4180. AWS-Amazon LambdaAWS, Serverless, and Lambda
Build serverless applications with Amazon Lambda.
1. Serverless and Amazon Lambda
1.1 Serverless Concept
History of cloud: Data center->IaaS->PaaS->Containers->Serverless.

1.2 Amazon Lambda
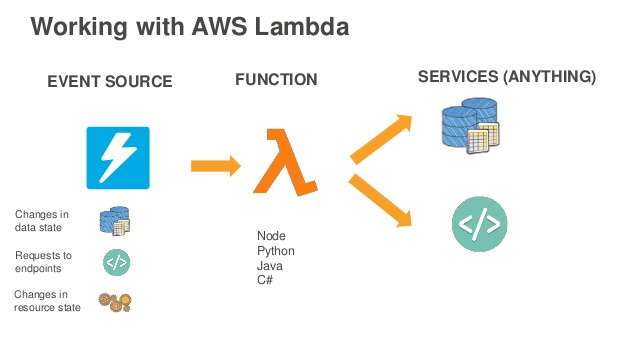
AWS Lambda is a compute service where you can upload your code and create a Lambda function. AWE Lambda takes care of provisioning and managing the servers that you use to run the code. You don’t have to worry about operating systems, patching, scaling, etc.
Lambda Is The Ultimate Abstraction Layer:
- Data Centers
- Hardware
- Assembly Code/Protocols
- High Level Languages
- Operating Systems
- Application Layer/AWS APIs
- AWS Lambda
You can use Lambda in the following ways:
- As an event-driven compute service where AWS Lambda runs your code in response to events. These events could be changes to data in an Amazon S3 bucket or an Amazon DynamoDB table.
- As a compute service to run your code in response to HTTP requests using Amazon API Gateway or API calls made using AWS SDKs.
Lambda usage cases.
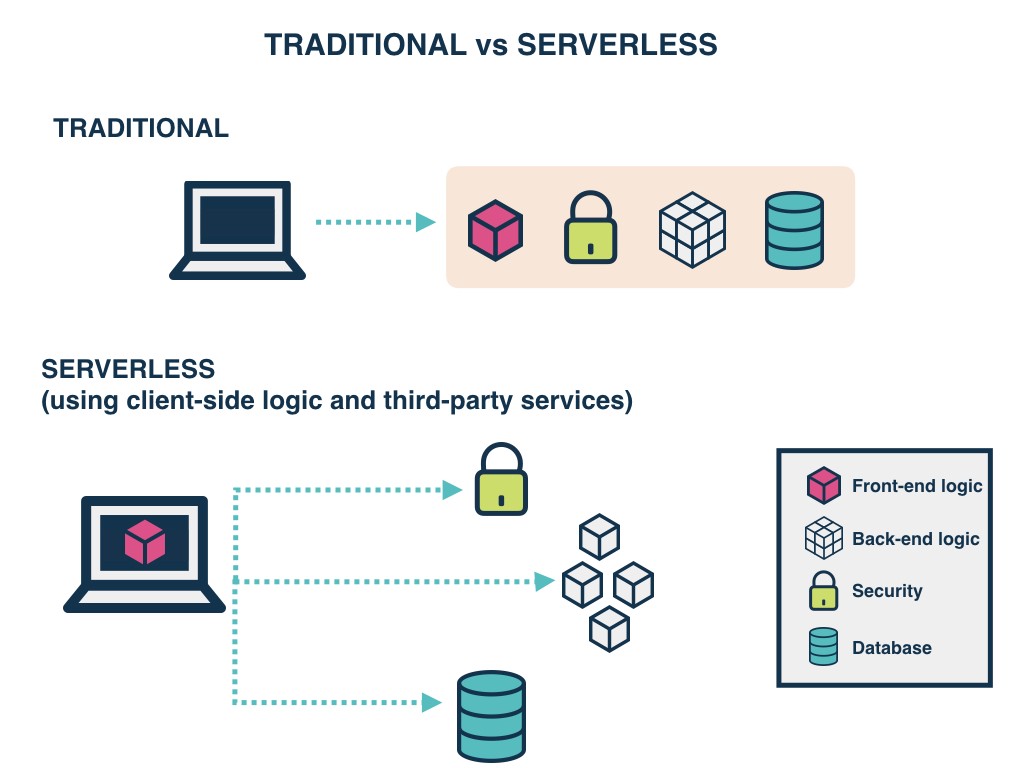
 Traditional vs. Serverless Architecture
Traditional vs. Serverless Architecture
What Languages Does Lambda Support?
- Node.js
- Java
- Python
- C#
- Go
- PowerShell
How lamda is priced?
- Number Of Requests
- First 1 million requests are free. $0.20 per 1 million requests thereafter.
- Duration
- Duration is calculated from the time your code begins executing until it returns or otherwise terminates, rounded up to the nearest 100ms. The price depends on the amount of memory you allocate to your function. You are charged $0.00001667 for every GB-second used.
Why Is Lambda Cool?
- NO SERVERS!
- Continuous Scaling
- Super super super cheap!
1.3 Summary
- Lambda scales out (not up) automatically
- Lambda functions are independent, 1 event =1 function
- Lambda is serverless
- Know what services are serverless!
- Lambda functions can trigger other lambda functions, 1 event can = x functions if functions trigger other functions
- Architectures can get extremely complicated, AWS X-ray allows you to debug what is happening
- Lambda can do things globally, you can use it to back up S3 buckets to other S3 buckets etc
- Know your triggers
2. Lab - Amazon Lambda
Create a serverless website.
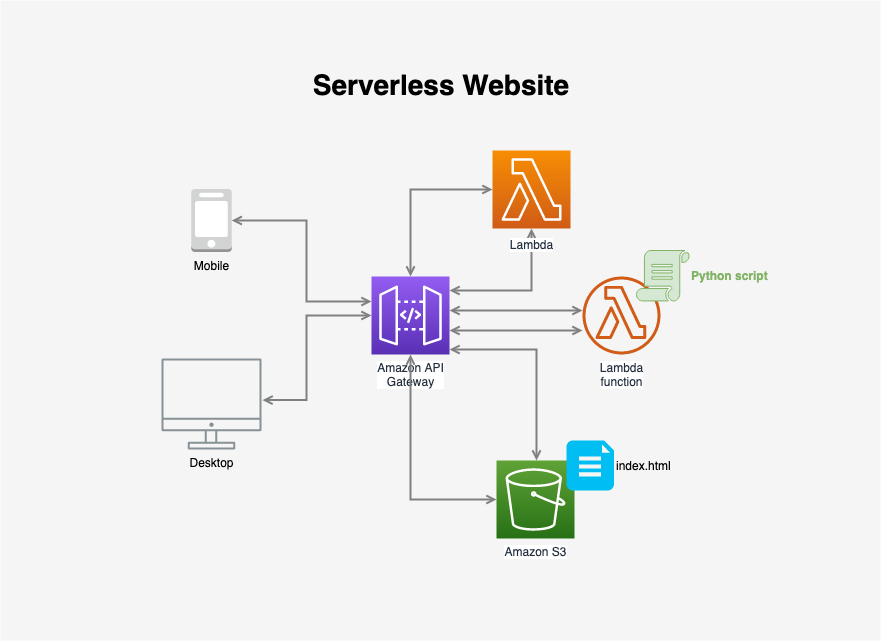
2.1 Creating Lambda Function
Go to Services->Compute->Lambda, create a function.
