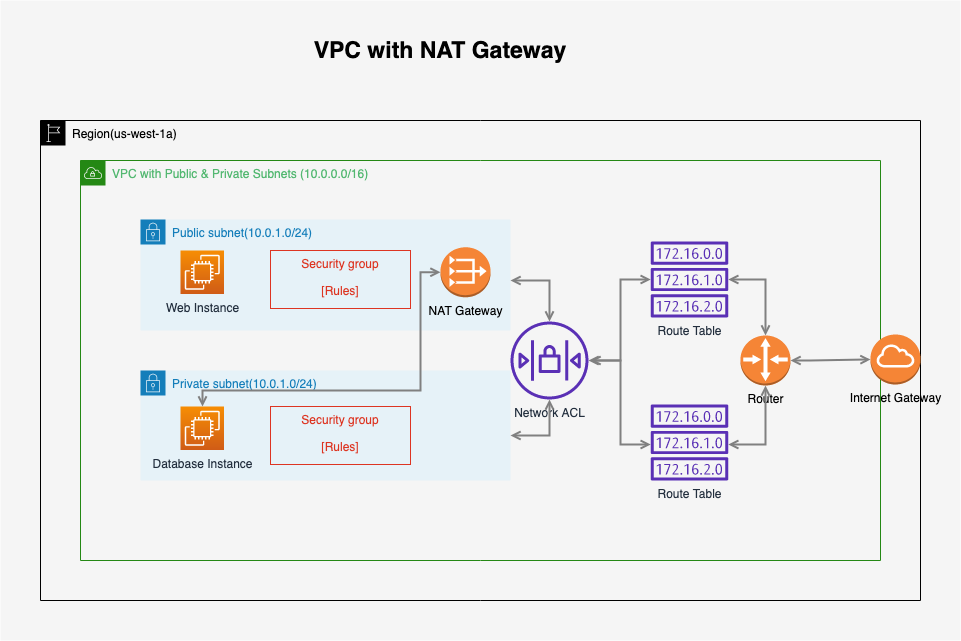
4162. AWS-VPC-NATAWS, VPC, and NAT
Use NAT Instance and NAT Gateway to setup public connection to internet.
1. Network Address Translation (NAT)
1.1 What is NAT?
Network address translation (NAT) is a method of remapping an IP address space into another by modifying network address information in the IP header of packets while they are in transit across a traffic routing device. Network Address Translation allows a single device, such as a router, to act as an agent between the Internet (or “public network”) and a local (or “private”) network.
AWS offers two kinds of NAT devices — NAT instance or NAT gateway.
1.2 NAT Instance
- When creating a NAT instance, disable Source/Destination Check on the Instance.
- NAT instances must be in a public subnet.
- There must be a route out of the private subnet to the NAT instance, in order for this to work.
- The amount of traffic that NAT instances can support depends on the instance size. If you are bottlenecking, increase the instance size.
- You can create high availability using Autoscaling Groups, multiple subnets in different AZs, and a script to automate failover.
- Behind a Security Group.
1.3 NAT Gateway
- Redundant inside the Availability Zone
- Preferred by the enterprise
- Starts at 5Gbps and scales currently to 45Gbps
- No need to patch
