3502. Installing Docker Toolbox and Kitematic on MacDocker and Kitematic
Use Kitematic to easily manage docker containers without using Docker command-line.
1. What is Docker Toolbox?
The Docker Toolbox is an installer to quickly and easily install and setup a Docker environment on your computer.
Toolbox includes these Docker tools:
- Docker Machine for running docker-machine commands
- Docker Engine for running the docker commands
- Docker Compose for running the docker-compose commands
- Kitematic, the Docker GUI
- a shell preconfigured for a Docker command-line environment
- Oracle VirtualBox
2. What is Kitematic?
Kitematic is an open source project built to simplify and streamline using Docker on a Mac or Windows PC. Kitematic automates the Docker installation and setup process and provides an intuitive graphical user interface (GUI) for running Docker containers. Kitematic integrates with Docker Machine to provision a VirtualBox VM and install the Docker Engine locally on your machine. You can find its source files repository on GitHub.
3. Installing Docker Toolbox
Go to https://www.docker.com/products/docker-toolbox, select the installer for Mac. Download and follow the wizard to install.
Note:
- If you’ve already installed Oracle VirtualBox on your Mac, then this component won’t be installed.
- You don’t need to install Kitematic separately, it is installed as you install Docker Toolbox.
After the installation is finished. You can launch Kitematic.
4. Terminals
It’s necessary to understand the structure of docker and what terminal can access it.
4.1 Without Virtual Machine
If you install docker manually, like what I did for Ubuntu mentioned in the posting Installing and Using Docker on Ubuntu, the docker is hosted directly by host machine. The host terminal can access both docker and host system.
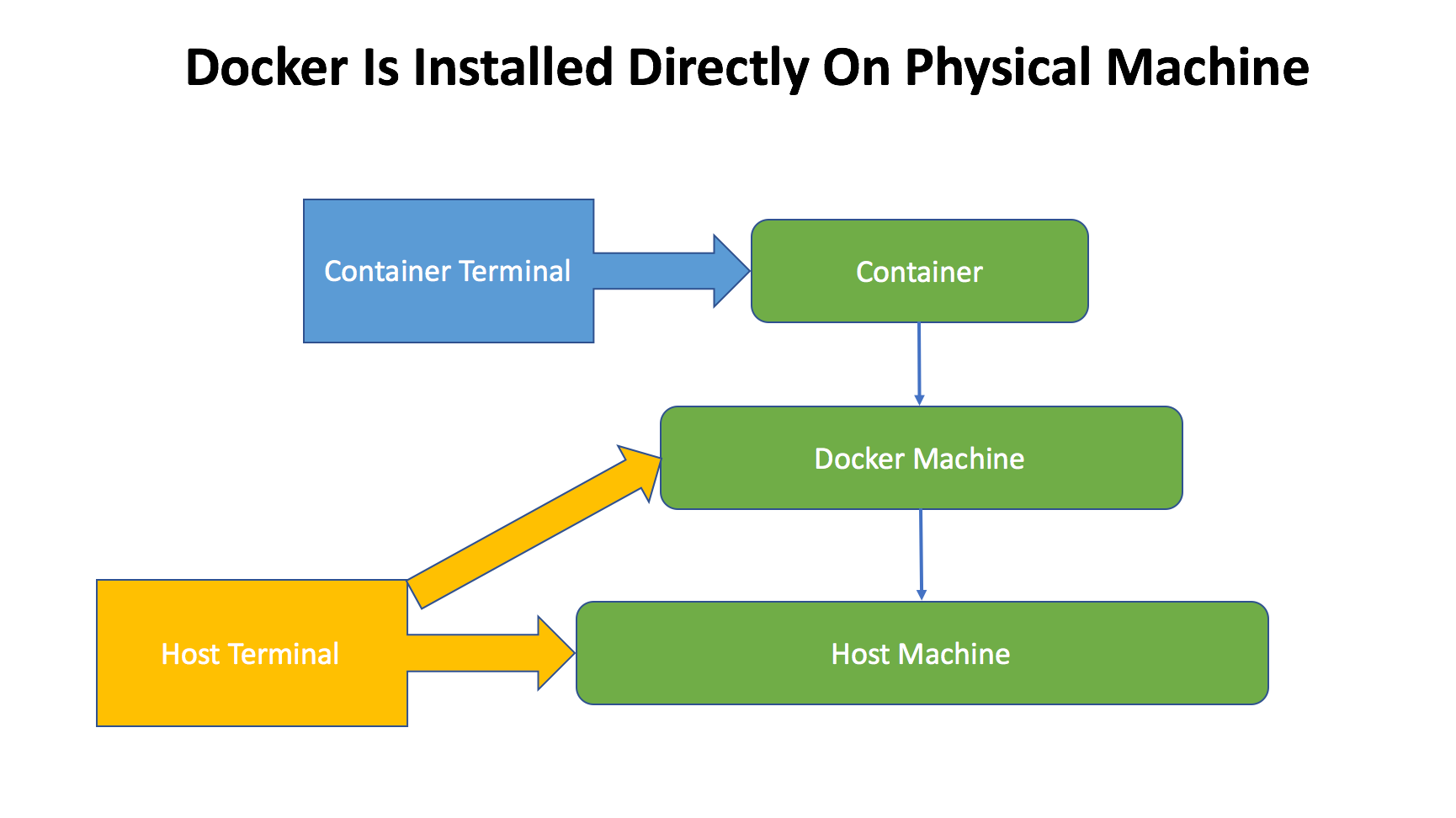
4.2 With Virtual Machine
If you install docker through Docker Toolbox, like what we did in this posting, the structure is different. There is one more VirtualBox VM between host machine and docker machine. In this case, you can only use Docker QuickStart Terminal to access docker.