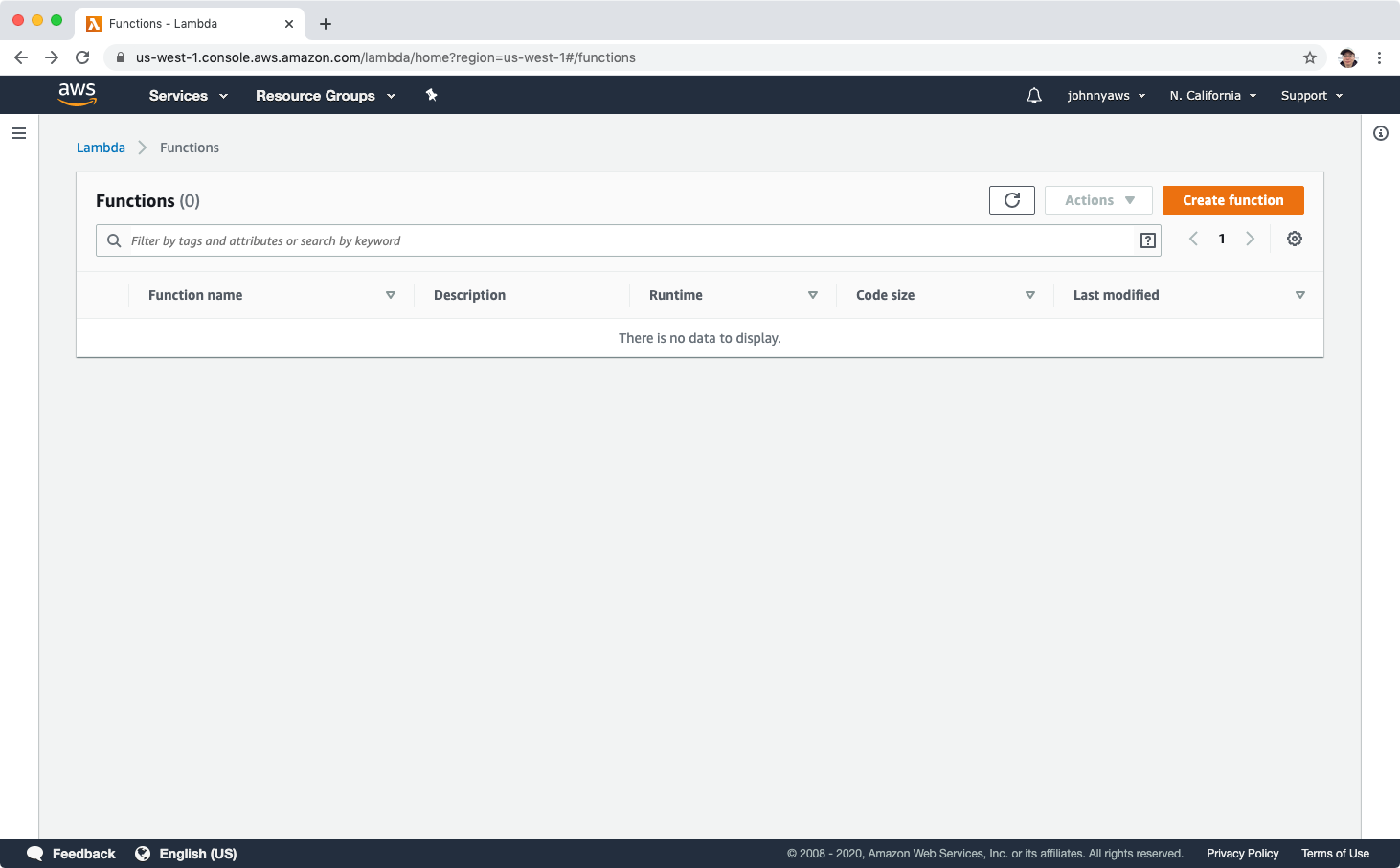 Choose “Author from scratch”, set name, choose python 3.8 for runtime.
Choose “Author from scratch”, set name, choose python 3.8 for runtime.
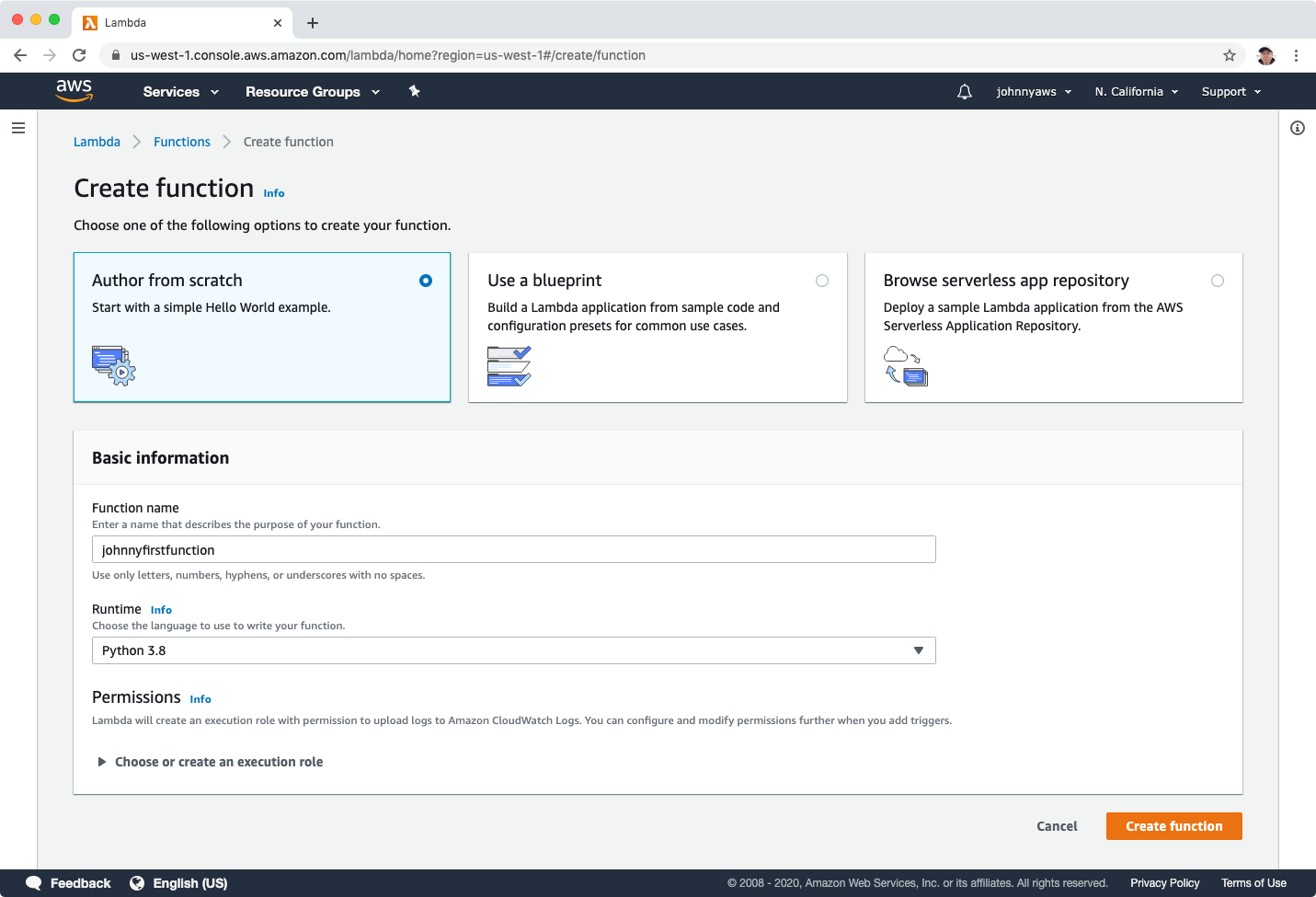 Create a new role and select ‘Simple microservice permissions’ policy template, click “Create function”.
Create a new role and select ‘Simple microservice permissions’ policy template, click “Create function”.