- Not associated with security groups
- Automatically assigned a public ip address
- Remember to update your route tables.
- No need to disable Source/Destination Checks
- If you have resources in multiple Availability Zones and they share one NAT gateway, in the event that the NAT gateway’s Availability Zone is down, resources in the other Availability Zones lose internet access. To create an Availability Zone-independent architecture, create a NAT gateway in each Availability Zone and configure your routing to ensure that resources use the NAT gateway in the same Availability Zone.
2. Lab - NAT Instance
Continue with the VPC lab. Currently, there is one problem with the database server, it has no public connection to internet. We will create NAT instance and NAT Gateway to setup the connection for database server.
2.1 Creating NAT Instance
Launch new instance, search ‘nat’ in the ‘Community AMIs’, select the first one.
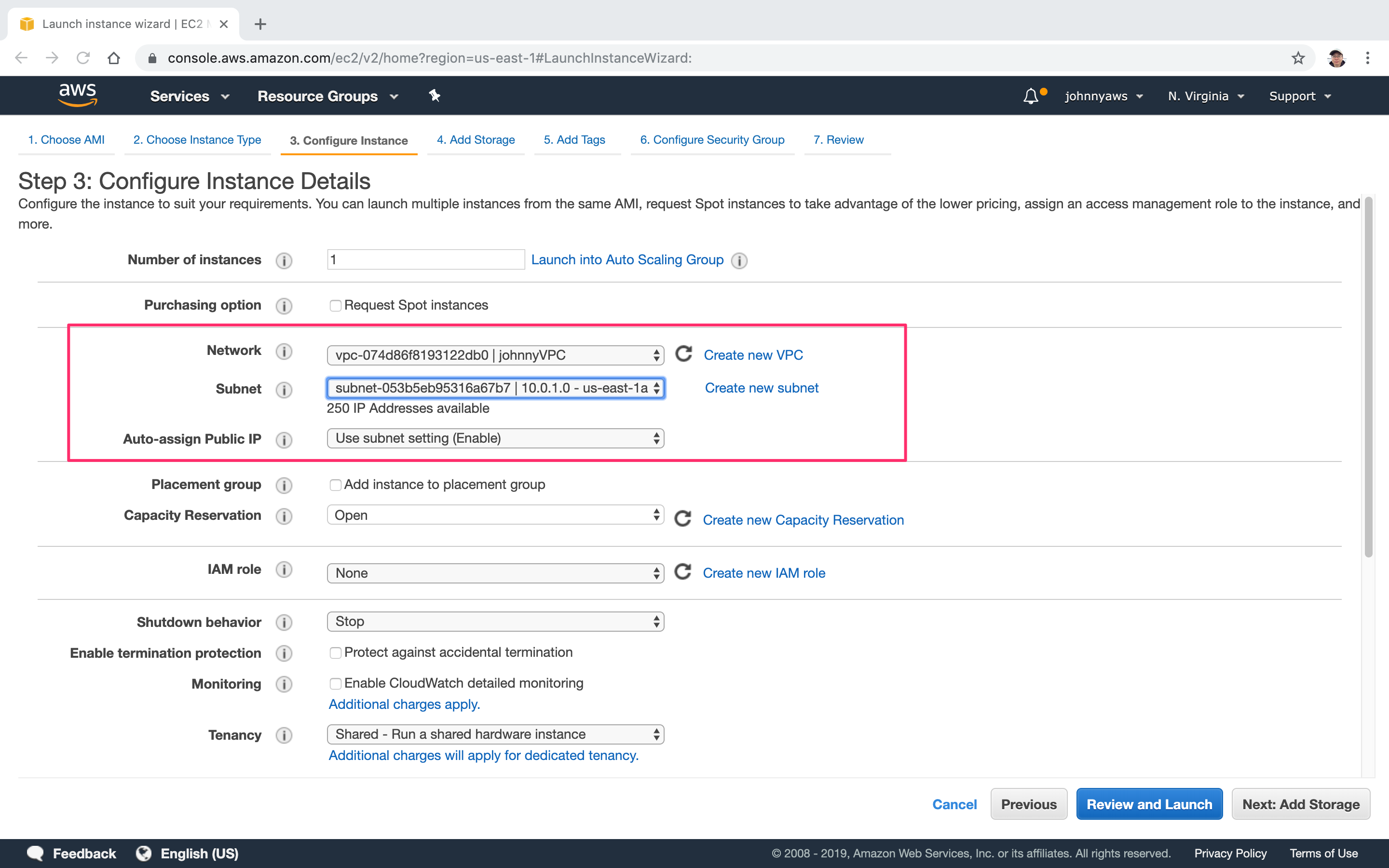
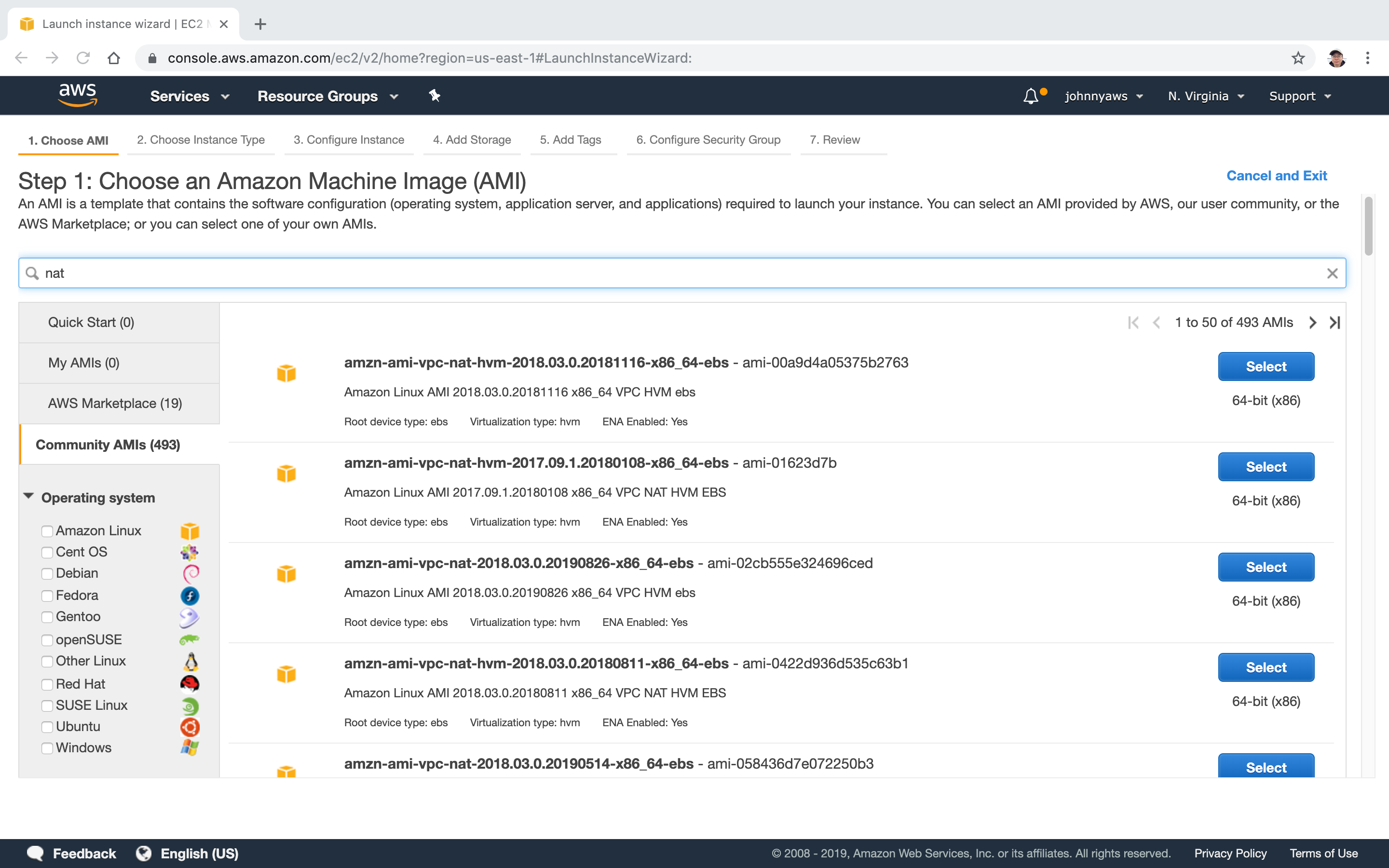 Select the custom VPC and choose the public subnet(10.0.1.0).
Select the custom VPC and choose the public subnet(10.0.1.0).
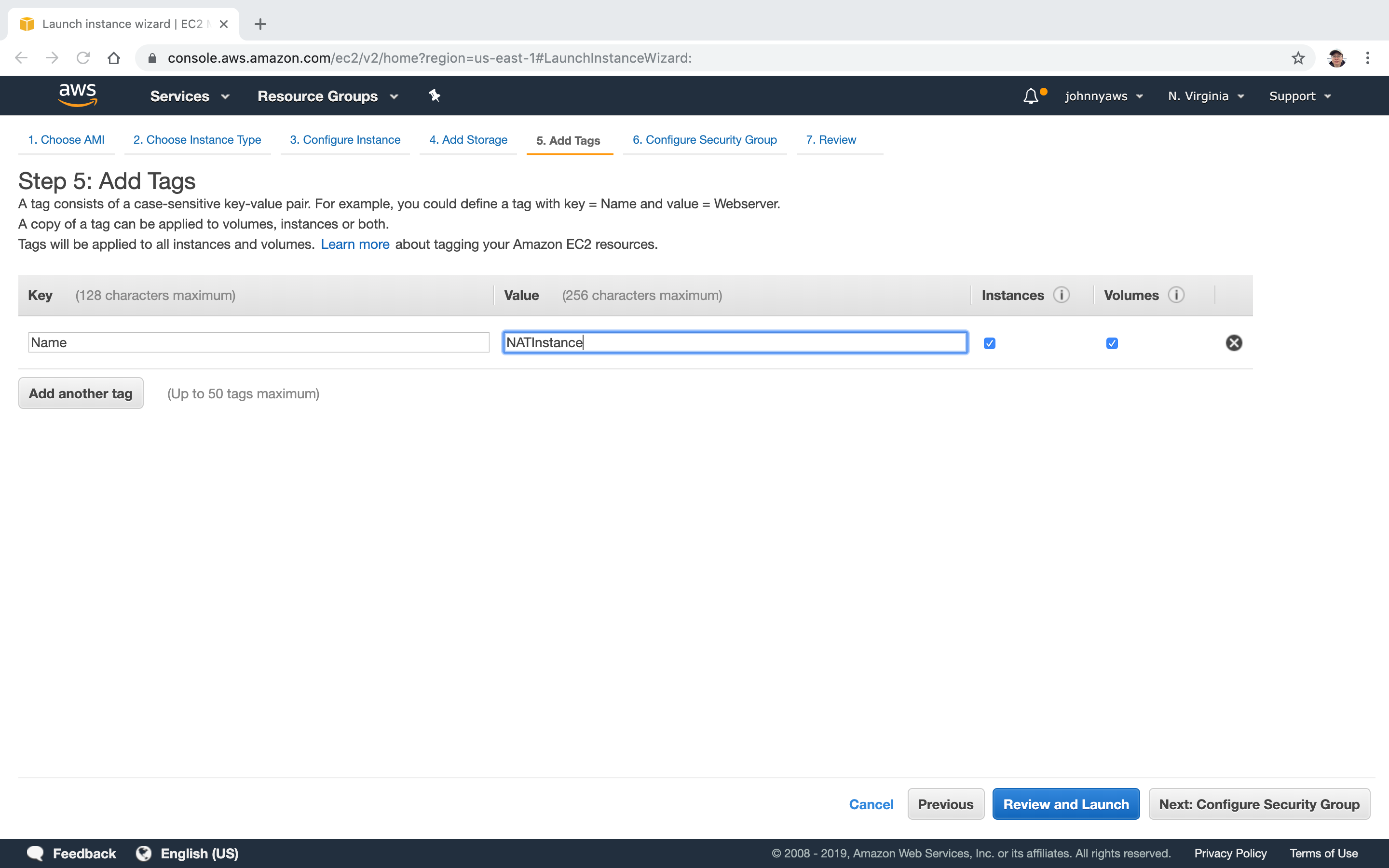
 Add name to indicate it is a NAT instance.
Add name to indicate it is a NAT instance.
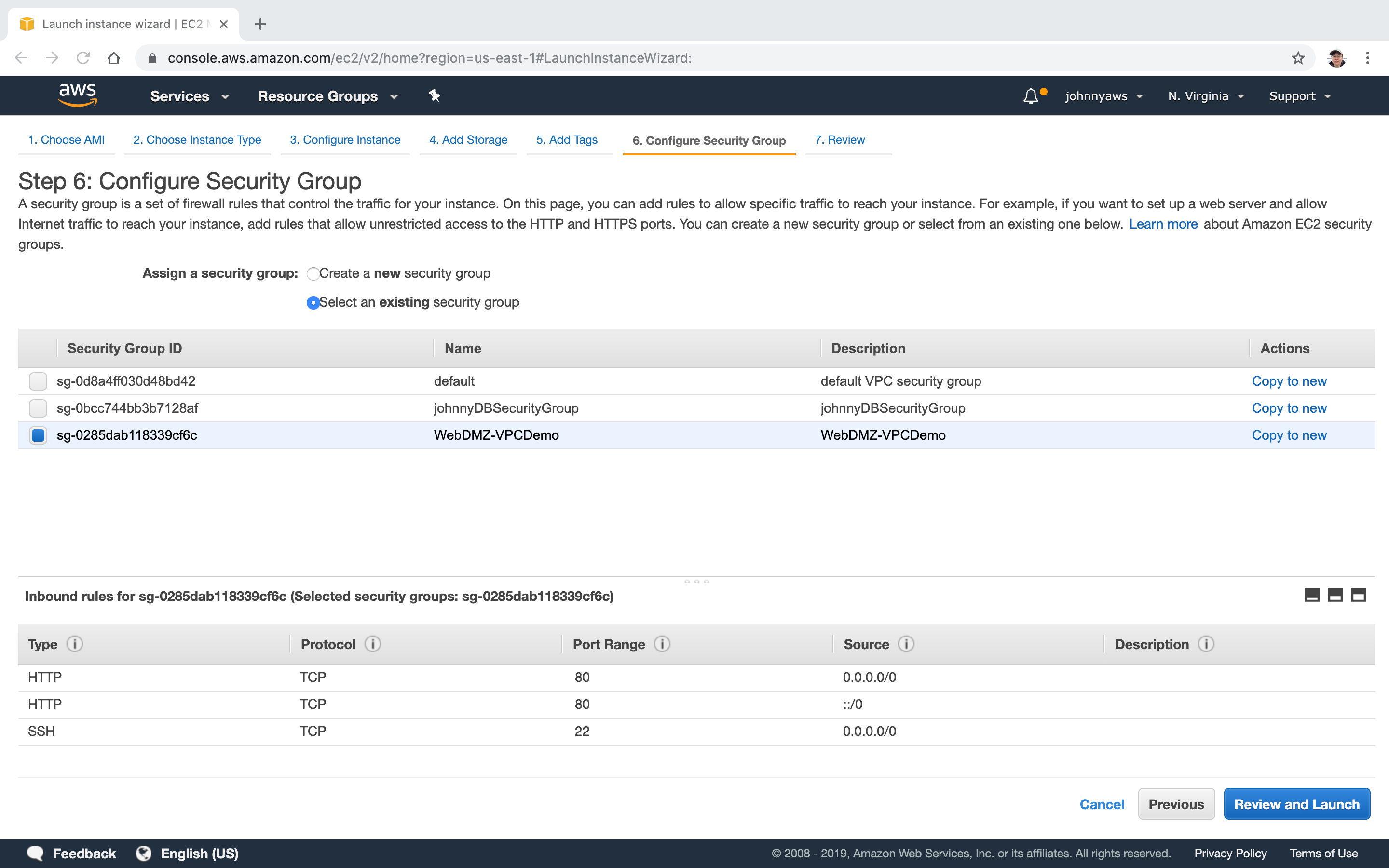
 Select the WebDMZ group, Review and Launch.