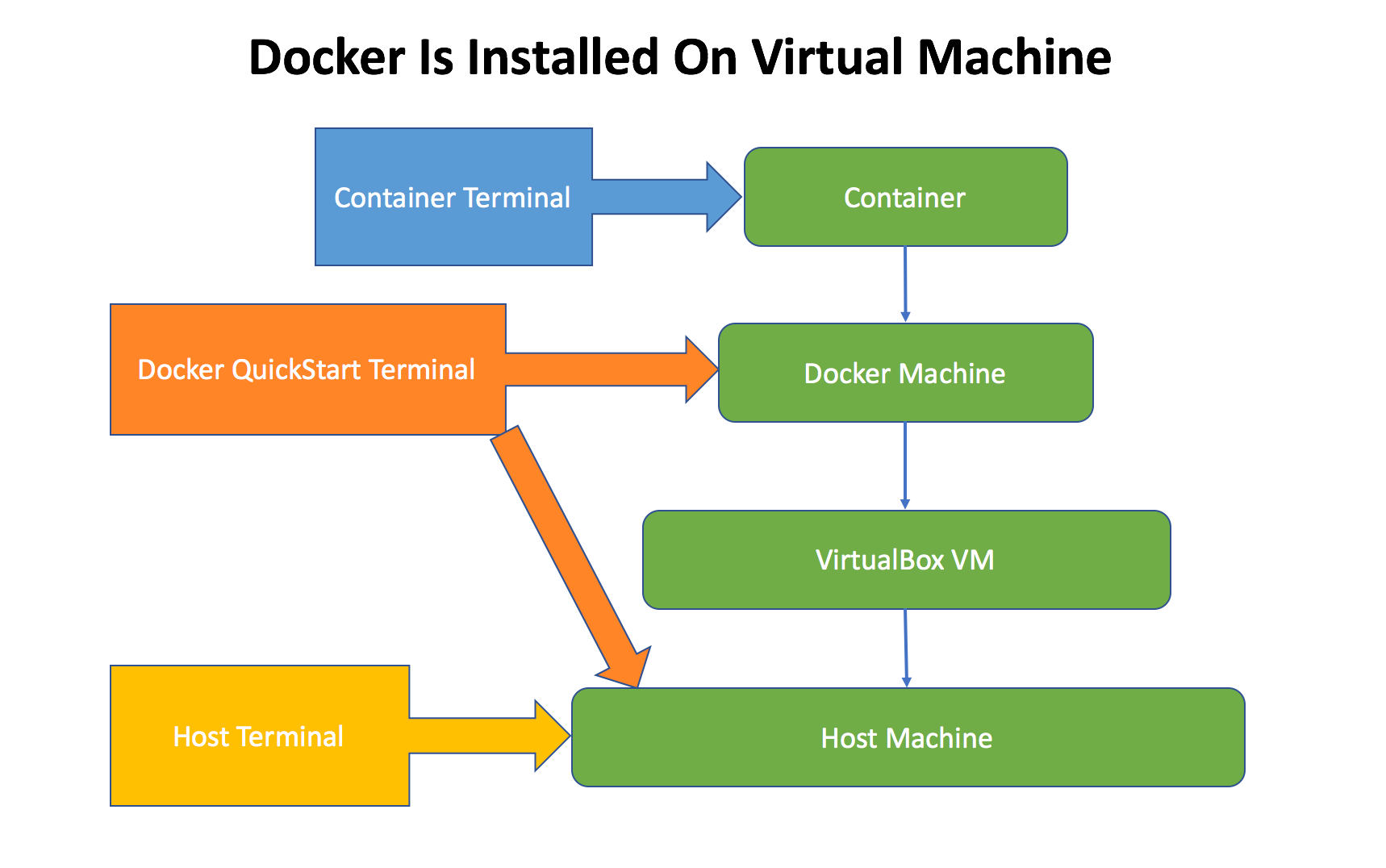
4.3 Types of Terminal
There are three types of terminal if docker is hosted on virtual machine.
| Type | Description | How to launch? |
|---|---|---|
| Host Terminal | The system terminal of host OS | Spotlight Search->terminal |
| Docker QuickStart Terminal | The terminal for docker | Spotlight Search->Docker QuickStart Terminal |
| Container Terminal | The terminal within container | In Docker Terminal, execute ‘docker exec -it <container> sh’ |
Whenever you start to work in command lines, be sure you are in the right terminal. For example, you cannot access docker in host terminal if it’s in the virtual machine.