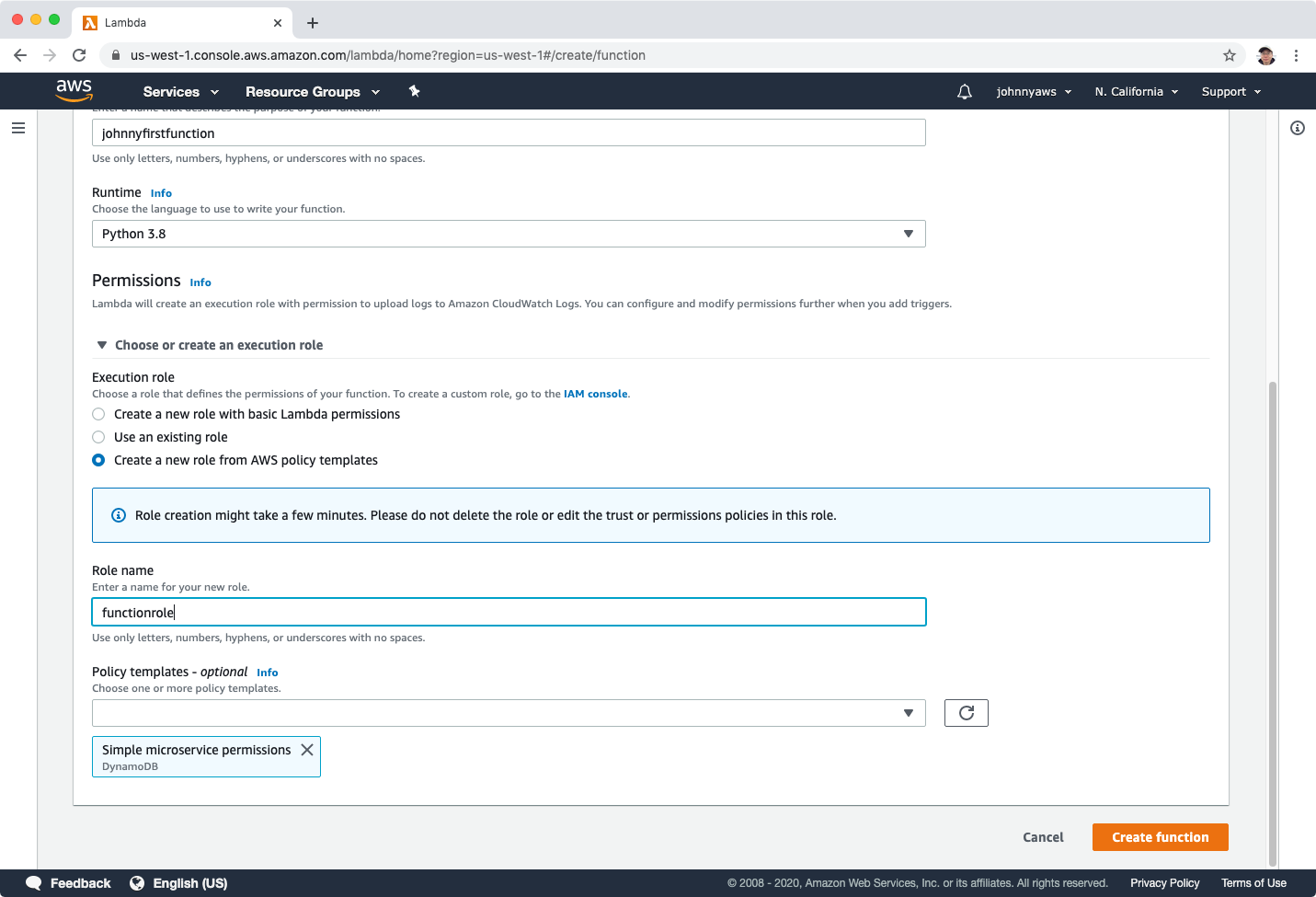 Lambda function is created.
Lambda function is created.
2.2 Configuring Lambda Function
Copy the following python codes.
def lambda_handler(event, context):
print("In lambda handler")
resp = {
"statusCode": 200,
"headers": {
"Access-Control-Allow-Origin": "*",
},
"body": "Johnny"
}
return resp
Paste them to the function code editor, save the change.
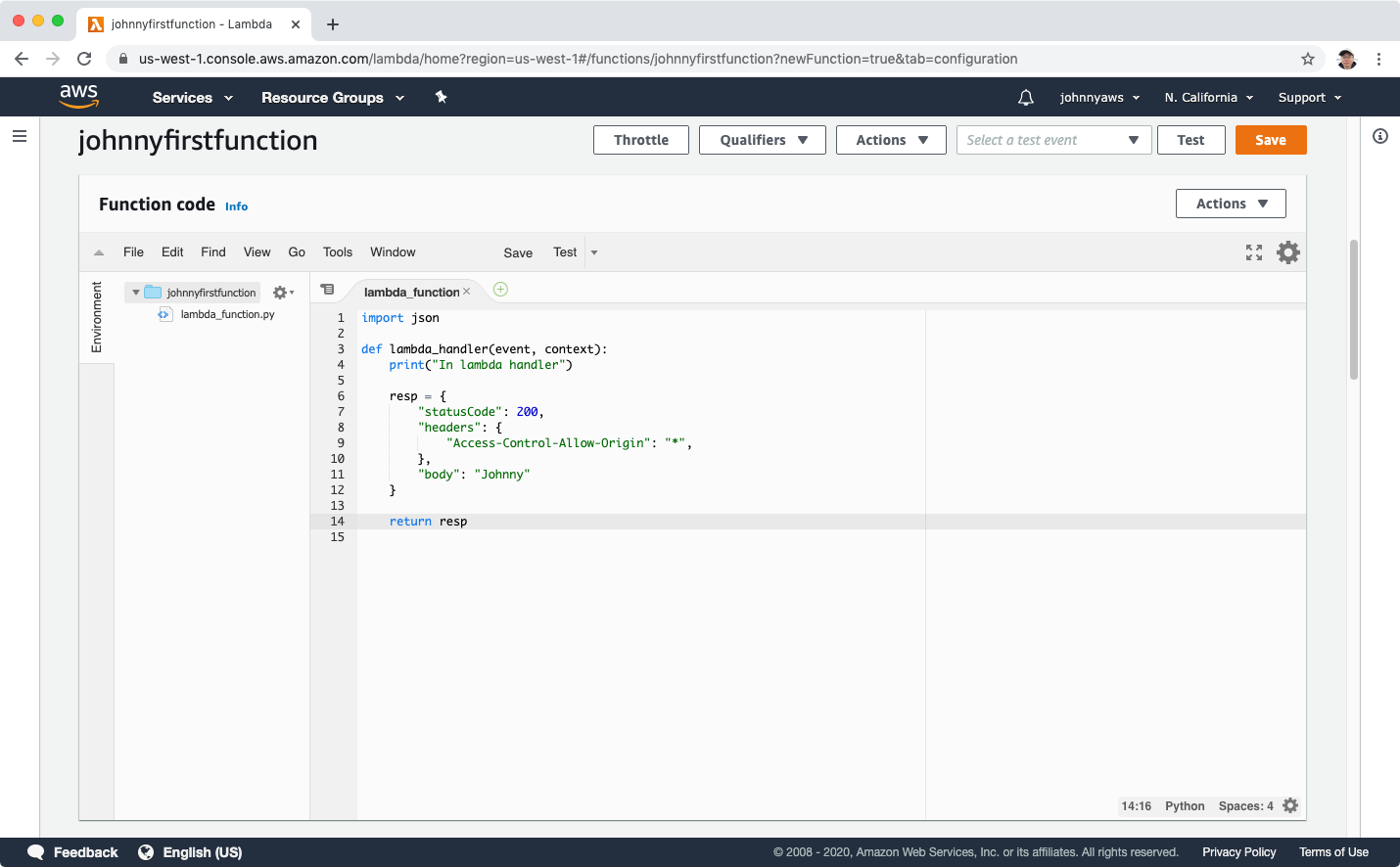 Scroll down, edit the “Basic settings” and set the description.
Scroll down, edit the “Basic settings” and set the description.
