in following two ways:
- By implementing the
Runnableinterface. - By extending the
Threadclass.
1.1 Runnable Interface
public interface Runnable {
void run();
}
Create a new class to implement Runnable interface.
public class MyRunnable implements Runnable {
public void run(){
System.out.println("MyRunnable is running ...");
}
}
Then, create thread with the instance of MyRunnable as input parameter.
Thread thread = new Thread(new MyRunnable());
thread.start();
Output.
MyRunnable is running ...
1.2 Thread Class
Create a new class to extend Thread class.
public class MyThread extends Thread {
public void run() {
System.out.println("MyThread is running ...");
}
}
Then, create an instance for this MyThread class and run it.
MyThread myThread = new MyThread();
myThread.start();
Output.
MyThread is running ...
1.3 Methods in Thread class
- getName() - Obtain thread’s name
- getPriority() - Obtain thread’s priority
- isAlive() - Determine if a thread is still running
- join() - Wait for a thread to terminate
- run() - Entry point for the thread
- sleep() - Suspend a thread for a period of time
- start() - Start a thread by calling its run method
1.4 Daemon Threads
A daemon is simply a thread that has no other role in life than to serve others. Examples are timer threads that send regular ‘timer ticks’ to other threads or threads that clean up stale cache entries.
t.setDaemon(true);
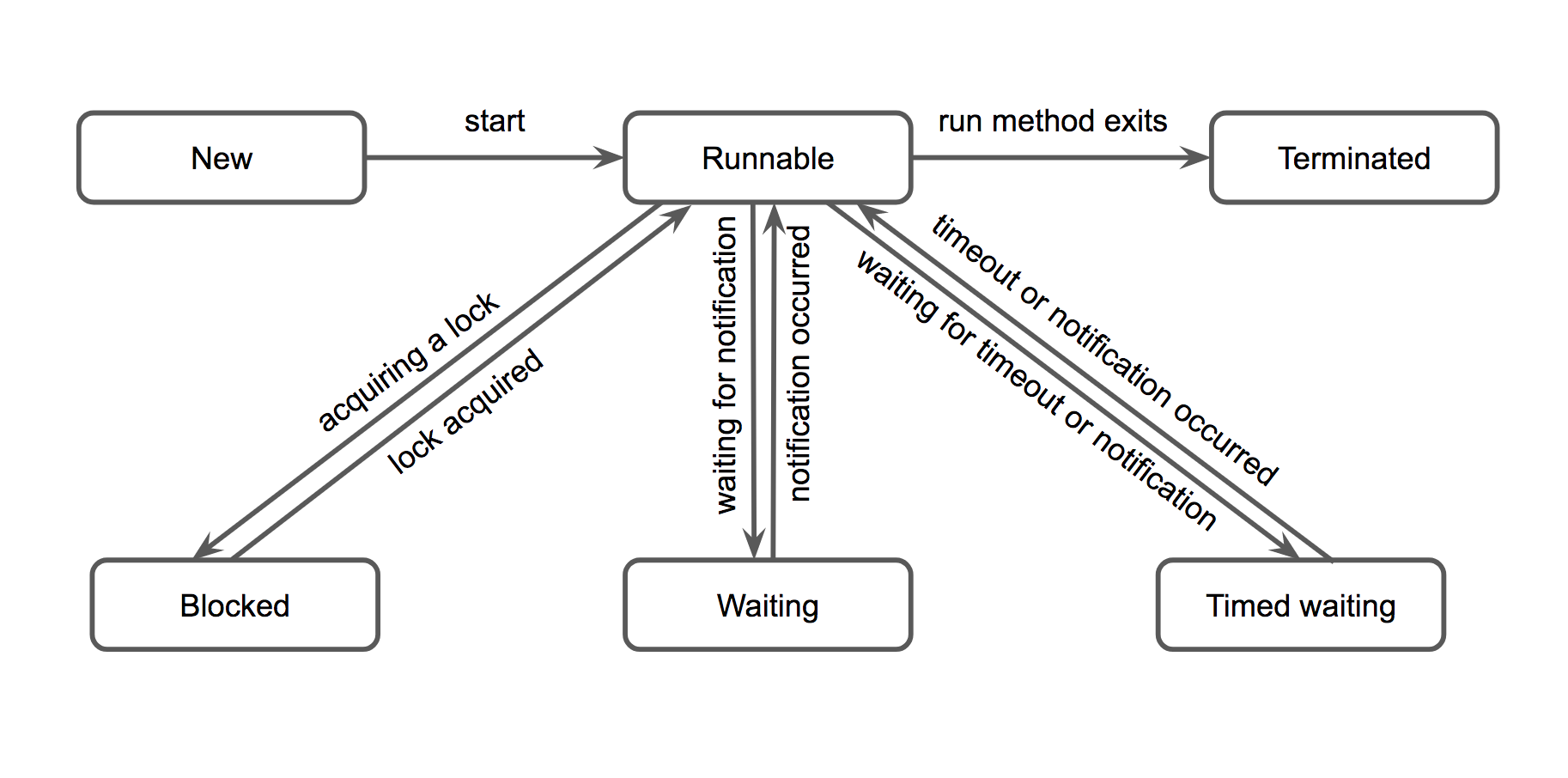
2. Thread States
New- When a new thread is created, it is in the new state. (new Thread();)Runnable- A thread that is ready to run is moved to runnable state. (t1.run();)Blocked- When a thread is temporarily inactive, e.g. (require a lock)Waiting- When a thread is temporarily inactive, e.g. (wait on a condition);Timed Waiting- A thread lies in timed waiting state when it calls a method with a time out parameter. (Thread.sleep(1000);)Terminated- A thread terminates because of either of the following reasons: Normally exits or interrupted.