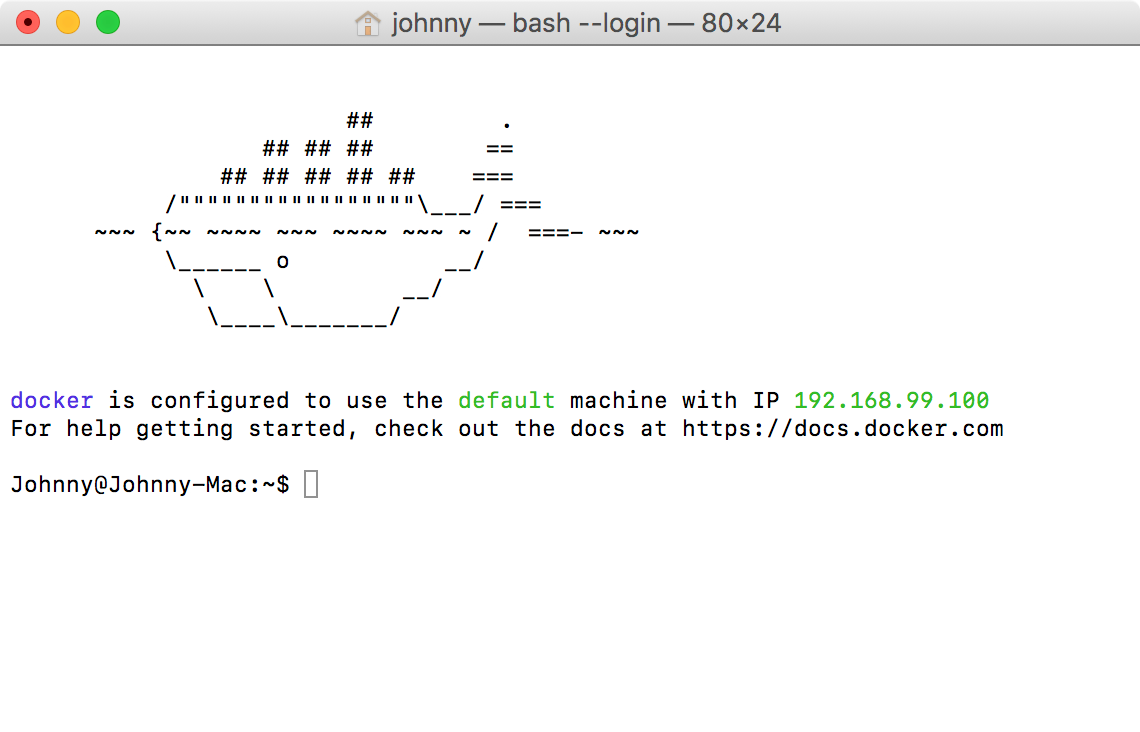
When Docker Terminal is started, you will see there is an IP address, eg. 192.168.99.100. Be aware that all your containers created on Docker machine have this same IP address. They are running at different ports. With this IP address and port, container can be accessed from the outside world.