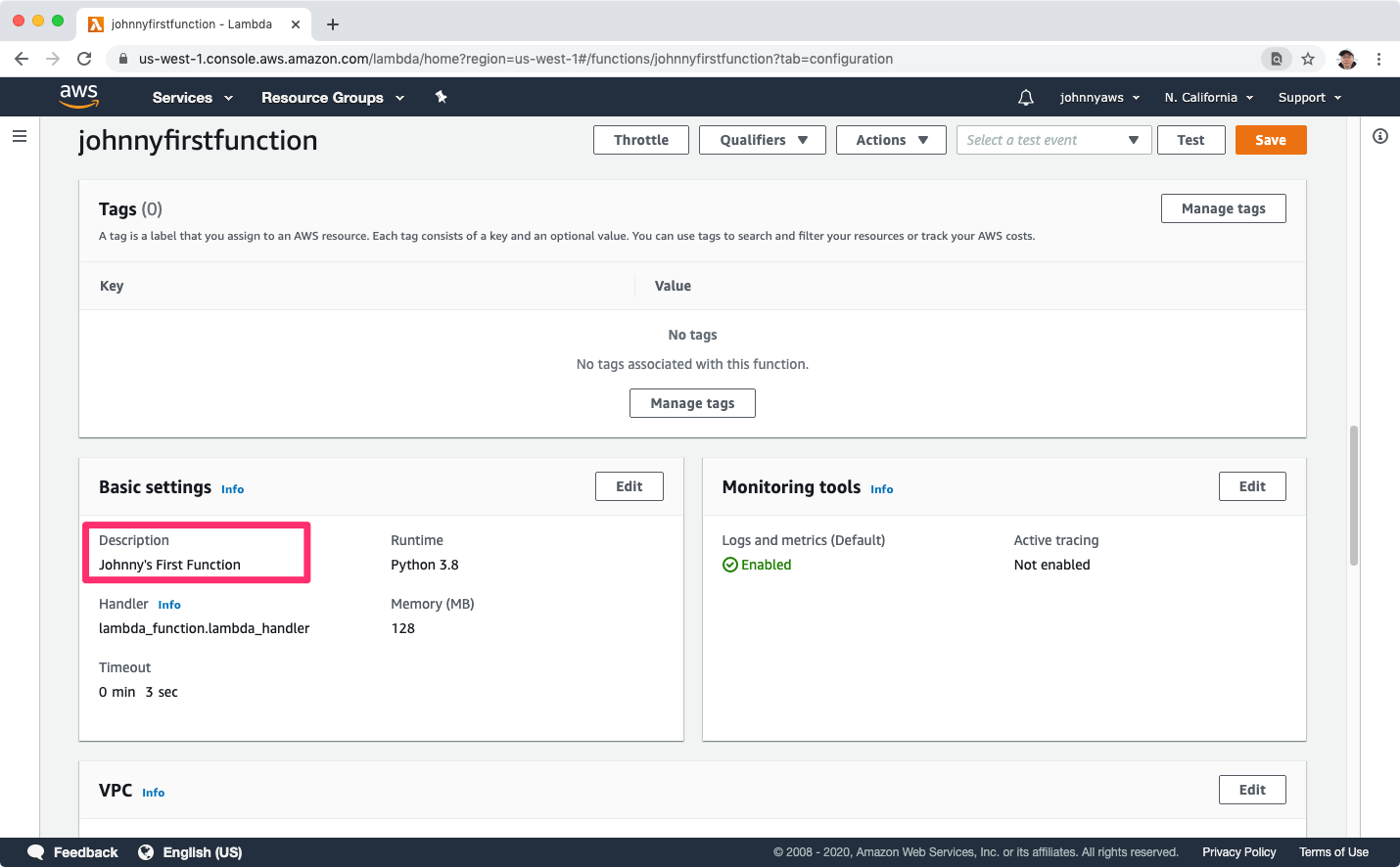 Scroll up and go back to the Designer, click ‘Add trigger’.
Scroll up and go back to the Designer, click ‘Add trigger’.
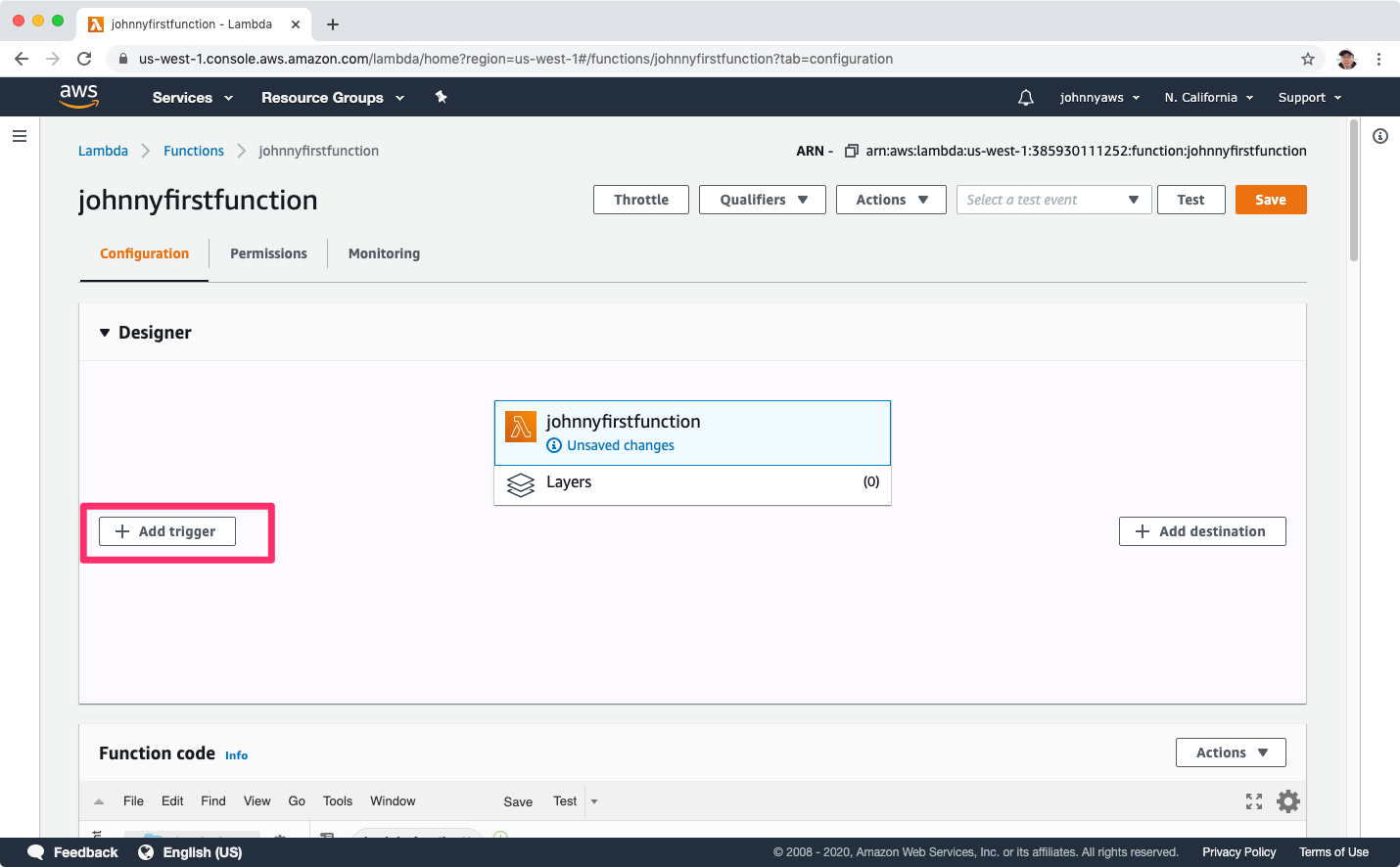 Select ‘API Gateway’, choose “Create an API”, select “HTTP API” as API type and select “Open” for security, click “Add” button.
Select ‘API Gateway’, choose “Create an API”, select “HTTP API” as API type and select “Open” for security, click “Add” button.
