3024. Hadoop Architecture - DraftHadoop
Hadoop Architecture Overview.
1. Hadoop Overview
1.1 What is Hadoop?
Apache Hadoop is a framework that allows for the distributed processing of large data sets across clusters of computers using simple programming models. It is designed to scale up from single servers to thousands of machines, each offering local computation and storage. Rather than rely on hardware to deliver high-availability, the library itself is designed to detect and handle failures at the application layer, so delivering a highly-available service on top of a cluster of computers, each of which may be prone to failures.
1.2 Advantages of Hadoop
- It gives access to the user to rapidly write and test the distributed systems and then automatically distributes the data and works across the machines and in turn utilizes the primary parallelism of the CPU cores.
- Hadoop libraries are developed to find/search and handle the failures at the application layer.
- Servers can be added or removed from the cluster dynamically at any point of time.
- It is open source based on Java applications and hence compatible on all the platforms.
1.3 Hadoop Features and Characteristics
Apache Hadoop is the most popular and powerful big data tool, which provides world’s best reliable storage layer –HDFS(Hadoop Distributed File System), a batch Processing engine namely MapReduce and a Resource Management Layer like YARN.
Distributed Processing: The data storage is maintained in a distributed manner in HDFS across the cluster, data is processed in parallel on cluster of nodes.Fault Tolerance: By default the three replicas of each block is stored across the cluster in Hadoop and it’s changed only when required. Hadoop’s fault tolerance can be examined in such cases when any node goes down, the data on that node can be recovered easily from other nodes. Failures of a particular node or task are recovered automatically by the framework.Reliability: Due to replication of data in the cluster, data can be reliable which is stored on the cluster of machine despite machine failures. Even if your machine goes down, your data will be stored reliably.High Availability: Data is available and accessible even hardware failure occurs. If any incidents occurred such as if your machine or few hardware crashes, then data will be accessed from other path.Scalability: Hadoop is highly scalable and hardware can be easily added to the nodes in a unique way. It also provides horizontal scalability which means new nodes can be added on the top without any downtime.Economic: Hadoop is not very expensive as it runs on cluster of commodity hardware. We do not require any specialized machine for it. Hadoop provides huge cost reduction since it is very easy to add more nodes on the top here. So if the requirement increases, then there is an increase of nodes, without any downtime and without any much of pre planning.Easy to use: No need for client to deal with distributed computing, framework takes care of all the things. So it is easy to use.Data Locality: Hadoop works on data locality principle. When client submits the program for computing, then the program is moved to the cluster where data locates instead of moving data to the location where the program locates.
2. Hadoop Design
2.1 Assumptions
Hadoop is composed of large number of computers and is built upon the following assumptions:
- Hardware may fail due to any external or technical malfunction where instead commodity hardware can be used.
- Processing will be run in batches and there is an emphasis on high throughput as opposed to low latency.
- Applications which run on HDFS have large sets of data. A typical file in HDFS may be from gigabytes to terabytes in size.
- Applications require a write-once-read-many access model.
- Moving computation programs is cheaper than moving data.
2.2 Hadoop Design Principles
The following are the design principles on which Hadoop works:
- System shall manage and heal itself as per the requirement occurred.
- Fault tolerance happens automatically and transparent to client.
- Performance is scaled based on linearity.
- Computation programs must be moved to data, not data to programs.
- Data locality leads to lower latency and lower bandwidth.
- It is based on simple core, modular and extensible (Economical).
3. Hadoop Architecture
3.1 Core Concepts
Hadoop MapReduce(Processing/Computation layer): MapReduce is a parallel programming model mainly used for writing large amount of data distribution applications devised from Google for efficient processing of large amounts of datasets, on large group of clusters.Hadoop HDFS(Storage layer): Hadoop Distributed File System or HDFS is based on the Google File System (GFS) which provides a distributed file system that is especially designed to run on commodity hardwares. It reduces the faults or errors and helps incorporate low-cost hardware. It gives high level processing throughput access to application data and is suitable for applications with large datasets.Hadoop YARN: Hadoop YARN is a framework used for job scheduling and cluster resource management.Hadoop Common: This includes Java libraries and utilities which provide those java files which are essential to start Hadoop.Task Tracker: It is a node which is used to accept the tasks such as shuffle and Mapreduce form job tracker.Job Tracker: It is a service provider which runs Mapreduce jobs on cluster.Name Node: It is a node where Hadoop stores all file location information(data stored location) in Hadoop distributed file system.Data Node: The data is stored in the Hadoop distributed file system.