Select the WebDMZ group, Review and Launch.
 Choose the second option and continue.
Choose the second option and continue.
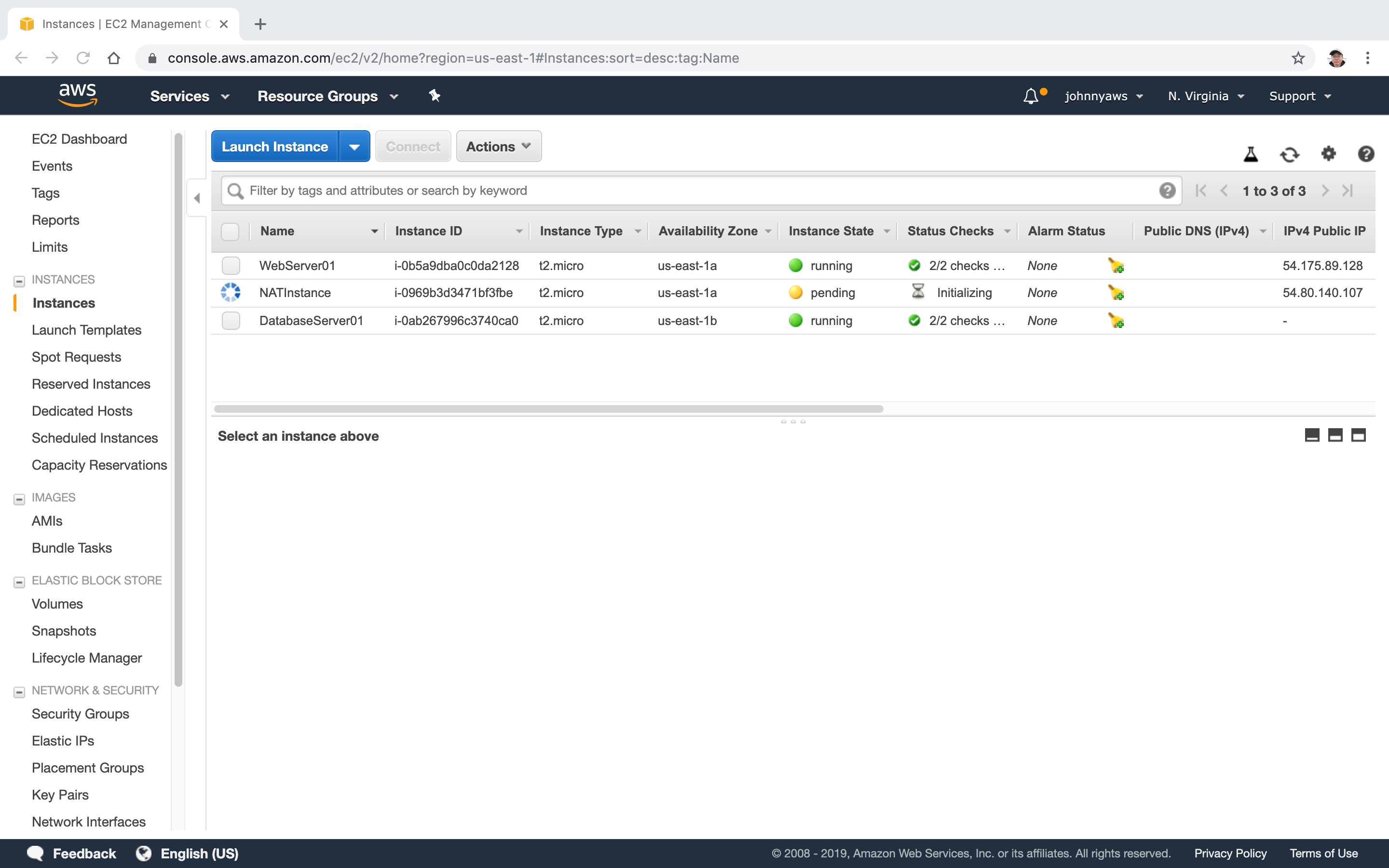
 The NAT instance is created, it’s running in the same AZ with the web server. It has its own public ip address.
The NAT instance is created, it’s running in the same AZ with the web server. It has its own public ip address.
2.2 Disabling Source/Destination Checks
Select the NAT instance, actions->Networking->Change Source/Dest. Check.
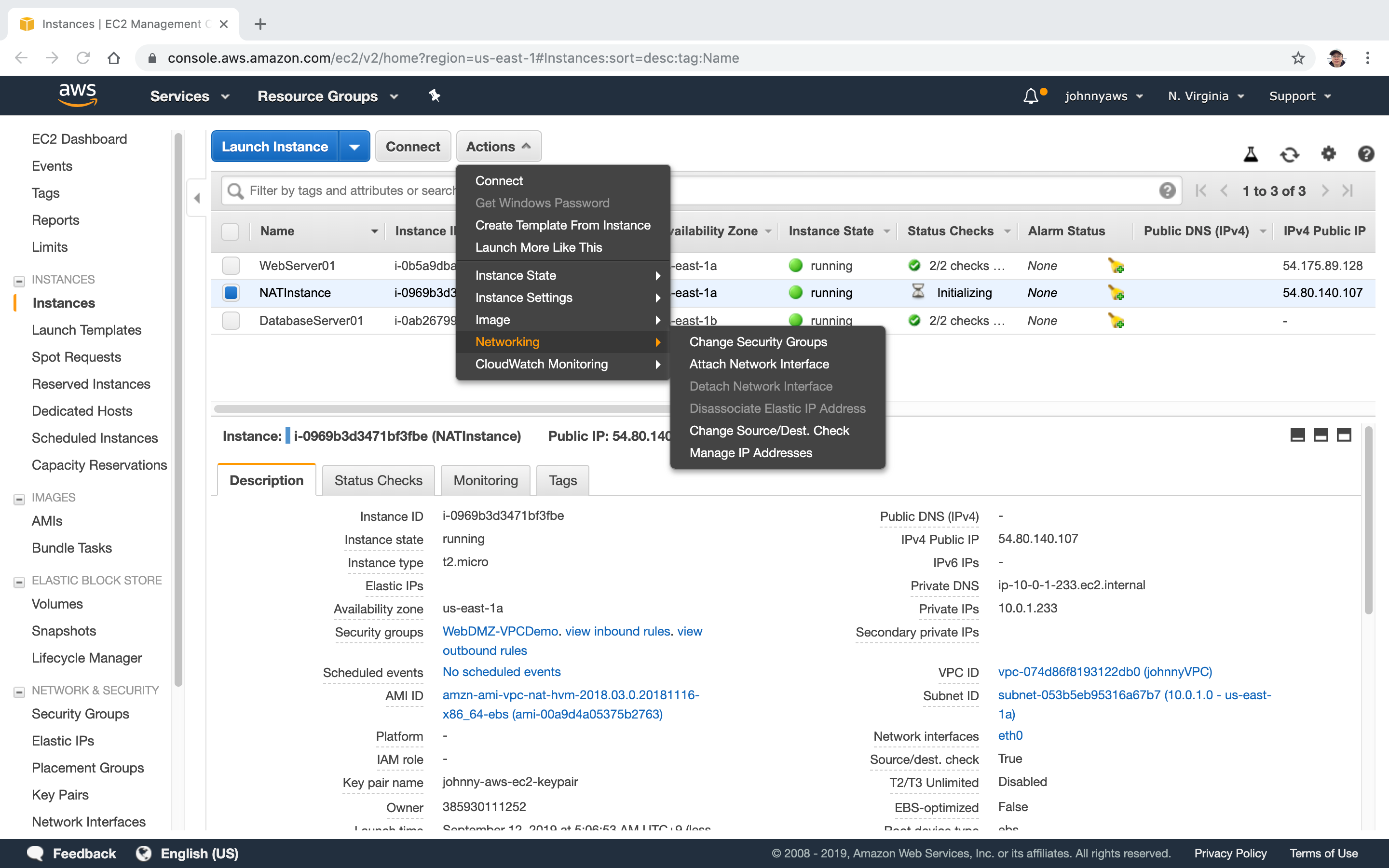 Disable it.