 The API Gateway trigger is created.
The API Gateway trigger is created.
 Save the function.
Save the function.
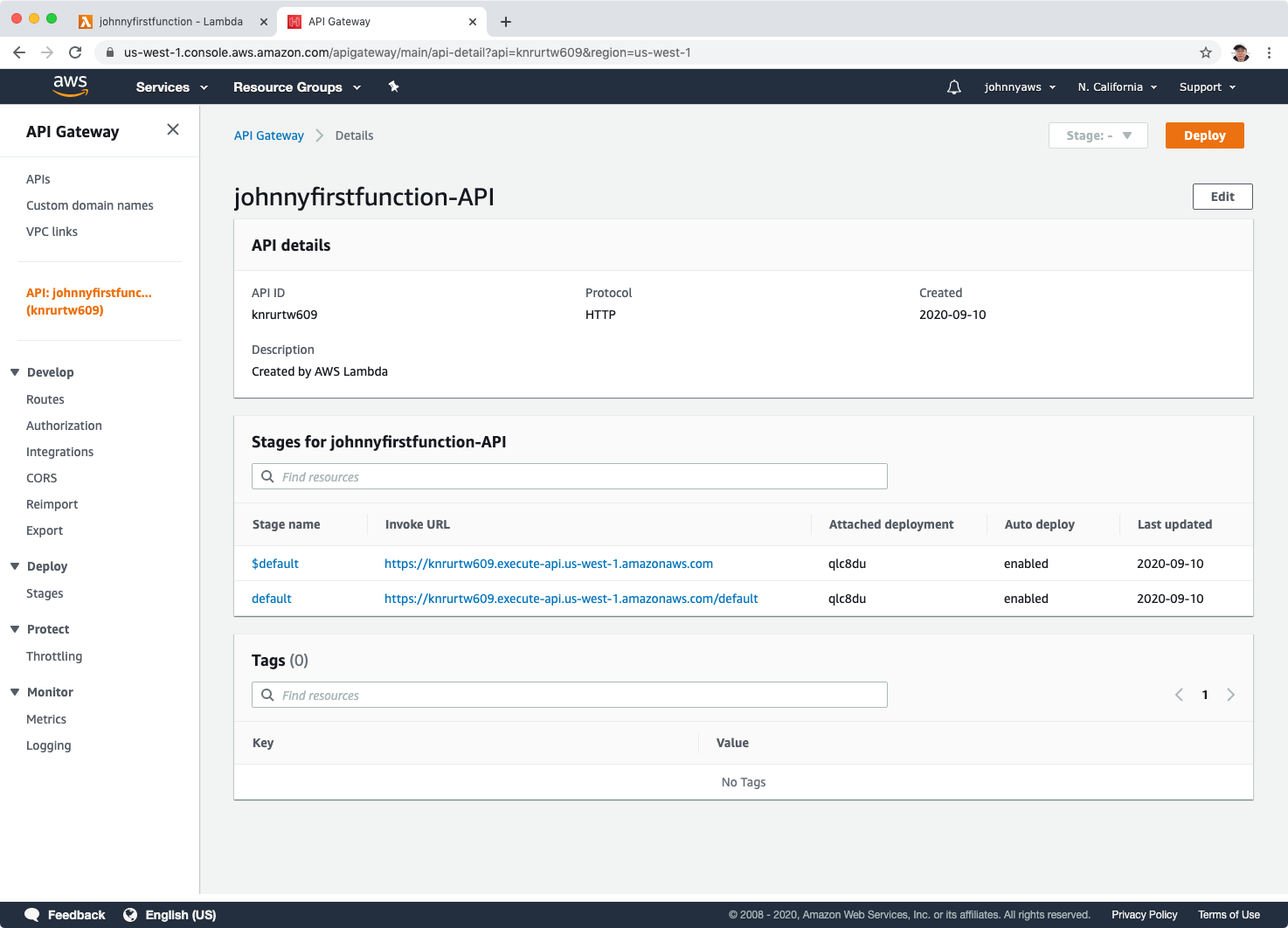
2.3 Deploying Function
Click the api link in the API Gateway section. A new window will be opened, click the Deploy button. Wait for a while, then click on any invoke url(with default or w/o default), eg. https://knrurtw609.execute-api.us-west-1.amazonaws.com/default.
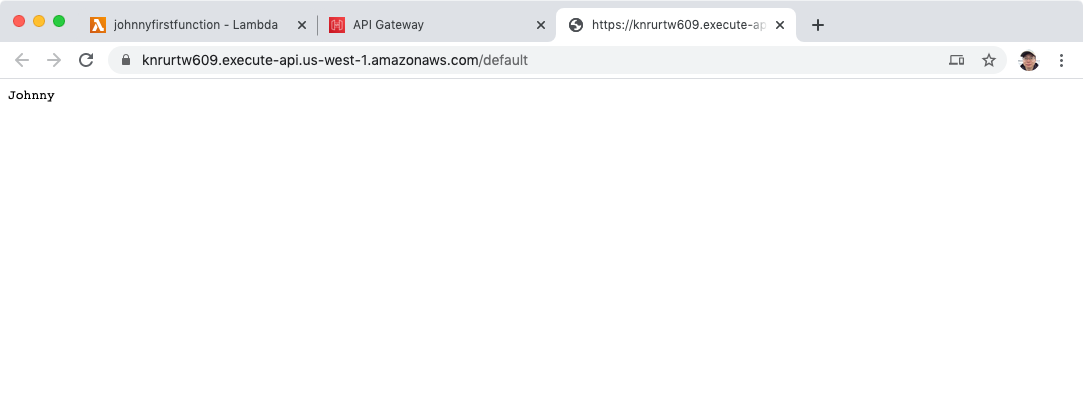
 Another window is opened. It should return “Johnny”, which is defined in the python script.
Another window is opened. It should return “Johnny”, which is defined in the python script.
2.4 Creating S3 Bucket
Now, our lambda function is working. We will create a static web page in S3 to call this function.
Go to Services->Storage->S3->Create bucket, set Bucket name and select region.