3.2 High-level Architecture
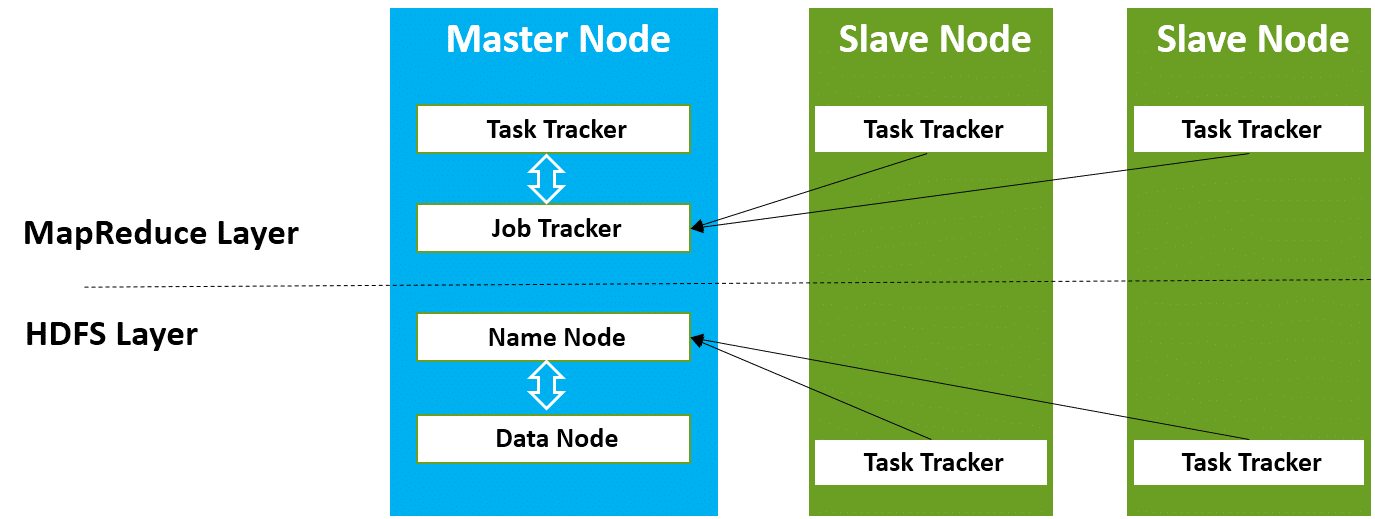
Hadoop follows a master-slave architecture design for data storage and distributed data processing, which uses HDFS and MapReduce respectively. The master node for data storage in hadoop HDFS is the Name Node and the master node for parallel processing of data using Hadoop MapReduce is the Job Tracker. The slave nodes in the hadoop architecture are the other machines which store data and perform complex computations. Every slave node has a Task Tracker daemon and a Data Node that synchronizes the processes with the Job Tracker and NameNode respectively. In Hadoop architectural implementation the master or slave systems can be setup in the cloud or on-premise.
 Other Hadoop views.
Other Hadoop views.