Disable it.
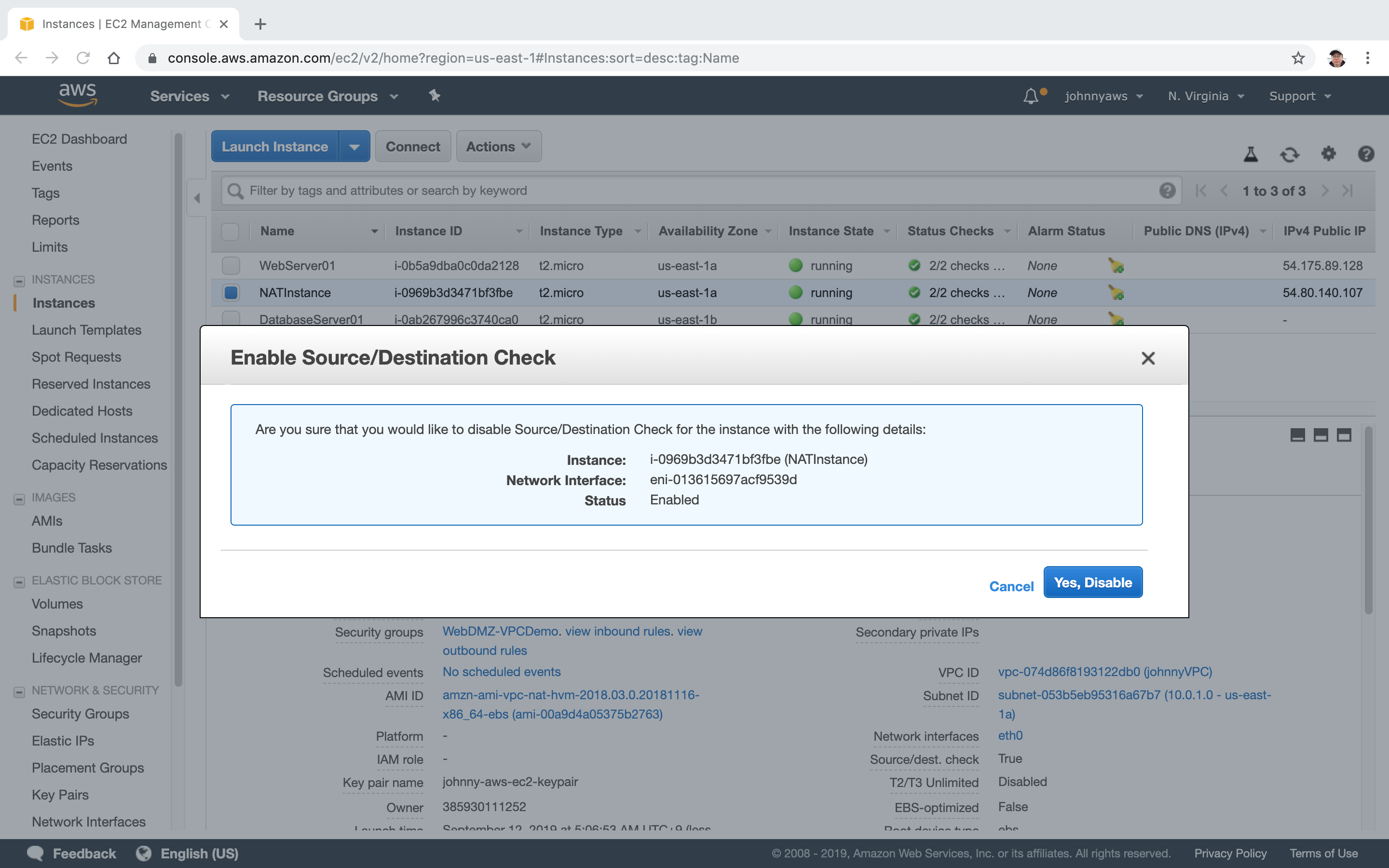
- Check NAT Instances for more details.
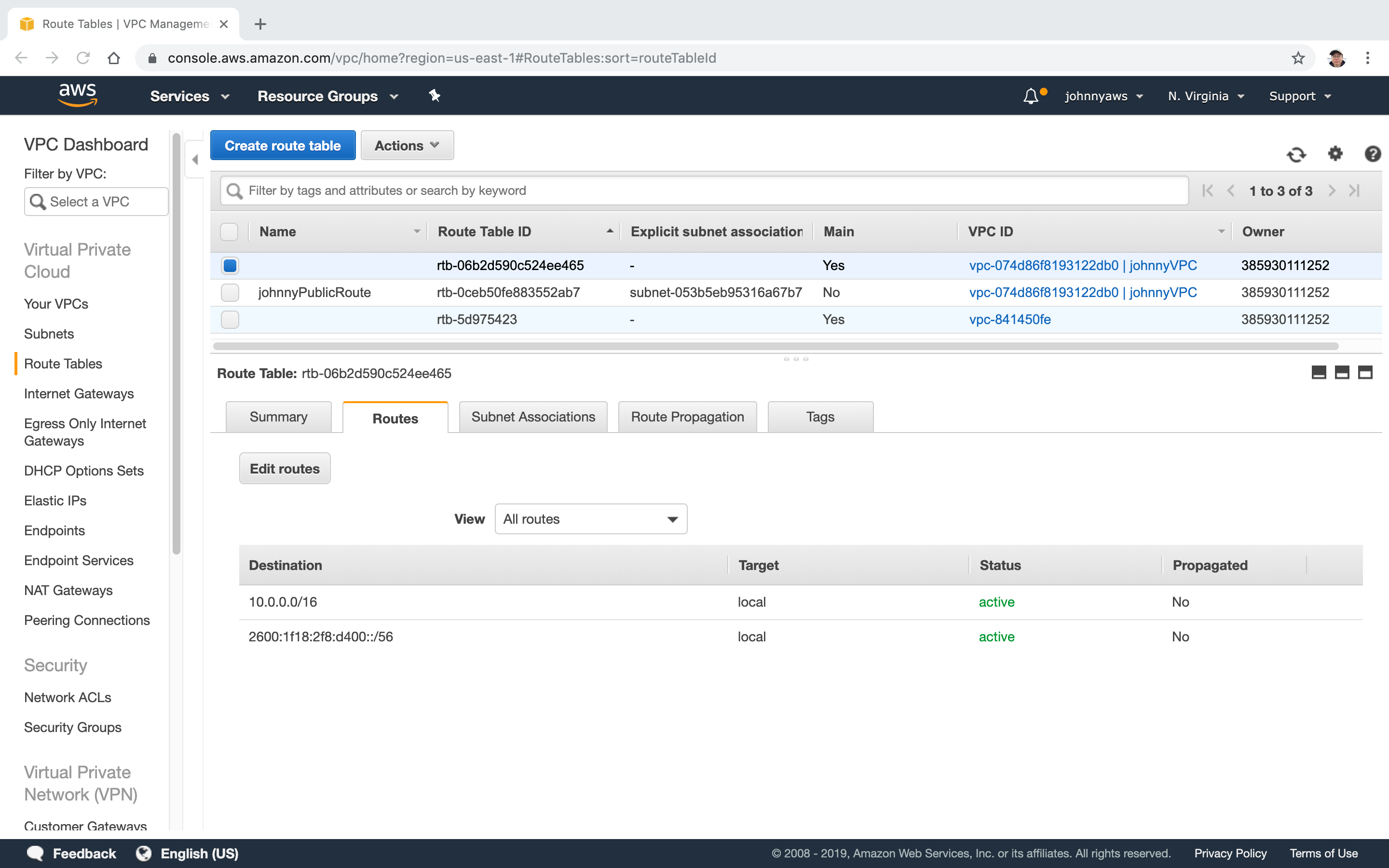
2.3 Creating Routes
Create routes to let database server talk to NAT instance.
Go to Services->VPC->Route Tables, select the main route table of the custom VPC, click “Edit rules”.