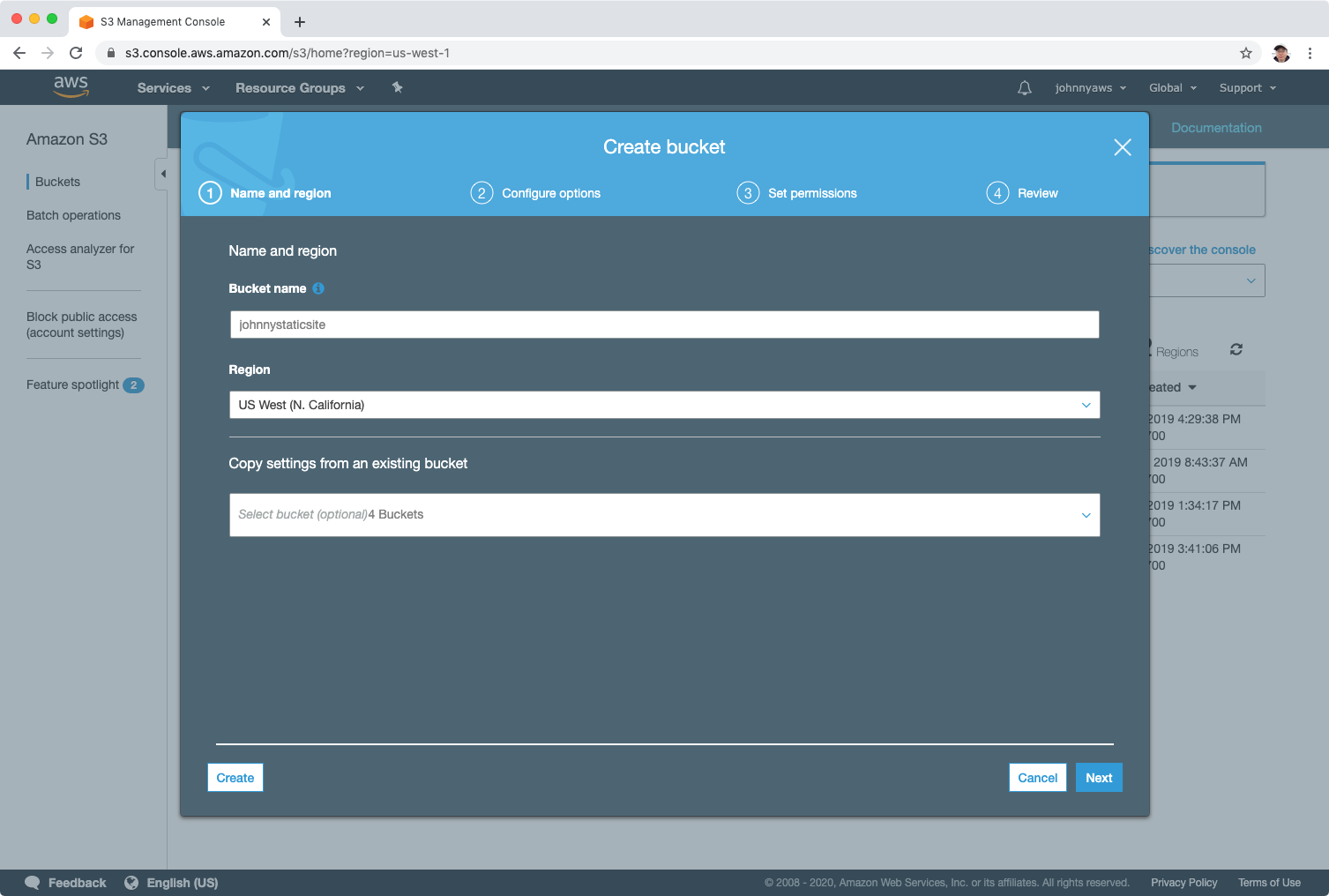 In the step “Set permissions”, uncheck “Block all public access”, next and create the bucket.
In the step “Set permissions”, uncheck “Block all public access”, next and create the bucket.
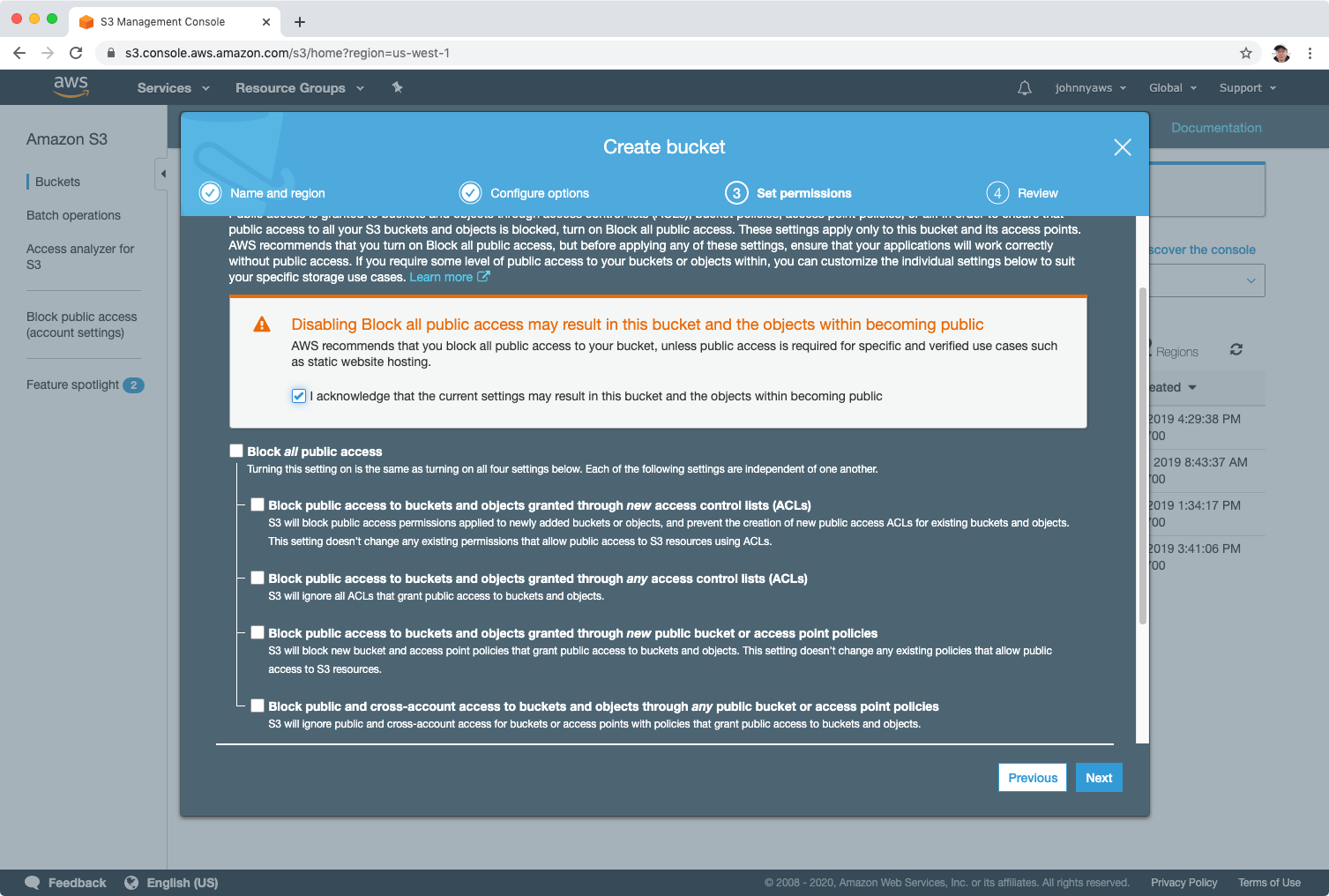 After the bucket is created, make sure the bucket is public.
After the bucket is created, make sure the bucket is public.