3.3 Hadoop Modules
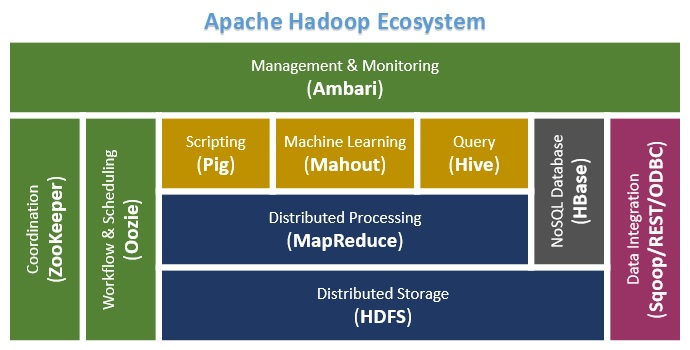 Hadoop comprises of 4 core components:
Hadoop comprises of 4 core components:
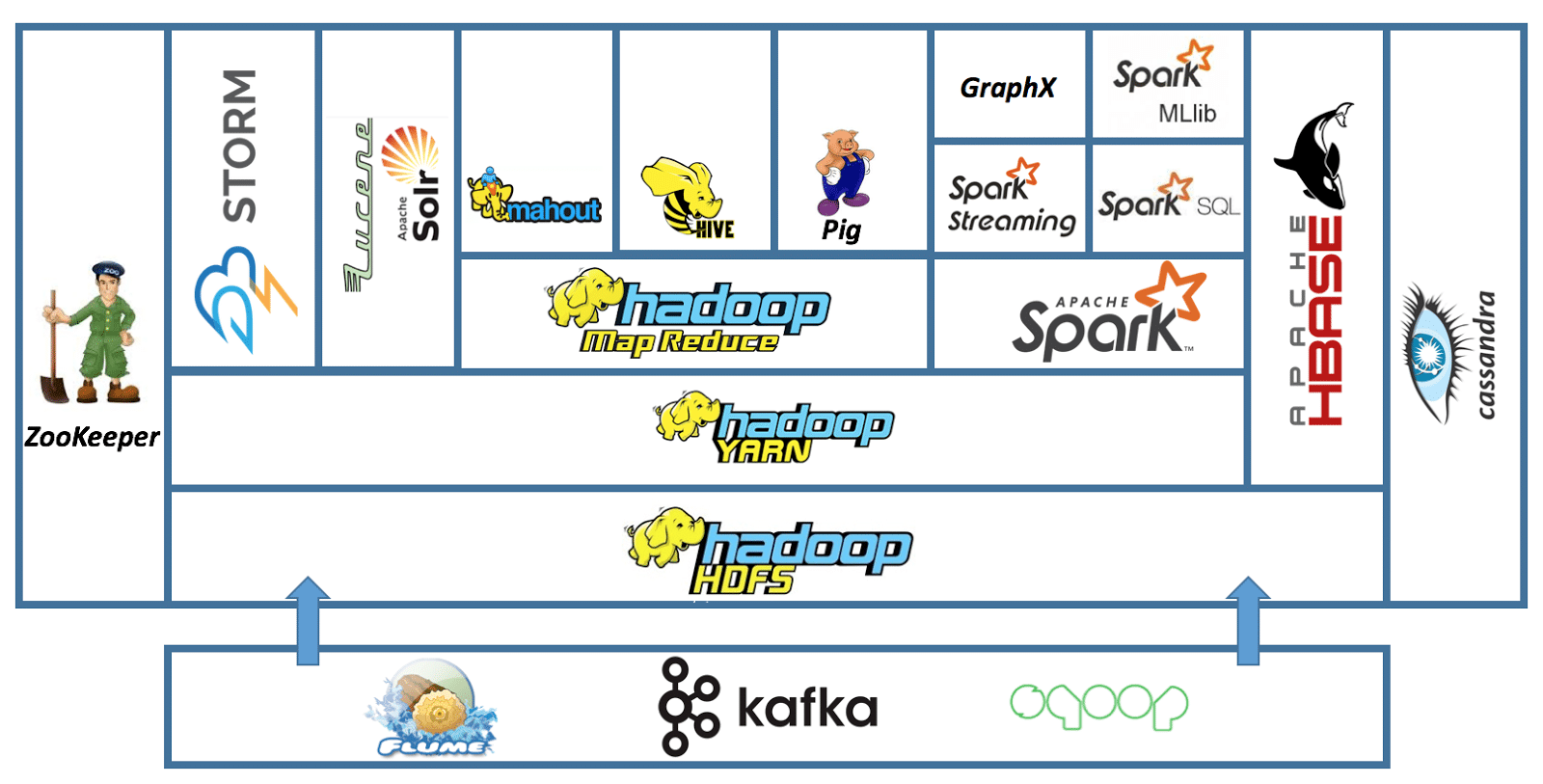
Hadoop Common: Common utilities which support other Hadoop modules.HDFS: Hadoop Distributed File System provides unrestricted, high-speed access to the data application.MapReduce: A highly efficient methodology for parallel processing of huge volumes of data.YARN: Stands for Yet Another Resource Negotiato. This technology is basically used for scheduling of job and efficient management of the cluster resource.