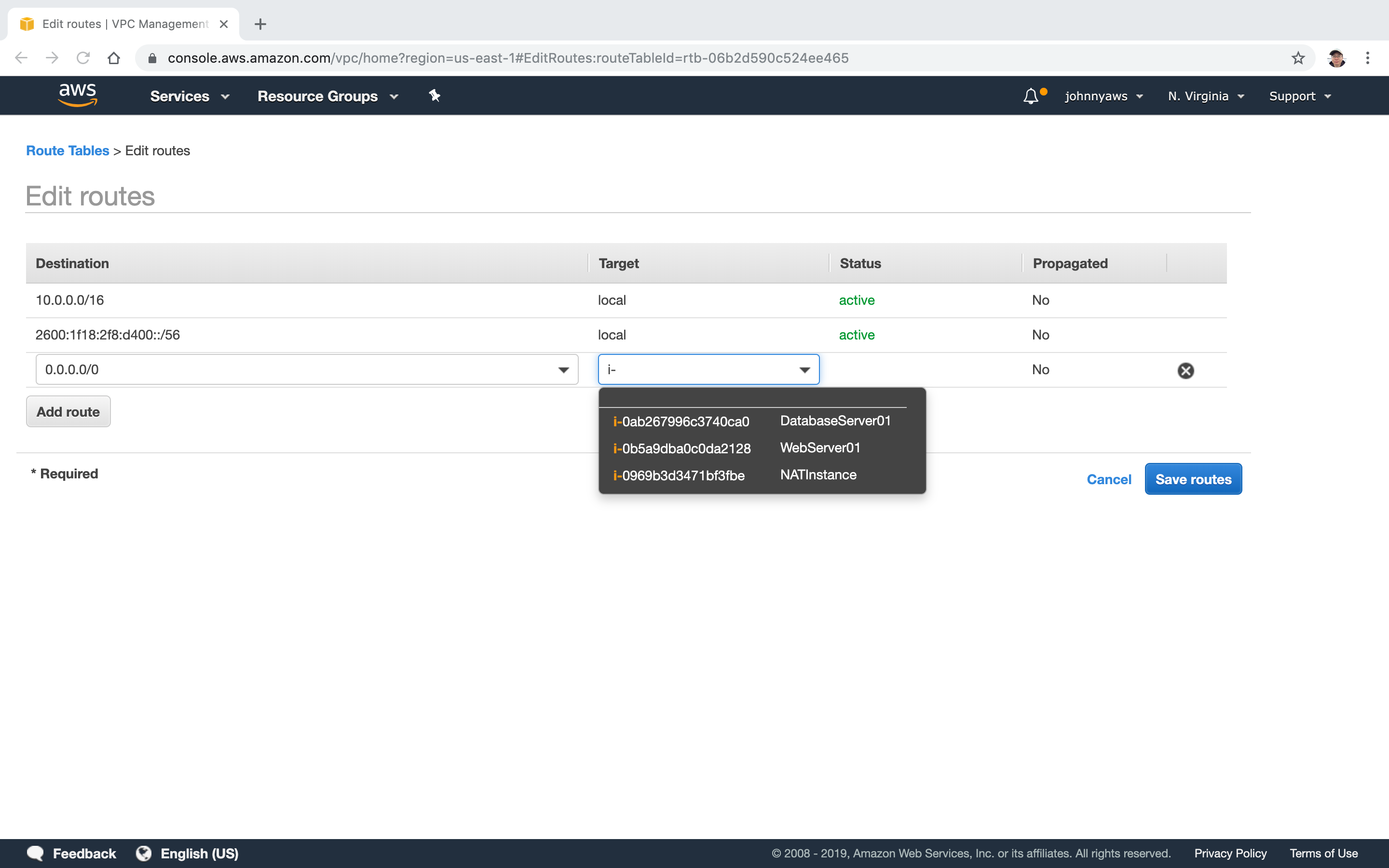
 Select the NAT instance as target, Save.
Select the NAT instance as target, Save.
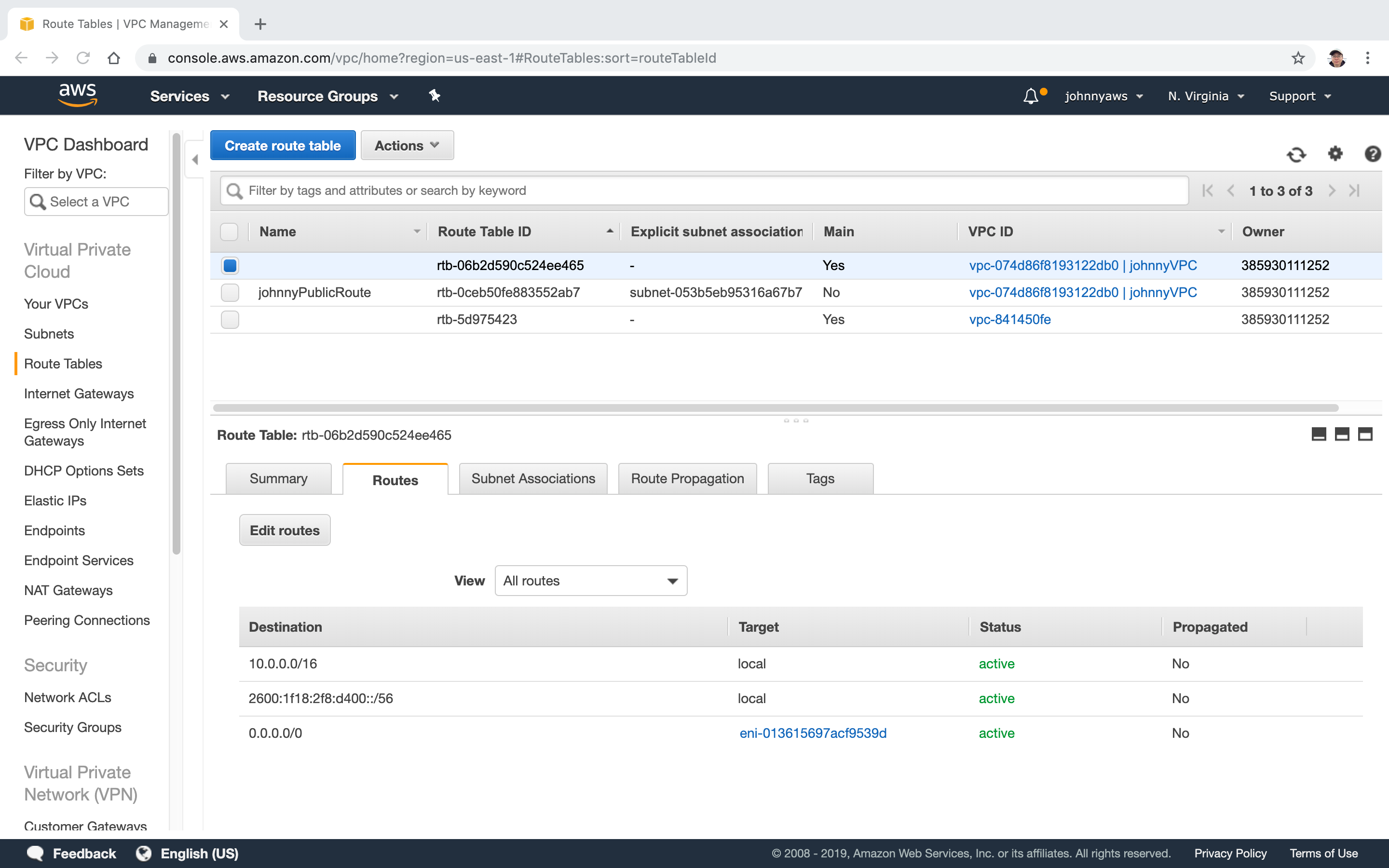
 New route is created.
New route is created.
 Now, if you ssh to your webserver, then ssh to your database server, you can run “yum install update”, and it will be able to download files from internet.
Now, if you ssh to your webserver, then ssh to your database server, you can run “yum install update”, and it will be able to download files from internet.
2.4 Drawback of NAT Instance
NAT instance is not good as it may be overloaded. If it is stopped, then database server will lose the internet connection and you will see the route status becomes to “blackhole”.