5. Using Kitematic
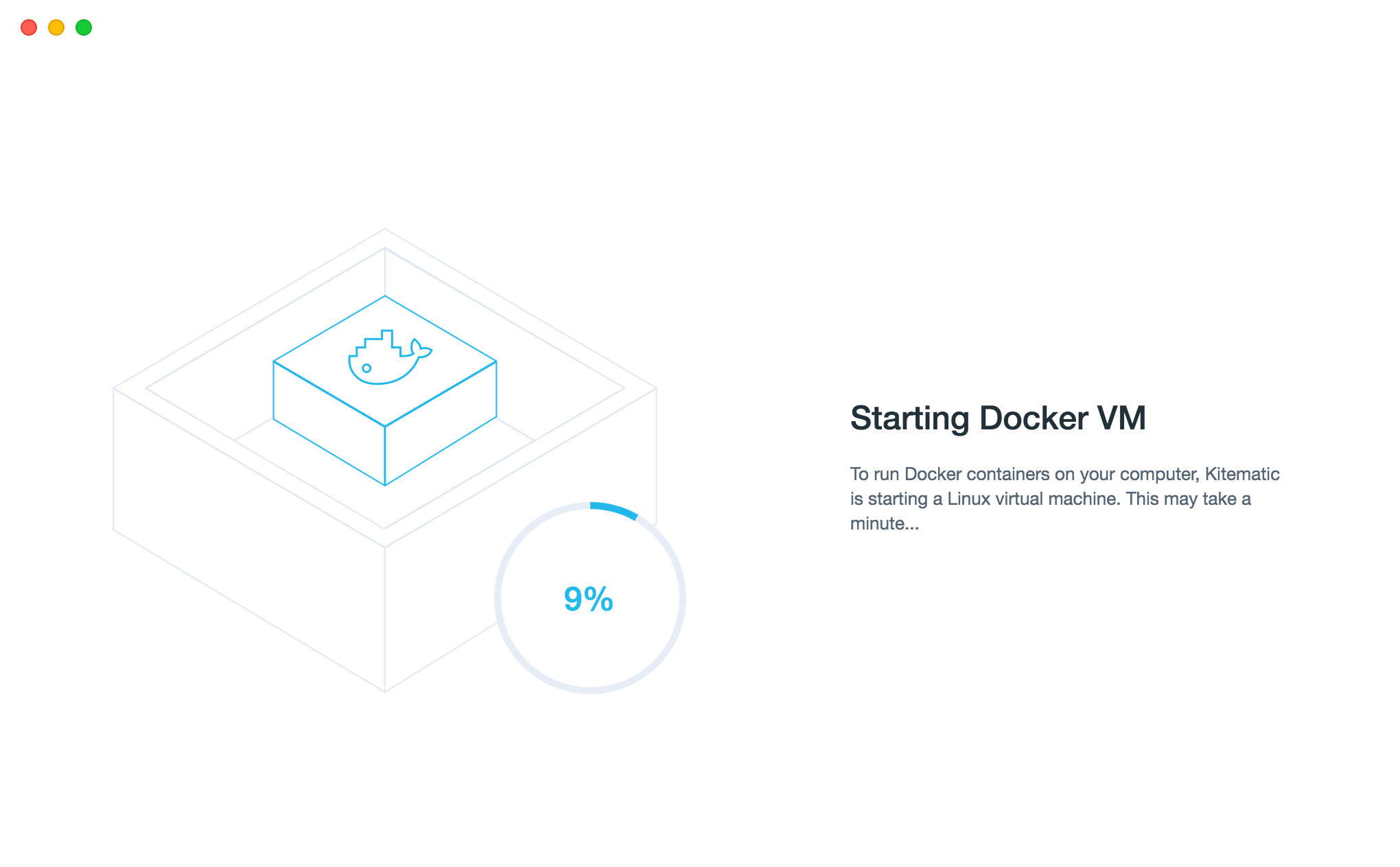
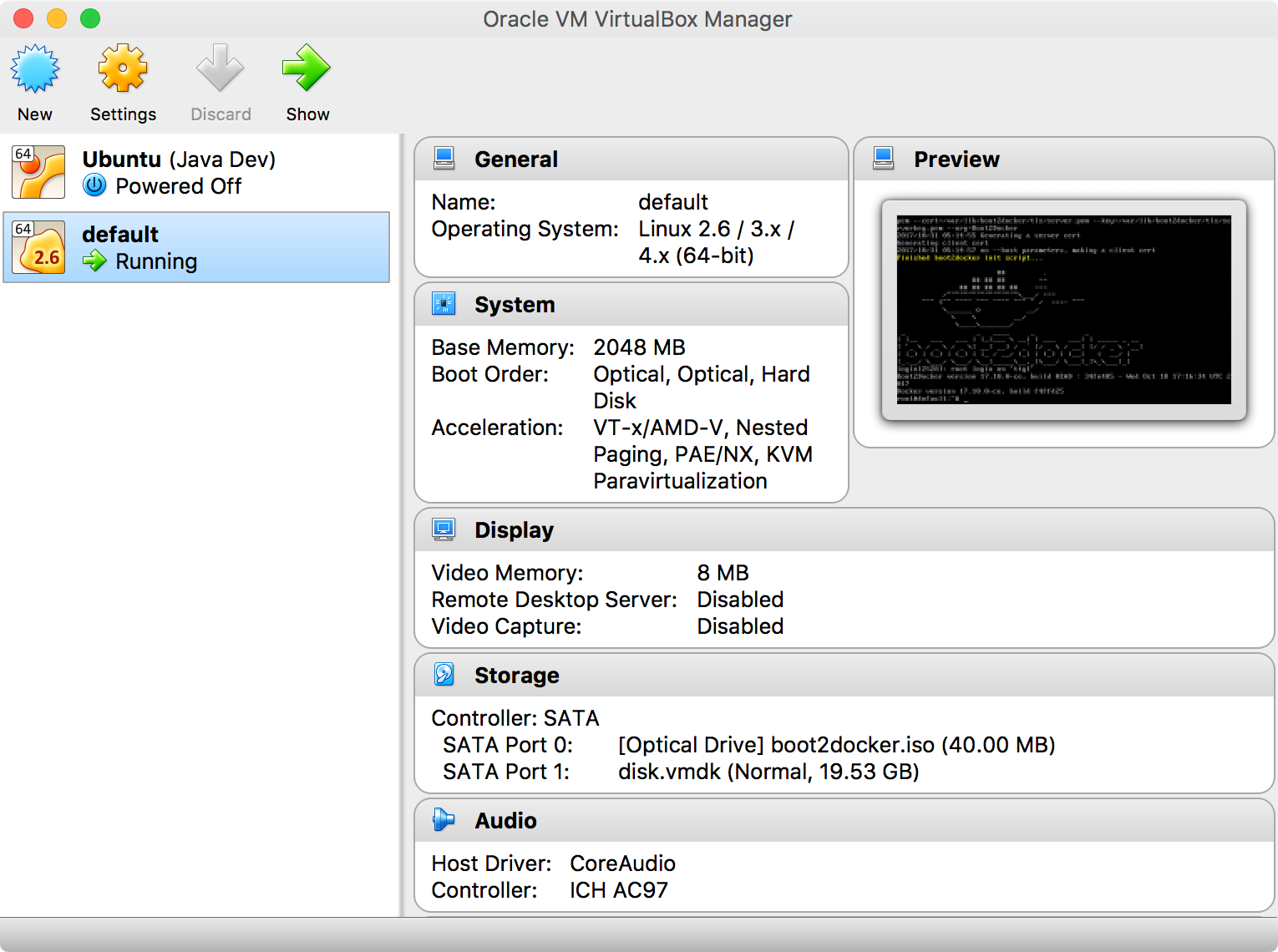
5.1 Virtual Machine for Docker Machine
The first time you start Kitematic, it will create a new virtual machine in VirtualBox.
5.2 Main Screen
Now, you see the main screen of Kitematic.