Other Hadoop ecosystem components:
Ambari: It is a tool for managing, monitoring and provisioning of the Hadoop clusters. Apache Ambari supports the HDFS and MapReduce programs. Major highlights of Ambari are:- Managing of the Hadoop framework is highly efficient, secure and consistent.
- Management of cluster operations with an intuitive web UI and a robust API
- The installation and configuration of Hadoop cluster are simplified effectively.
- It is used to support automation, smart configuration and recommendations.
- Advanced cluster security set-up comes additional with this tool kit.
- The entire cluster can be controlled using the metrics, heat maps, analysis and troubleshooting.
- Increased levels of customization and extension make this more valuable.
Cassandra: It is a distributed system to handle extremely huge amount of data which is stored across several commodity servers. The database management system (DBMS)is highly available with no single point of failure.HBase: it is a non-relational, distributed database management system that works efficiently on sparse data sets and it is highly scalable.Spark: This is highly agile, scalable and secure, the Big Data compute engine, versatiles the sufficient work on a wide variety of applications like real-time processing, machine learning, ETL and so on.Hive: It is a data warehouse tool basically used for analyzing, querying and summarizing of analyzed data concepts on top of the Hadoop framework.Pig: Pig is a high-level framework which ensures us to work in coordination either with Apache Spark or MapReduce to analyze the data. The language used to code for the frameworks are known as Pig Latin.Sqoop: This framework is used for transferring the data to Hadoop from relational databases. This application is based on a command-line interface.Oozie: This is a scheduling system for workflow management, executing workflow routes for successful completion of the task in Hadoop.Zookeeper: Open source centralized service which is used to provide coordination between distributed applications of Hadoop. It offers the registry and synchronization service at a high level.
4. Hadoop Details
1.1 Hadoop Architecture Explained
Hadoop skillset requires thoughtful knowledge of every layer in the hadoop stack right from understanding about the various components in the hadoop architecture, designing a hadoop cluster, performance tuning it and setting up the top chain responsible for data processing.
Hadoop follows a master slave architecture design for data storage and distributed data processing using HDFS and MapReduce respectively. The master node for data storage is hadoop HDFS is the NameNode and the master node for parallel processing of data using Hadoop MapReduce is the Job Tracker. The slave nodes in the hadoop architecture are the other machines in the Hadoop cluster which store data and perform complex computations. Every slave node has a Task Tracker daemon and a DataNode that synchronizes the processes with the Job Tracker and NameNode respectively. In Hadoop architectural implementation the master or slave systems can be setup in the cloud or on-premise.
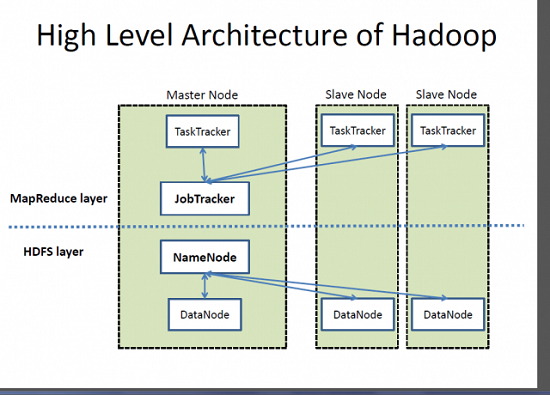
1.2 Role of Distributed Storage - HDFS
A file on HDFS is split into multiple bocks and each is replicated within the Hadoop cluster. A block on HDFS is a blob of data within the underlying file system with a default size of 64MB.The size of a block can be extended up to 256 MB based on the requirements.
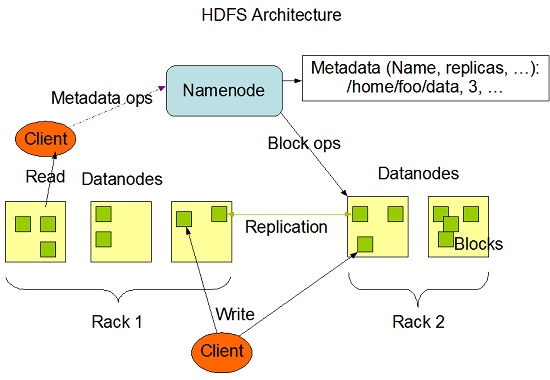 Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) stores the application data and file system metadata separately on dedicated servers.
Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) stores the application data and file system metadata separately on dedicated servers. NameNode and DataNode are the two critical components of the Hadoop HDFS architecture. Application data is stored on servers referred to as DataNodes and file system metadata is stored on servers referred to as NameNode. HDFS replicates the file content on multiple DataNodes based on the replication factor to ensure reliability of data. The NameNode and DataNode communicate with each other using TCP based protocols. For the Hadoop architecture to be performance efficient, HDFS must satisfy certain pre-requisites:
- All the hard drives should have a high throughput.
- Good network speed to manage intermediate data transfer and block replications.
NameNode
All the files and directories in the HDFS namespace are represented on the NameNode by Inodes that contain various attributes like permissions, modification timestamp, disk space quota, namespace quota and access times. NameNode maps the entire file system structure into memory. Two files fsimage and edits are used for persistence during restarts.
Fsimagefile contains the Inodes and the list of blocks which define the metadata.It has a complete snapshot of the file systems metadata at any given point of time.- The edits file contains any modifications that have been performed on the content of the fsimage file.Incremental changes like renaming or appending data to the file are stored in the edit log to ensure durability instead of creating a new fsimage snapshot everytime the namespace is being altered.
When the NameNode starts, fsimage file is loaded and then the contents of the edits file are applied to recover the latest state of the file system. The only problem with this is that over the time the edits file grows and consumes all the disk space resulting in slowing down the restart process. If the hadoop cluster has not been restarted for months together then there will be a huge downtime as the size of the edits file will be increase. This is when Secondary NameNode comes to the rescue. Secondary NameNode gets the fsimage and edits log from the primary NameNode at regular intervals and loads both the fsimage and edit logs file to the main memory by applying each operation from edits log file to fsimage. Secondary NameNode copies the new fsimage file to the primary NameNode and also will update the modified time of the fsimage file to fstime file to track when then fsimage file has been updated.
DataNode
DataNode manages the state of an HDFS node and interacts with the blocks .A DataNode can perform CPU intensive jobs like semantic and language analysis, statistics and machine learning tasks, and I/O intensive jobs like clustering, data import, data export, search, decompression, and indexing. A DataNode needs lot of I/O for data processing and transfer.
On startup every DataNode connects to the NameNode and performs a handshake to verify the namespace ID and the software version of the DataNode. If either of them does not match then the DataNode shuts down automatically. A DataNode verifies the block replicas in its ownership by sending a block report to the NameNode. As soon as the DataNode registers, the first block report is sent. DataNode sends heartbeat to the NameNode every 3 seconds to confirm that the DataNode is operating and the block replicas it hosts are available.
1.3 Role of Distributed Computation - MapReduce
The heart of the distributed computation platform Hadoop is its java-based programming paradigm Hadoop MapReduce. Map or Reduce is a special type of directed acyclic graph that can be applied to a wide range of business use cases. Map function transforms the piece of data into key-value pairs and then the keys are sorted where a reduce function is applied to merge the values based on the key into a single output.
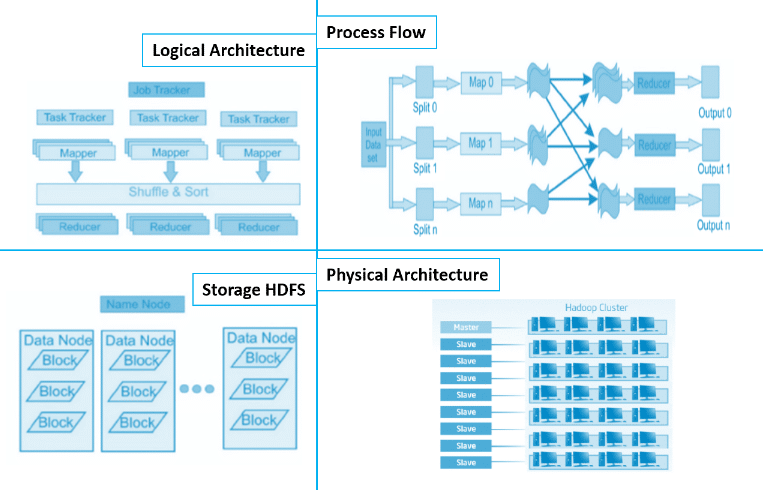
How does the Hadoop MapReduce architecture work?