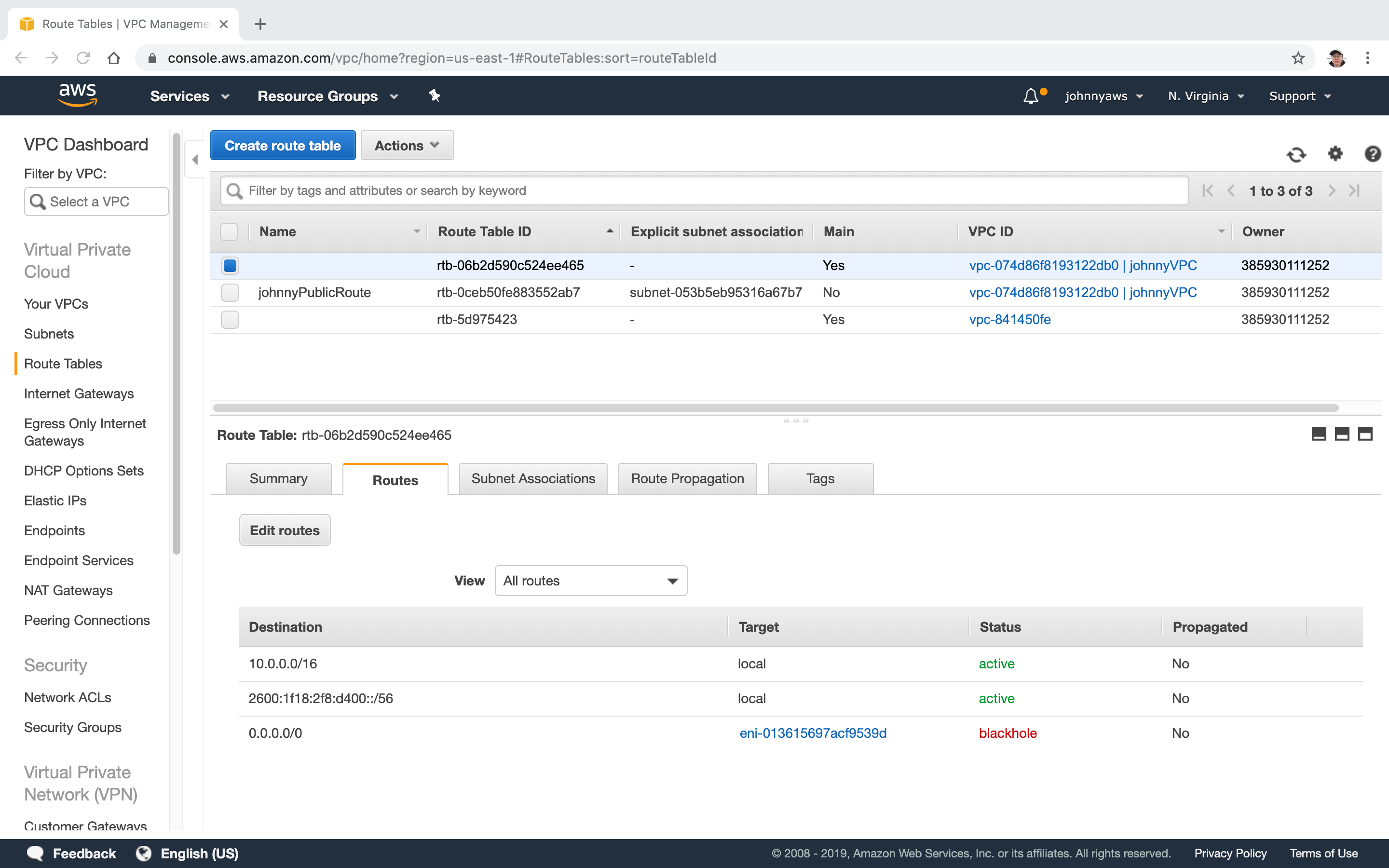 Create NAT gateway which is more reliable and flexible.
Create NAT gateway which is more reliable and flexible.
3. Lab - NAT Gateway
3.1 Creating NAT Gateway
Go to VPC->NAT Gateways->Create NAT Gateway.
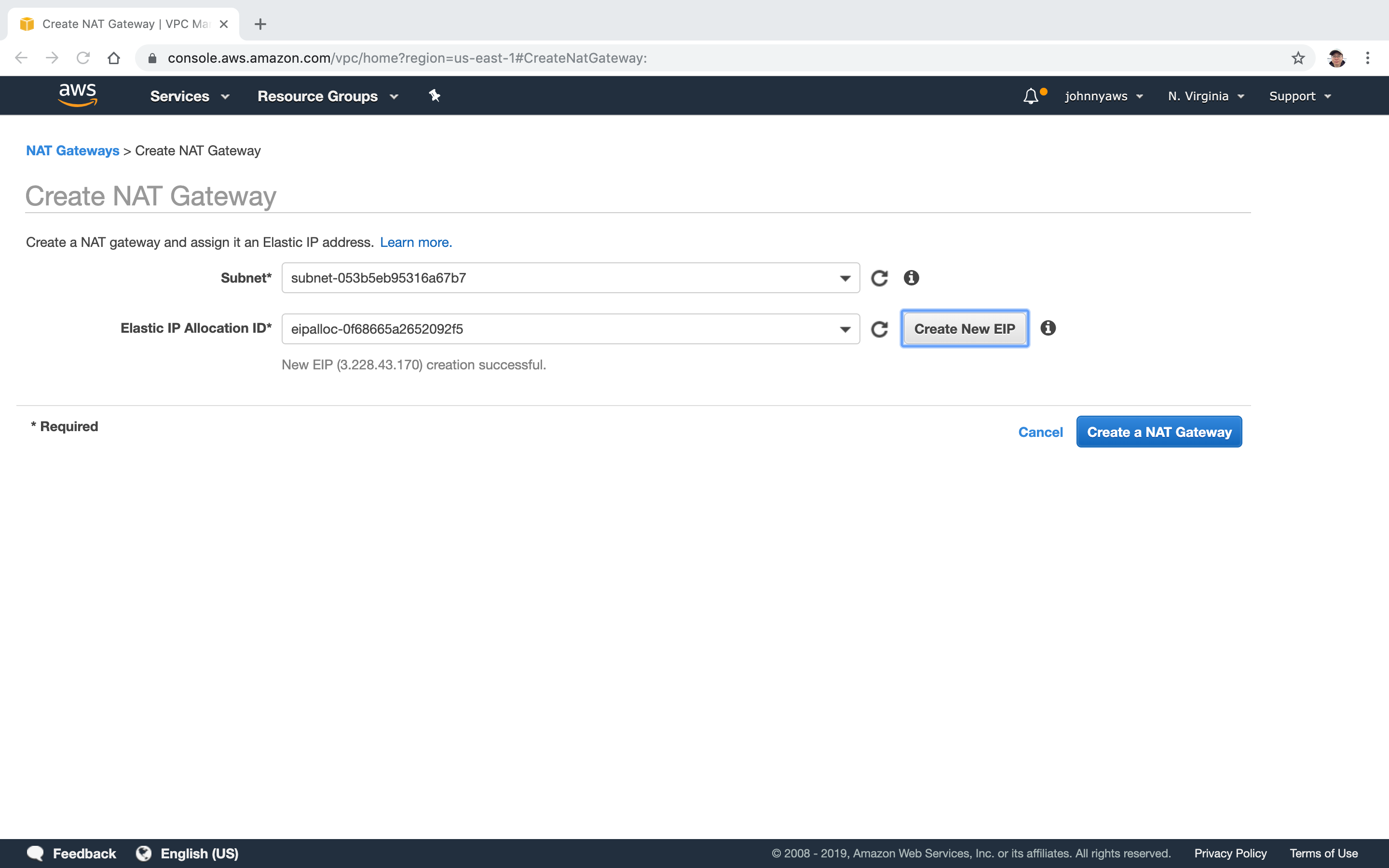
 Select the public subnet(10.0.1.0), click “Create New EIP”.
Select the public subnet(10.0.1.0), click “Create New EIP”.