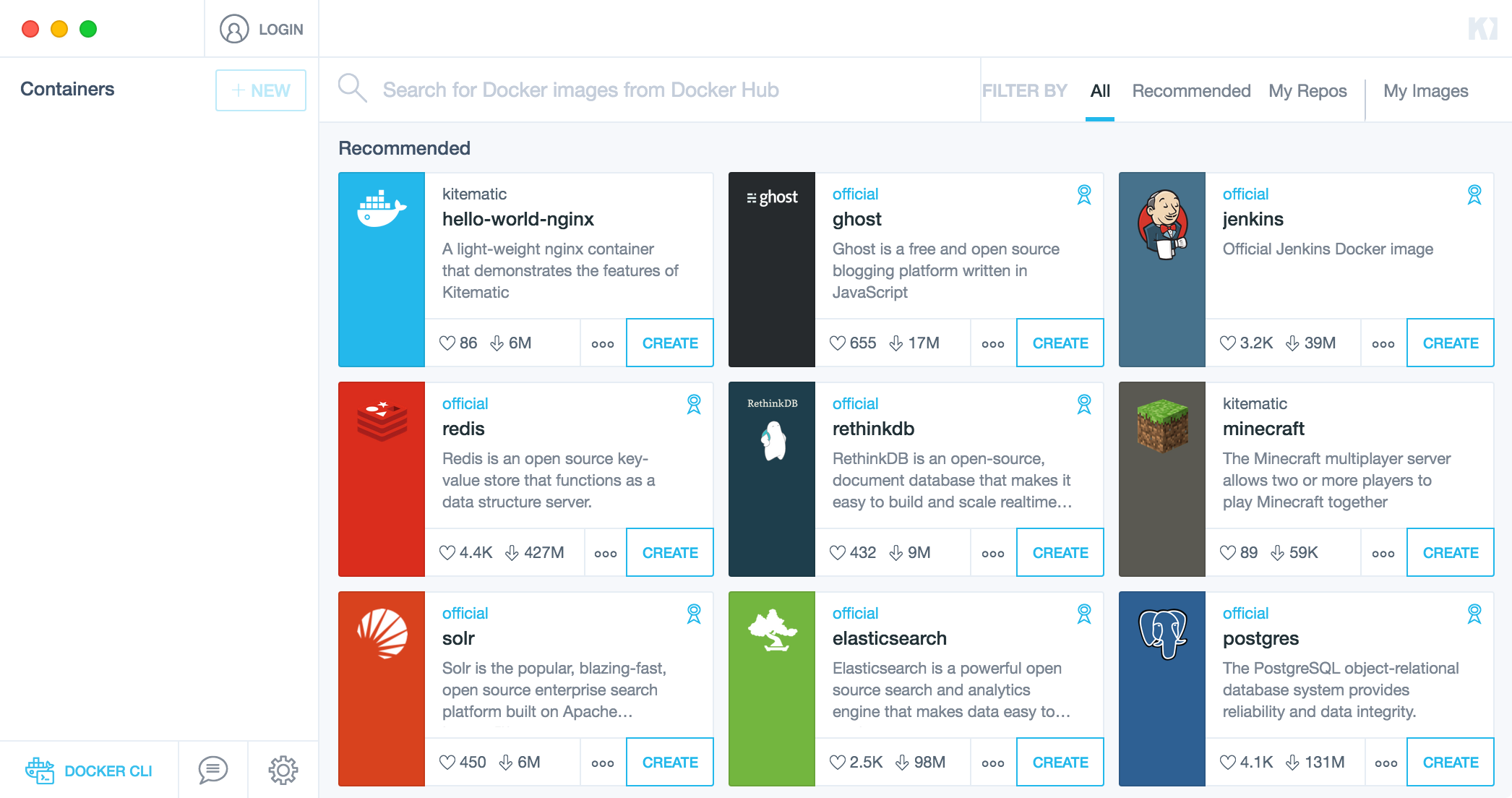
Options you have here:
- You can search Docker images through search box at top and click CREATE button to run containers for them.
- You can open a Docker-CLI terminal by clicking the whale button at the left bottom corner.
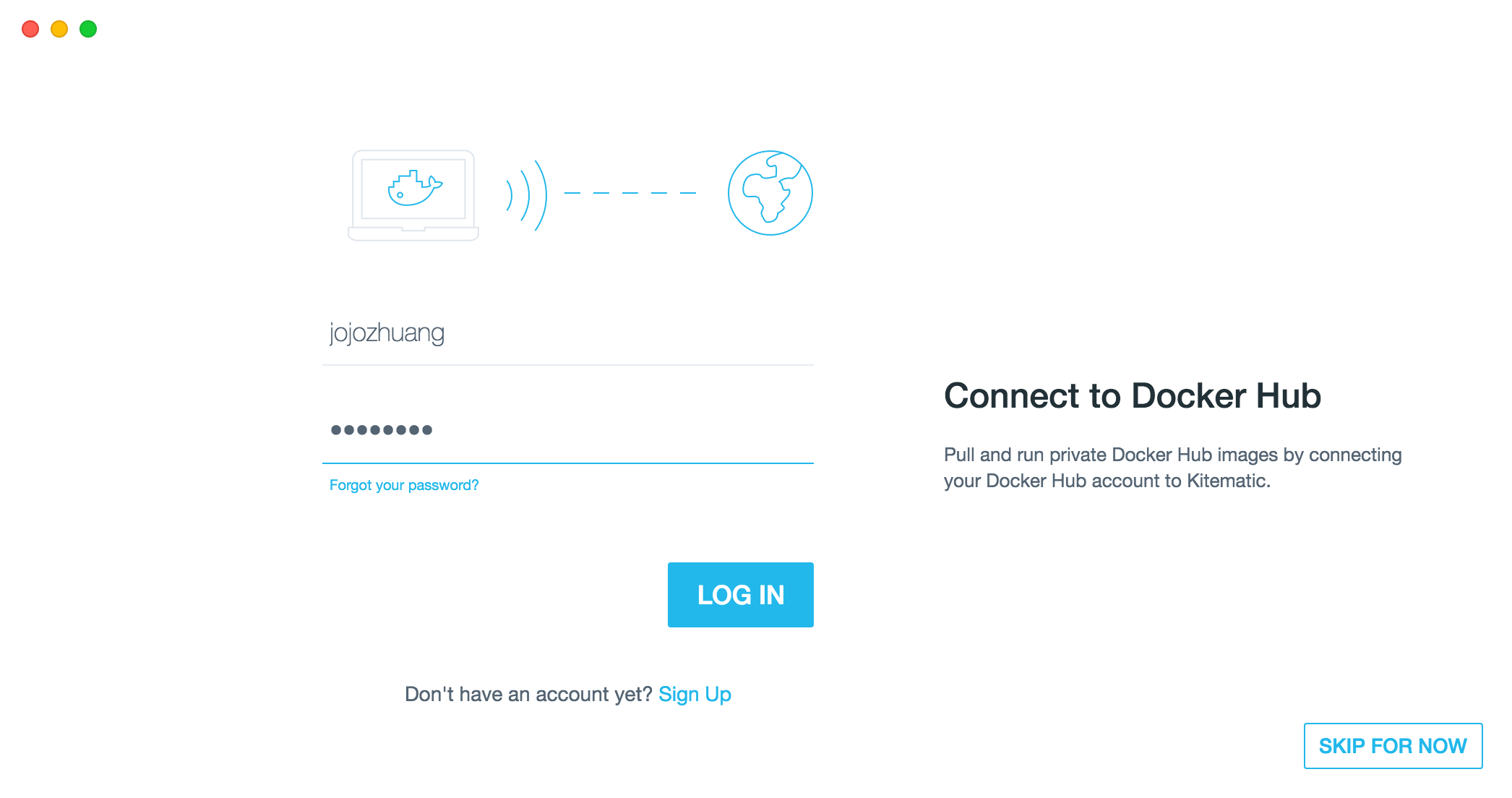
5.3 Logging In
If you’ve already registered a docker ID, you can use it to login now.