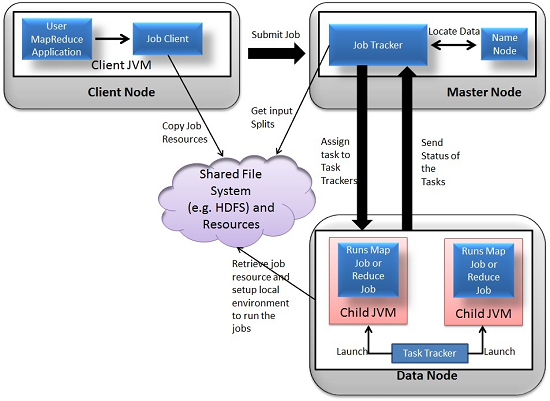
The execution of a MapReduce job begins when the client submits the job configuration to the Job Tracker that specifies the map, combine and reduce functions along with the location for input and output data. On receiving the job configuration, the job tracker identifies the number of splits based on the input path and select Task Trackers based on their network vicinity to the data sources. Job Tracker sends a request to the selected Task Trackers.
The processing of the Map phase begins where the Task Tracker extracts the input data from the splits. Map function is invoked for each record parsed by the “InputFormat” which produces key-value pairs in the memory buffer. The memory buffer is then sorted to different reducer nodes by invoking the combine function. On completion of the map task, Task Tracker notifies the Job Tracker. When all Task Trackers are done, the Job Tracker notifies the selected Task Trackers to begin the reduce phase. Task Tracker reads the region files and sorts the key-value pairs for each key. The reduce function is then invoked which collects the aggregated values into the output file.
2. Hadoop Architecture Design – Best Practices to Follow
- Use good-quality commodity servers to make it cost efficient and flexible to scale out for complex business use cases. One of the best configurations for Hadoop architecture is to begin with 6 core processors, 96 GB of memory and 104 TB of local hard drives. This is just a good configuration but not an absolute one.
- For faster and efficient processing of data, move the processing in close proximity to data instead of separating the two.
- Hadoop scales and performs better with local drives so use Just a Bunch of Disks (JBOD) with replication instead of redundant array of independent disks (RAID).
- Design the Hadoop architecture for multi-tenancy by sharing the compute capacity with capacity scheduler and share HDFS storage. Do not edit the metadata files as it can corrupt the state of the Hadoop cluster.
3. Hadoop Ecosystem Components and Its Architecture
3.1 Hadoop Ecosystem Components

3.2 Core Hadoop Components
The Hadoop Ecosystem comprises of 4 core components:
1) Hadoop Common
Apache Foundation has pre-defined set of utilities and libraries that can be used by other modules within the Hadoop ecosystem. For example, if HBase and Hive want to access HDFS they need to make of Java archives (JAR files) that are stored in Hadoop Common.
2) Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS)
The default big data storage layer for Apache Hadoop is HDFS. HDFS is the “Secret Sauce” of Apache Hadoop components as users can dump huge datasets into HDFS and the data will sit there nicely until the user wants to leverage it for analysis. HDFS component creates several replicas of the data block to be distributed across different clusters for reliable and quick data access. HDFS comprises of 3 important components-NameNode, DataNode and Secondary NameNode. HDFS operates on a Master-Slave architecture model where the NameNode acts as the master node for keeping a track of the storage cluster and the DataNode acts as a slave node summing up to the various systems within a Hadoop cluster.
3) MapReduce
MapReduce is a Java-based system created by Google where the actual data from the HDFS store gets processed efficiently. MapReduce breaks down a big data processing job into smaller tasks. MapReduce is responsible for the analysing large datasets in parallel before reducing it to find the results. In the Hadoop ecosystem, Hadoop MapReduce is a framework based on YARN architecture. YARN based Hadoop architecture, supports parallel processing of huge data sets and MapReduce provides the framework for easily writing applications on thousands of nodes, considering fault and failure management.