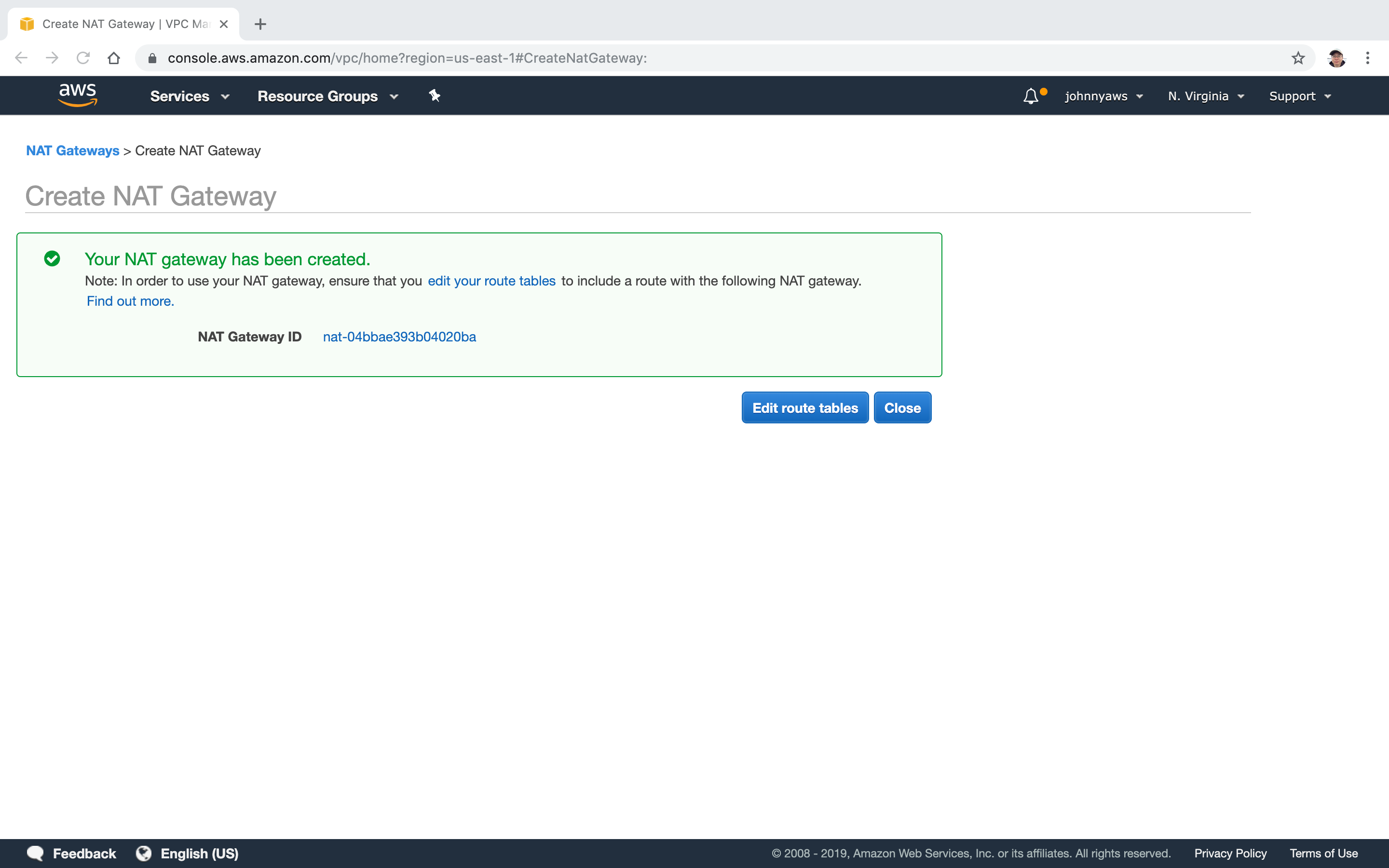
 Edit route tables.
Edit route tables.
 Select the main route table, click “Edit routes”.
Select the main route table, click “Edit routes”.
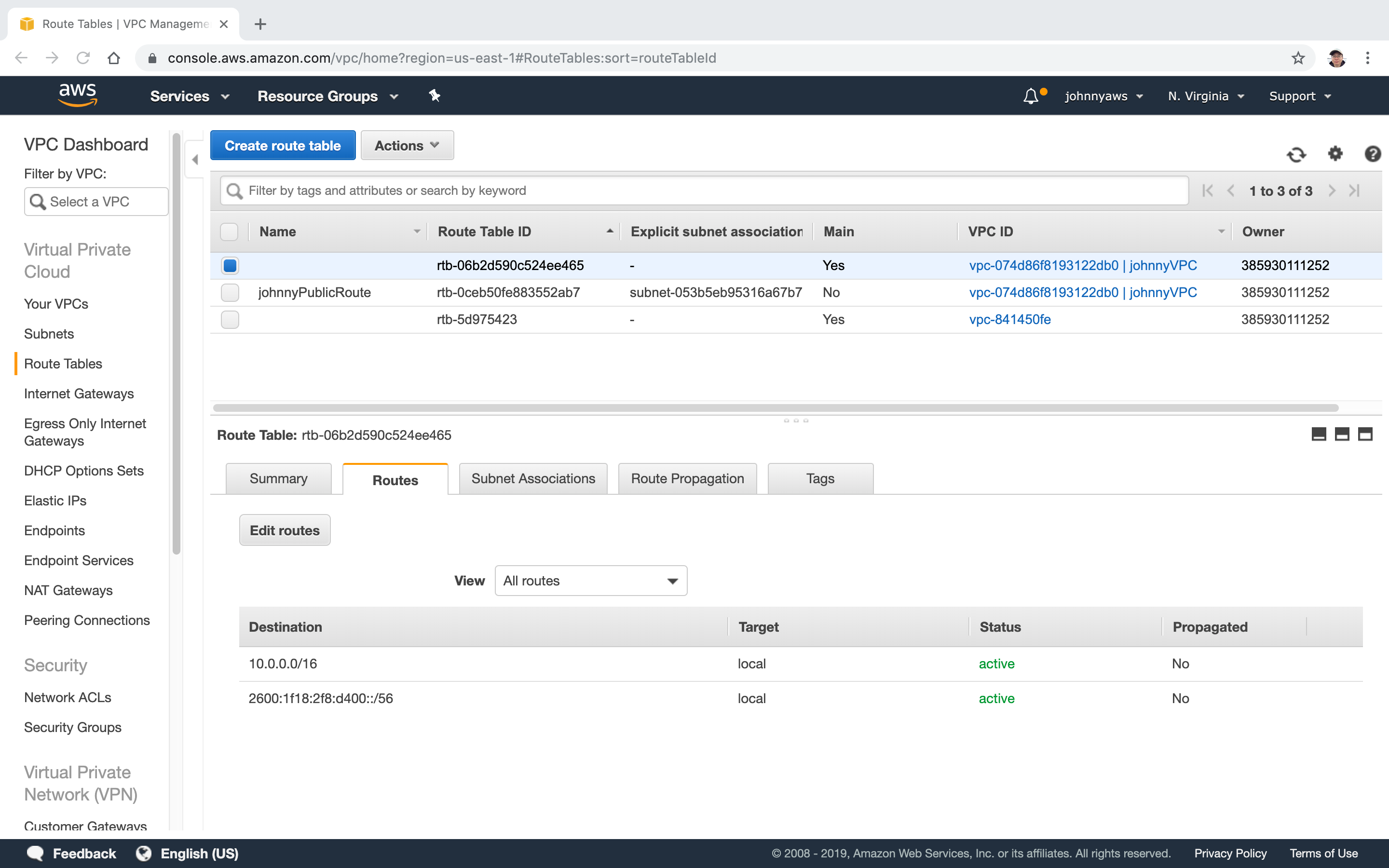 Select the NAT gateway as target, Save.
Select the NAT gateway as target, Save.
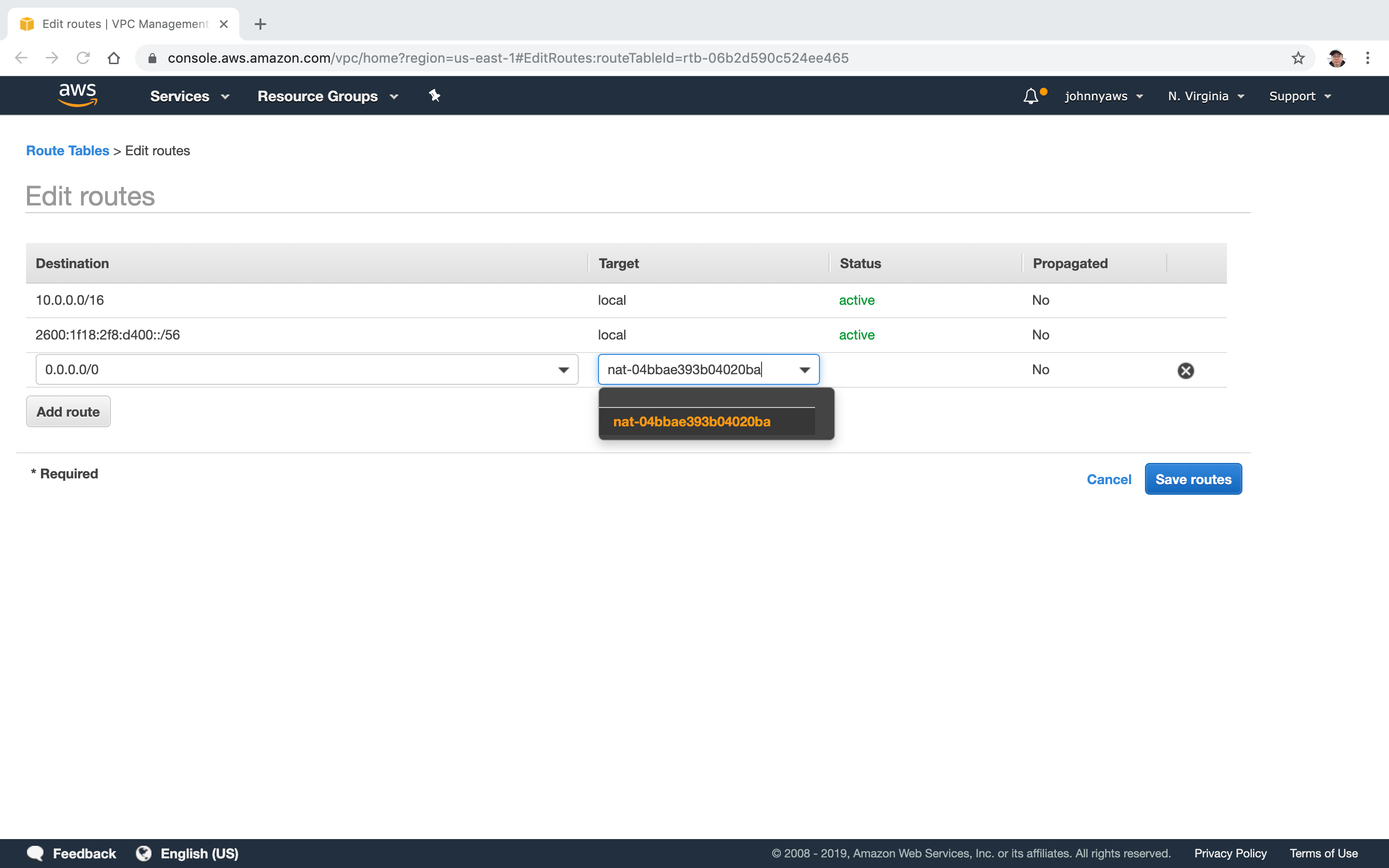 New route is created.