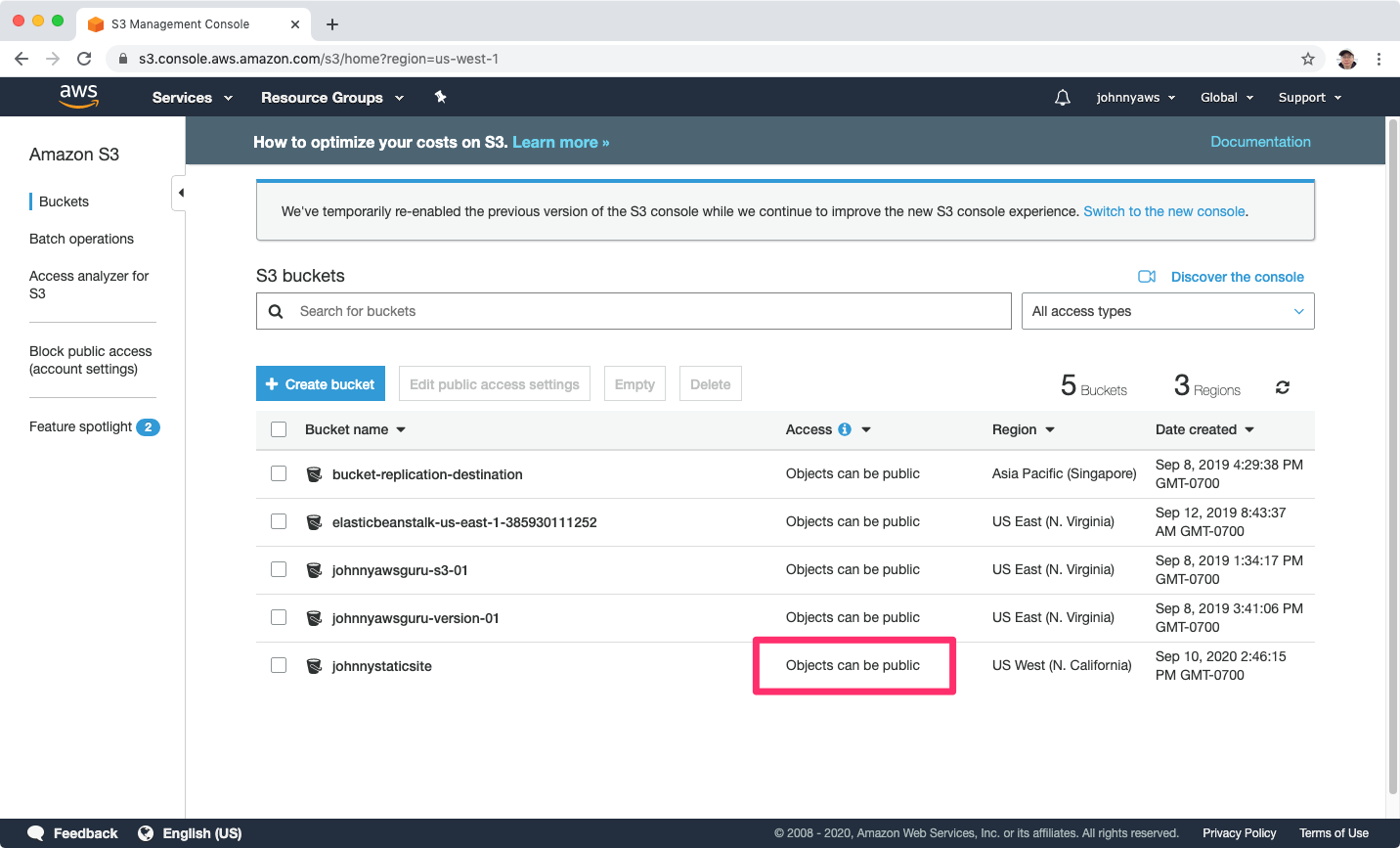 Click the bucket and switch to “Properties” tab, choose “Static website hosting”.
Click the bucket and switch to “Properties” tab, choose “Static website hosting”.
 Choose the “Use this bucket to host a website” option, set the index document(index.html) and error document(error.html), save.
Choose the “Use this bucket to host a website” option, set the index document(index.html) and error document(error.html), save.
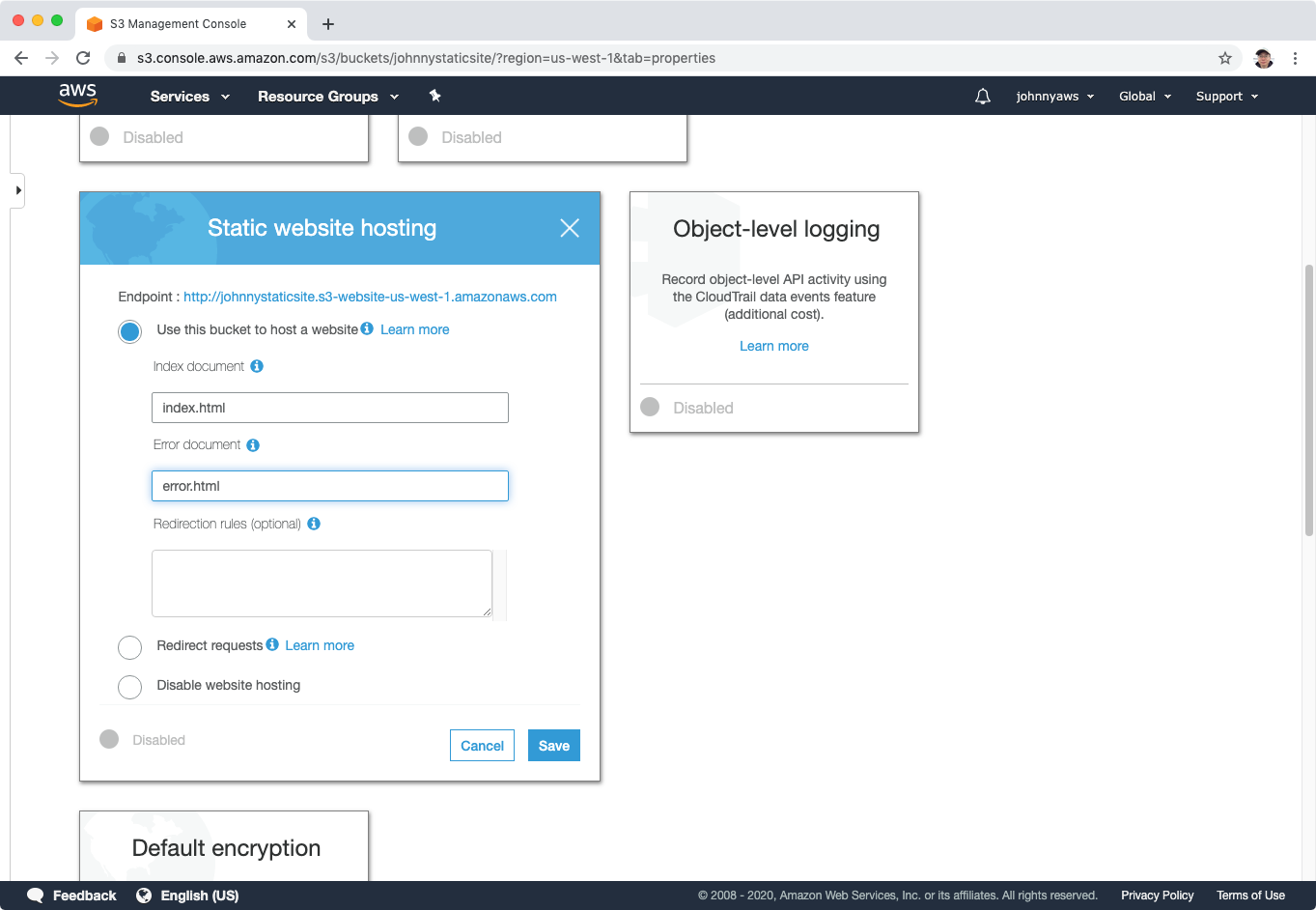 Static website hosting is set up.
Static website hosting is set up.
 Create two html files in your local machine with the following content respectively.
Create two html files in your local machine with the following content respectively.
index.html
<html>
<script>
function myFunction() {
var xhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhttp.onreadystatechange = function() {
if (this.readyState == 4 && this.status == 200) {
document.getElementById("my-demo").innerHTML = this.responseText;
}
};
xhttp.open("GET", "YOUR-API-GATEWAY-URL", true);
xhttp.send();
}
</script>
<body>
<div align="center"><br><br><br><br>
<h1>Hello <span id="my-demo">AWS Lamda!</span></h1>
<button onclick="myFunction()">Click me</button><br>
</div>
</body>
</html>
- Replace YOUR-API-GATEWAY-URL with the invoke URL of the lambda function, eg. https://knrurtw609.execute-api.us-west-1.amazonaws.com.
error.html
<html>
<body>
<h1>Oops! Error occurred!</h1>
</body>
</html>
Upload these two files into the bucket and make them public.