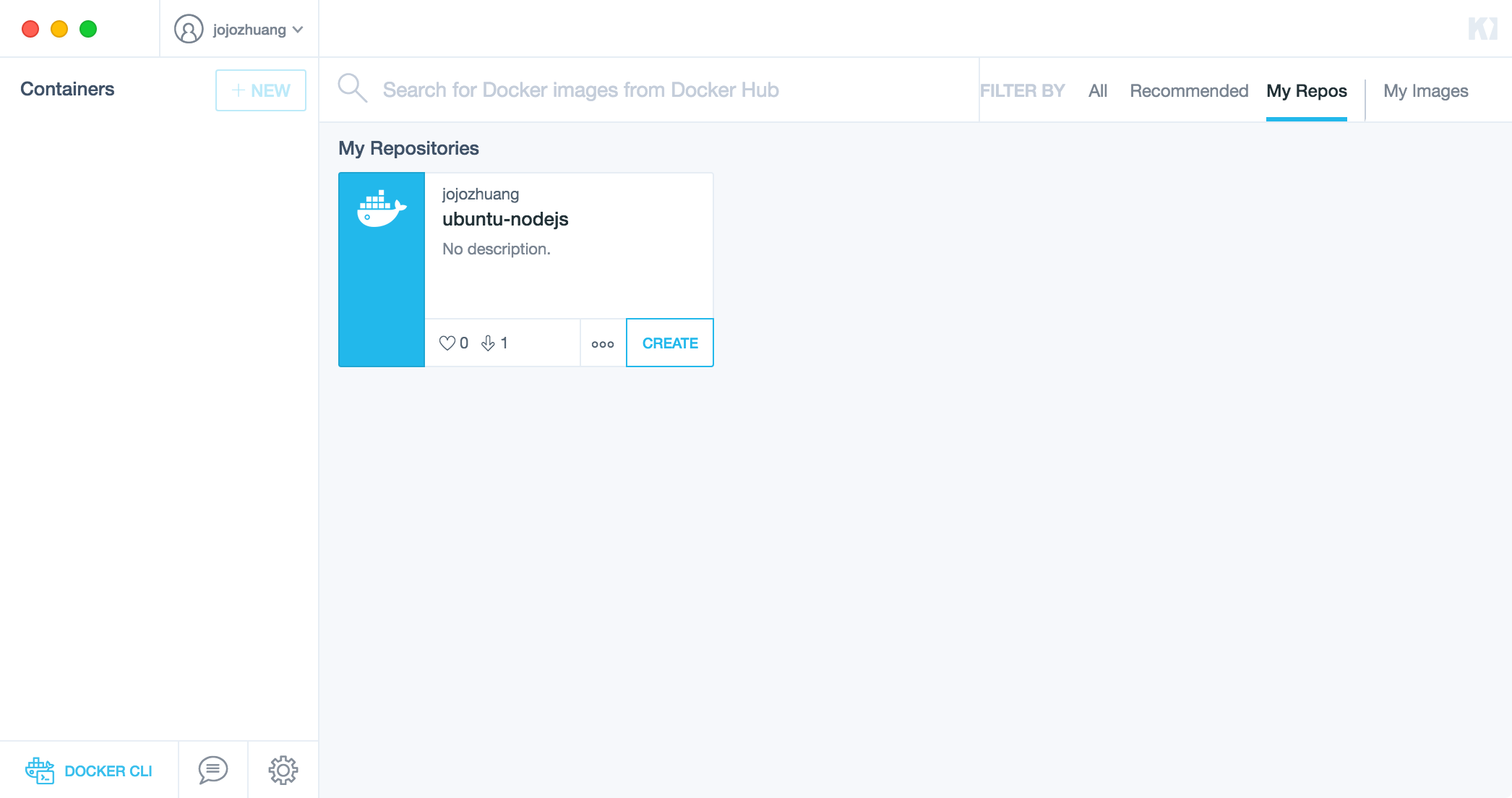
Switch to My Repos tab, the images on your Docker Hub will show up here.
6. Working with Container
Take jspmysql as example, which is a MySQL container(I will introduce how to create it later. Here, we assume we already had this container). Select it and click the Start button.