New route is created.
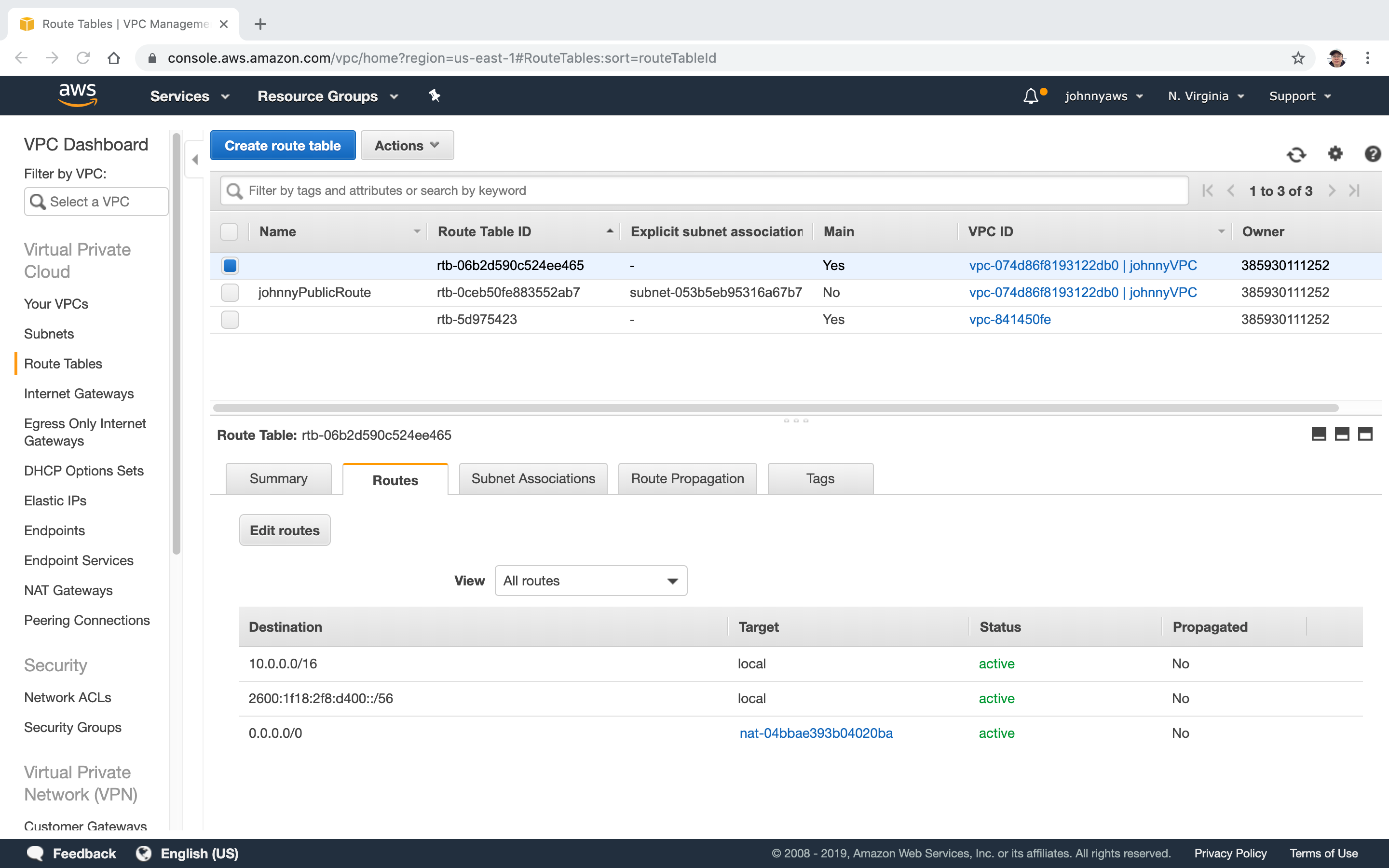 Go to Services->Networking & Content Delivery->VPC, select “NAT Gateways”, the new gateway is there.
Go to Services->Networking & Content Delivery->VPC, select “NAT Gateways”, the new gateway is there.
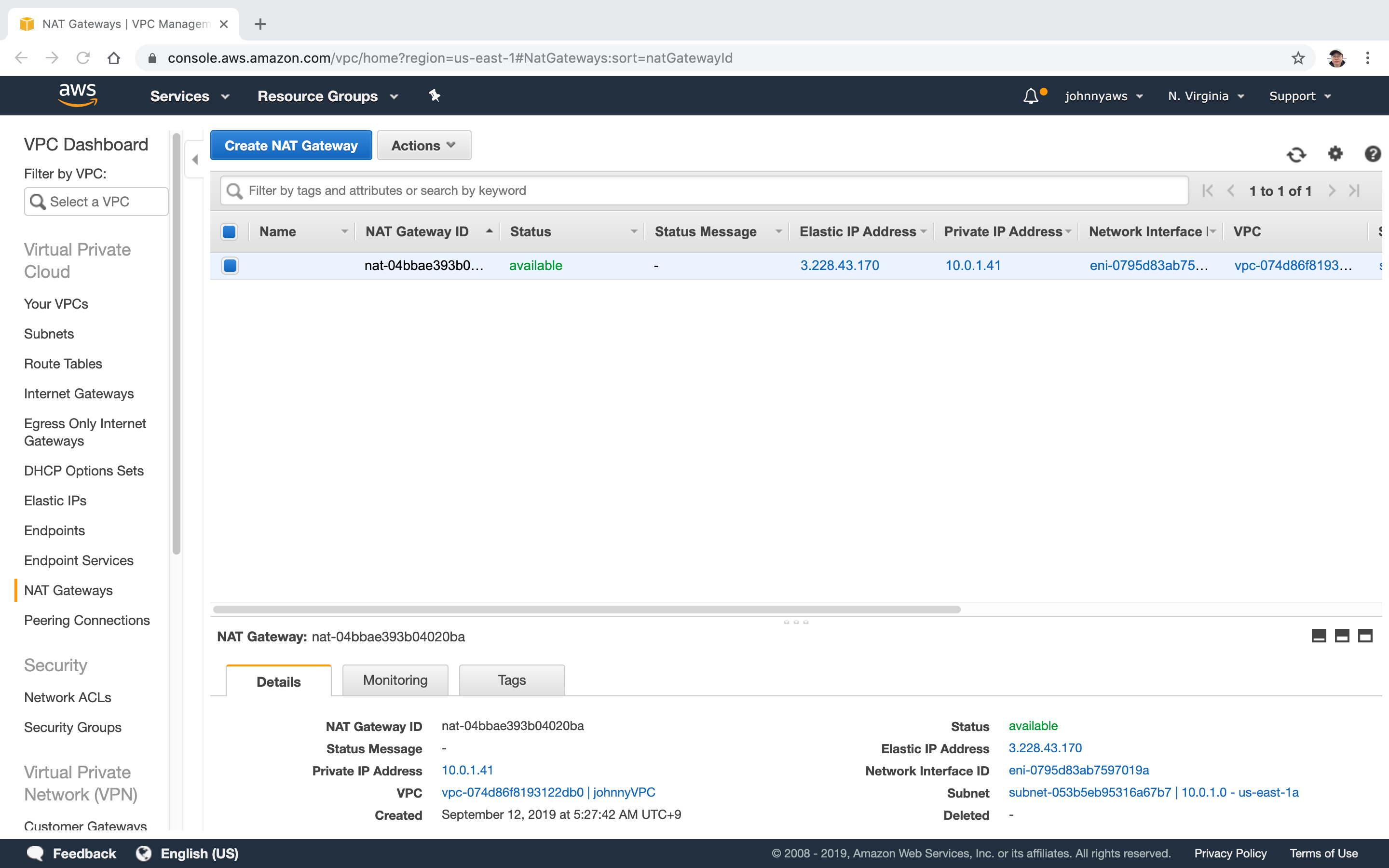 Now, the database server has the internet connection again. The VPC looks as follows.
Now, the database server has the internet connection again. The VPC looks as follows.