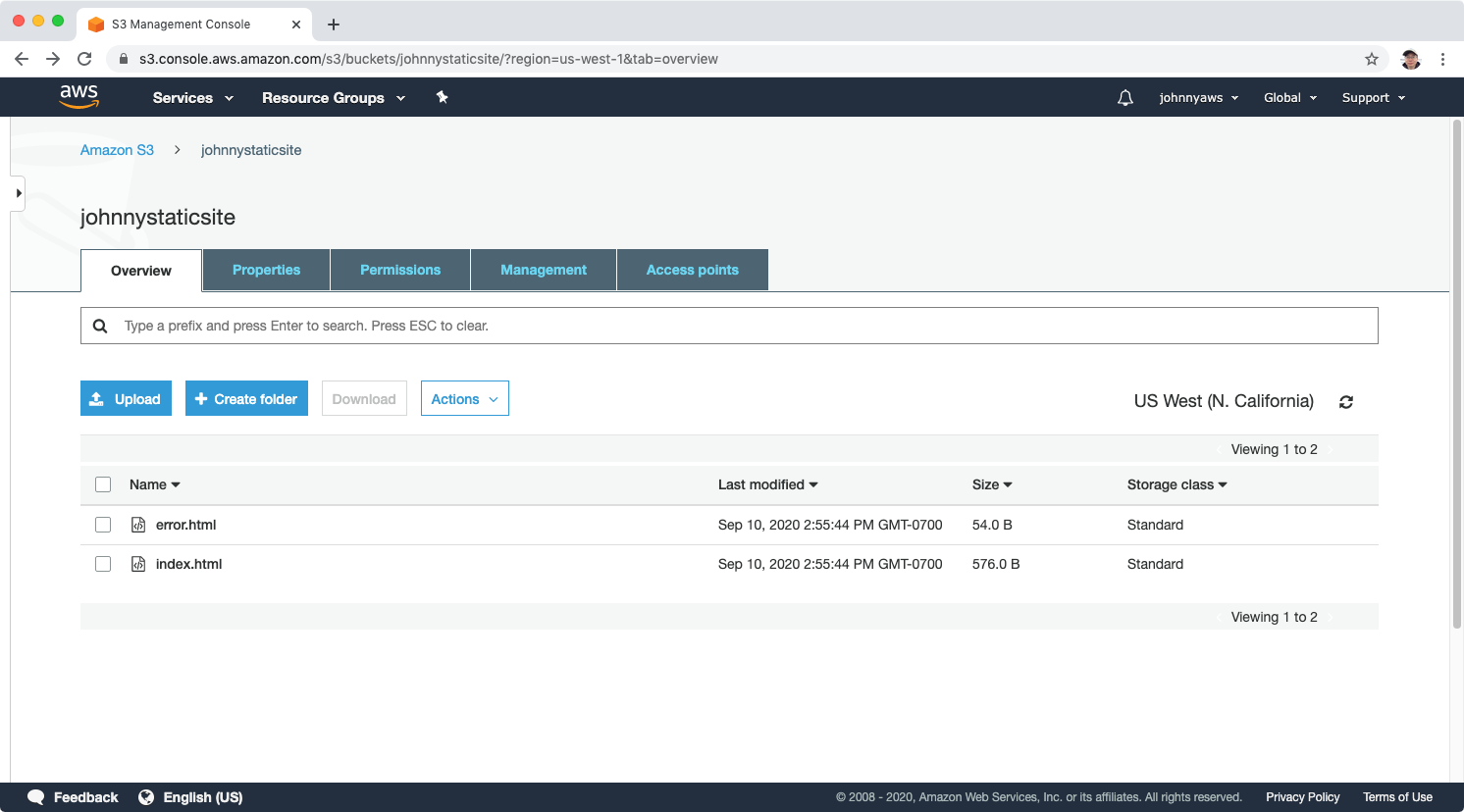
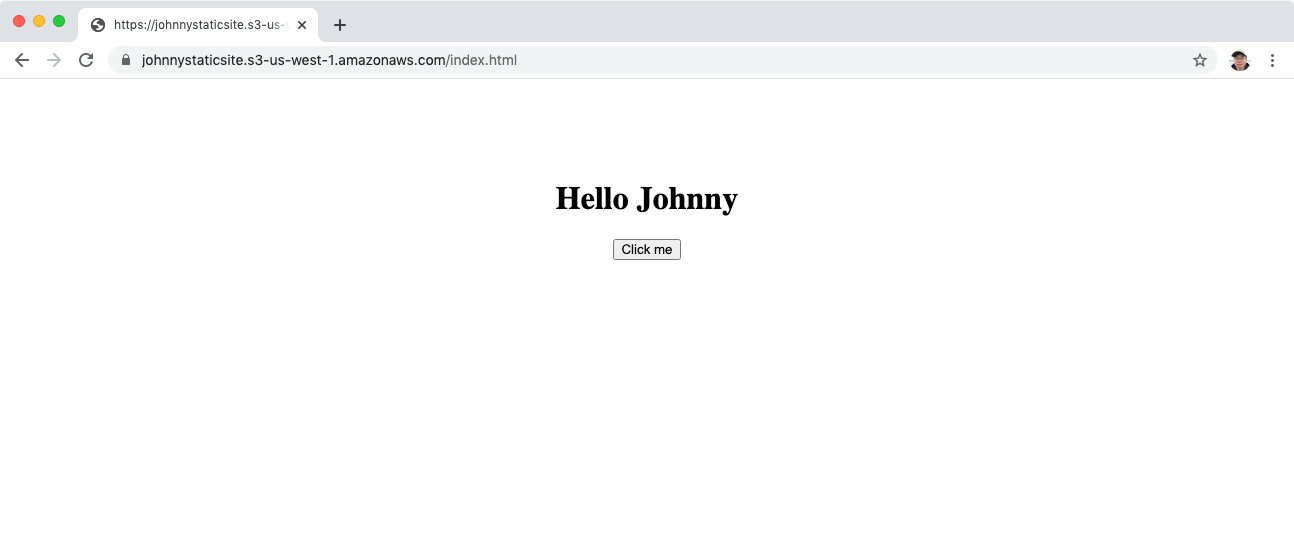
2.5 Testing Lambda Function
Visit the link of index.html in web browser. We should see the page.
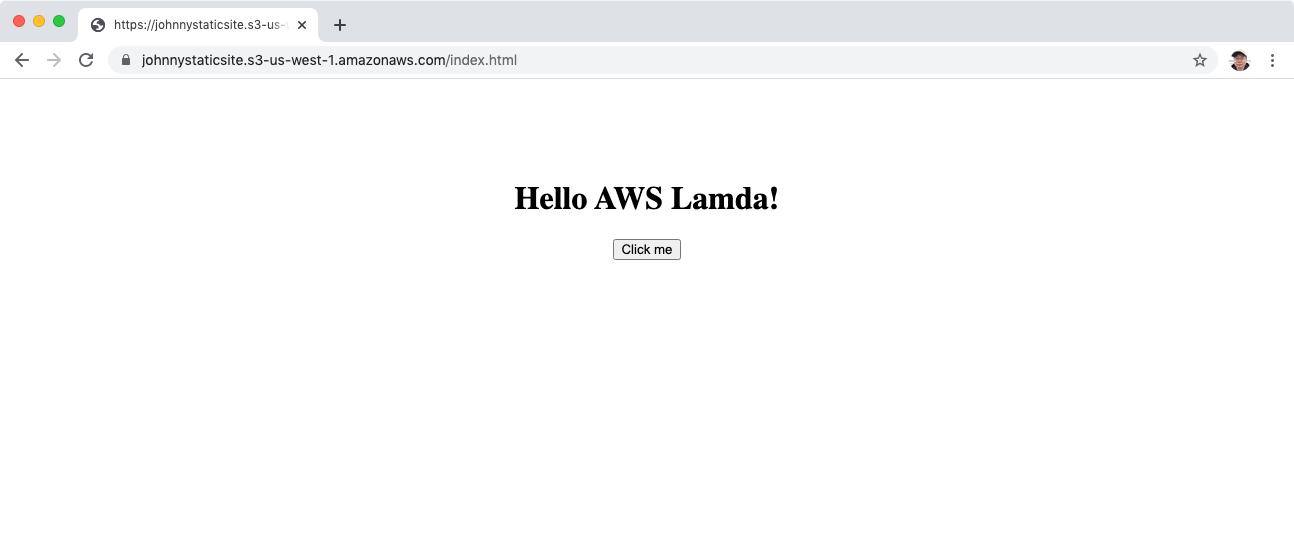 Click on the button, the title will be changed. A call to the lambda function is made to get the name.
Click on the button, the title will be changed. A call to the lambda function is made to get the name.