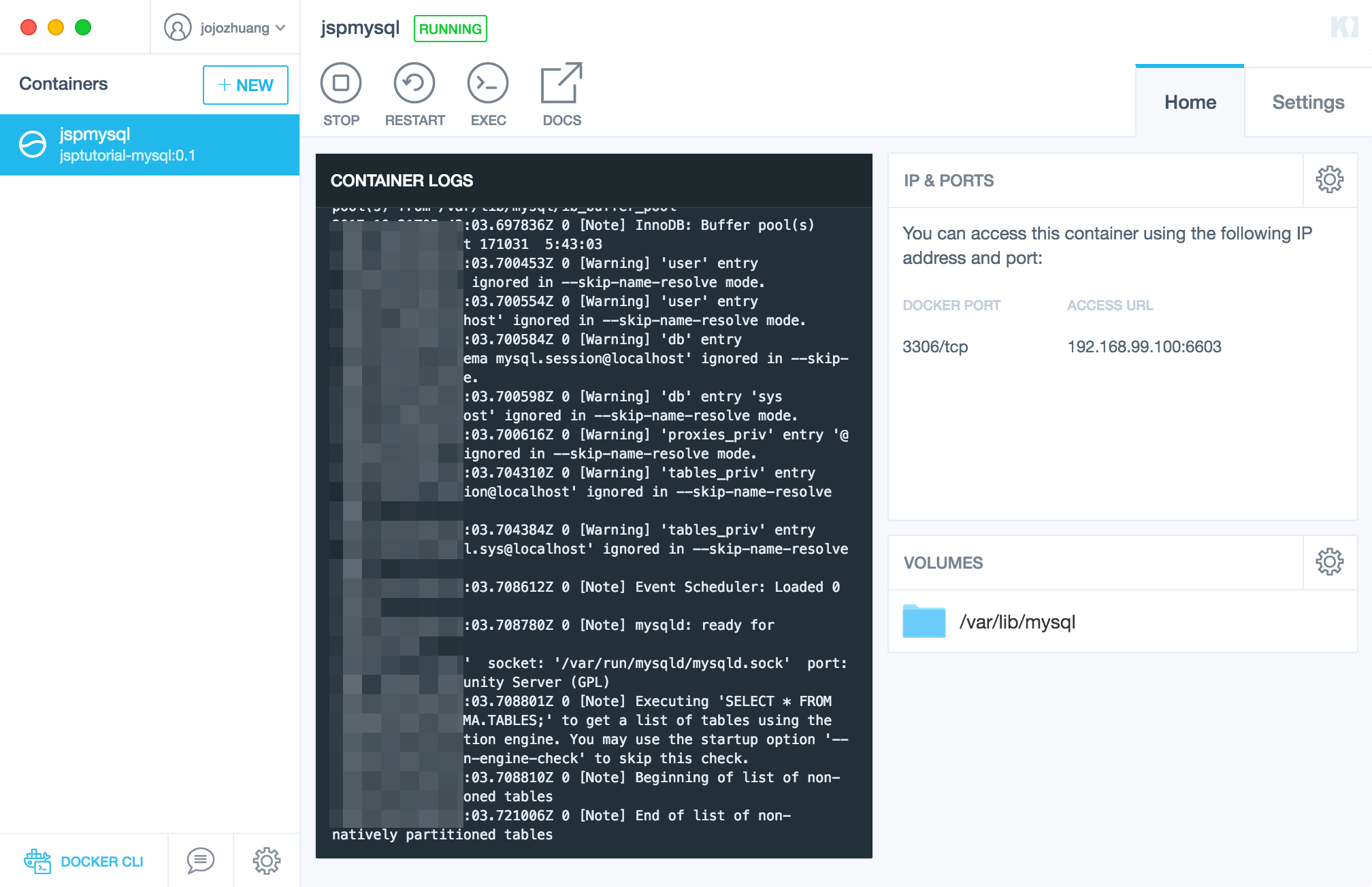
The container is started. And you see that Access URL, which is the public address can be accessed from outside of the container. For MySQL container, this is the url for applications to connect MySQL database remotely.
6.1 Starting Terminal in Container
To open the container terminal, we can type the following command in docker terminal.
$ docker exec -i -t <container> sh
In Kitematic, we just need to click the ‘EXEC’ button on the top, which is more convenient.