The basic principle of operation behind MapReduce is that the “Map” job sends a query for processing to various nodes in a Hadoop cluster and the “Reduce” job collects all the results to output into a single value. Map Task in the Hadoop ecosystem takes input data and splits into independent chunks and output of this task will be the input for Reduce Task. In The same Hadoop ecosystem Reduce task combines Mapped data tuples into smaller set of tuples. Meanwhile, both input and output of tasks are stored in a file system. MapReduce takes care of scheduling jobs, monitoring jobs and re-executes the failed task.
MapReduce framework forms the compute node while the HDFS file system forms the data node. Typically in the Hadoop ecosystem architecture both data node and compute node are considered to be the same.
The delegation tasks of the MapReduce component are tackled by two daemons- Job Tracker and Task Tracker as shown in the image below.
4) YARN
YARN forms an integral part of Hadoop 2.0.YARN is great enabler for dynamic resource utilization on Hadoop framework as users can run various Hadoop applications without having to bother about increasing workloads.
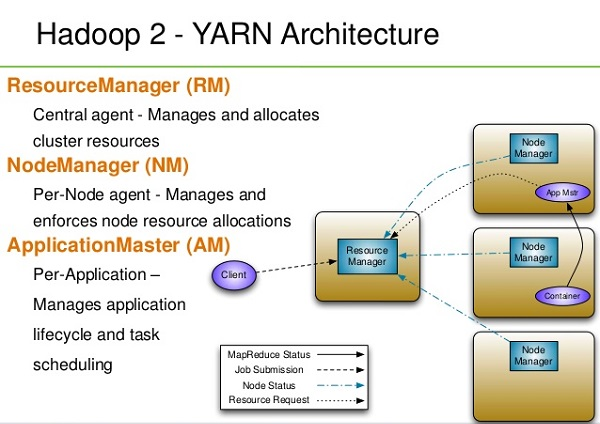 Key Benefits of Hadoop 2.0 YARN Component-
Key Benefits of Hadoop 2.0 YARN Component-
- It offers improved cluster utilization
- Highly scalable
- Beyond Java
- Novel programming models and services
- Agility
Pig and Hive Apache Pig is a convenient tools developed by Yahoo for analysing huge data sets efficiently and easily. It provides a high level data flow language Pig Latin that is optimized, extensible and easy to use. The most outstanding feature of Pig programs is that their structure is open to considerable parallelization making it easy for handling large data sets.
Hive developed by Facebook is a data warehouse built on top of Hadoop and provides a simple language known as HiveQL similar to SQL for querying, data summarization and analysis. Hive makes querying faster through indexing.
Sqoop Sqoop component is used for importing data from external sources into related Hadoop components like HDFS, HBase or Hive. It can also be used for exporting data from Hadoop o other external structured data stores. Sqoop parallelized data transfer, mitigates excessive loads, allows data imports, efficient data analysis and copies data quickly.
Flume component is used to gather and aggregate large amounts of data. Apache Flume is used for collecting data from its origin and sending it back to the resting location (HDFS).Flume accomplishes this by outlining data flows that consist of 3 primary structures channels, sources and sinks. The processes that run the dataflow with flume are known as agents and the bits of data that flow via flume are known as events.
HBase – HBase is a column-oriented database that uses HDFS for underlying storage of data. HBase supports random reads and also batch computations using MapReduce. With HBase NoSQL database enterprise can create large tables with millions of rows and columns on hardware machine. The best practice to use HBase is when there is a requirement for random ‘read or write’ access to big datasets.
Oozie is a workflow scheduler where the workflows are expressed as Directed Acyclic Graphs. Oozie runs in a Java servlet container Tomcat and makes use of a database to store all the running workflow instances, their states ad variables along with the workflow definitions to manage Hadoop jobs (MapReduce, Sqoop, Pig and Hive).The workflows in Oozie are executed based on data and time dependencies.
Zookeeper is the king of coordination and provides simple, fast, reliable and ordered operational services for a Hadoop cluster. Zookeeper is responsible for synchronization service, distributed configuration service and for providing a naming registry for distributed systems.
1.2 Hadoop Stack