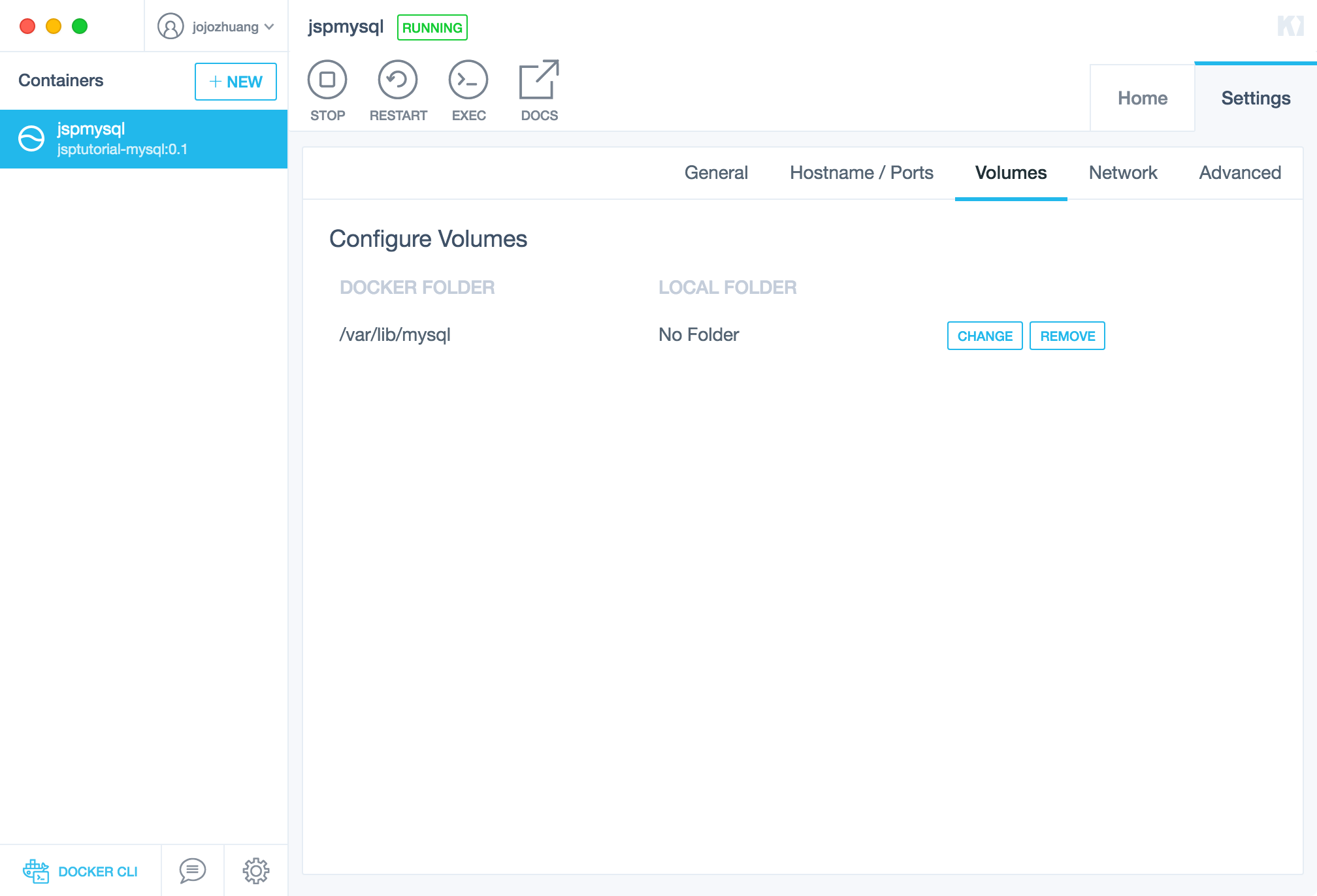
6.2 Settings of Container
Switch to Settings tab. In general sub tab, you can set environment variables here. See that MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD, it was set initially when this container was created. Now, you can easily update it in Kitematic.
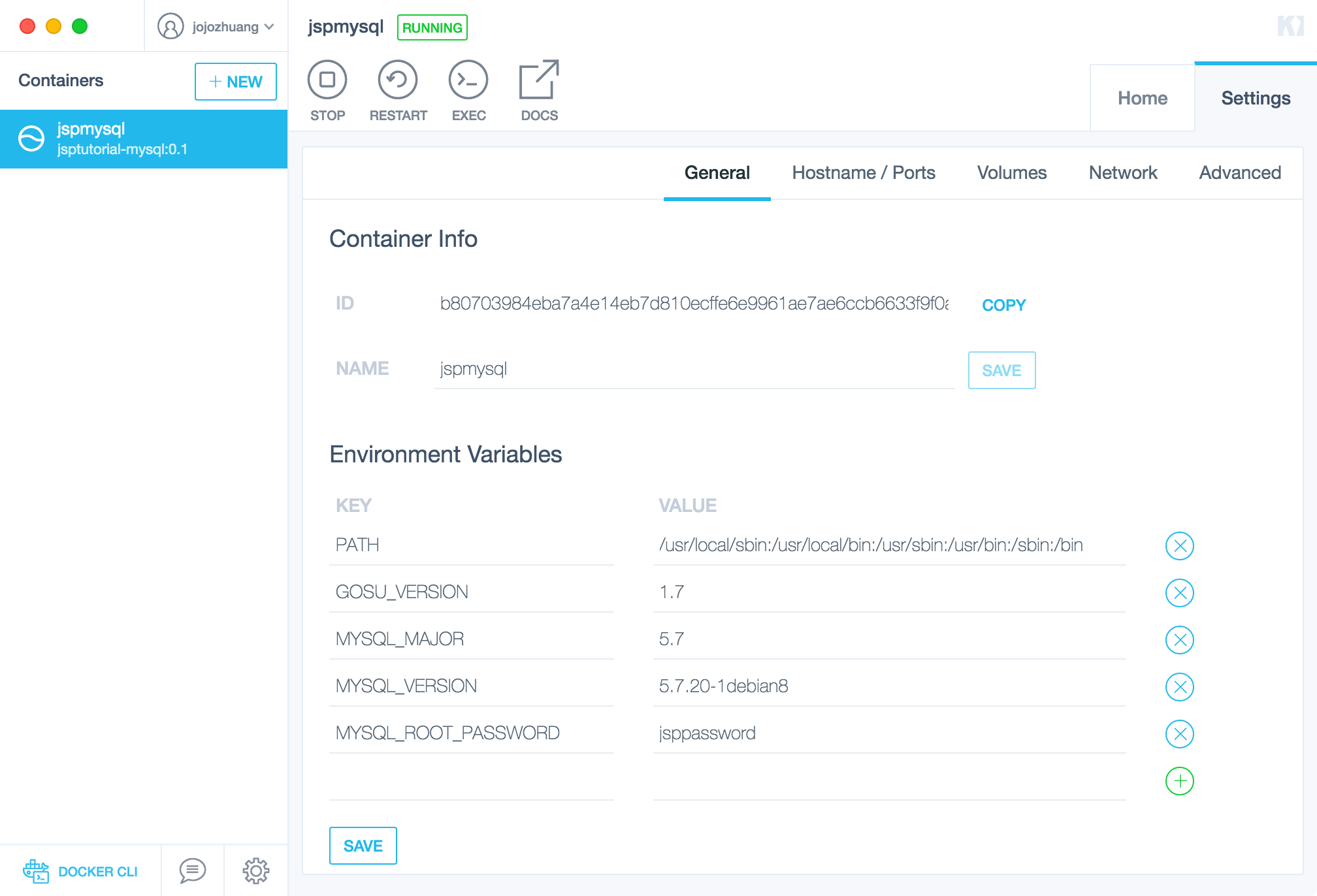
In Volumes tab, you are able set local and docker folder to share files between container and host machine.