2464. Java Advanced - Shallow Copy vs Deep CopyShallow Copy and Deep Copy
Compare the difference between shallow copy and deep copy.
1. Shallow Copy and Deep Copy
Shallow copy is creating a new object and then copying the non static fields of the current object to the new object. If the field is a value type, a bit by bit copy of the field is performed. If the field is a reference type, the reference is copied but the referred object is not copied, therefore the original object and its clone refer to the same object. A shallow copy of an object is a new object whose instance variables are identical to the old object.
Deep copy is creating a new object and then copying the non-static fields of the current object to the new object. If a field is a value type, a bit by bit copy of the field is performed. If a field is a reference type, a new copy of the referred object is performed. A deep copy of an object is a new object with entirely new instance variables, it does not share objects with the old.
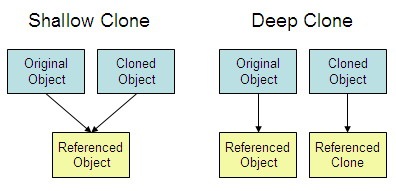
2. Example
2.1 Person Class
class Person {
private String name;
public Person(String n) {
this.name = n;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return this.name;
}
}
2.2 Shallow Copy
private static void shallowCopy() {
System.out.println("Shallow copy example:");
Person p1 = new Person("Johnny");
Person p2 = new Person("Sean");
List<Person> pList = new ArrayList<>();
pList.add(p1);
pList.add(p2);
//convert ArrayList to Array using shallow copy
Person[] pArray = pList.toArray(new Person[0]);
System.out.println("Original List = " + pList);
System.out.println("Array from ArrayList = " + Arrays.toString(pArray));
//let's change the list and array
pList.get(0).setName("David");
pArray[1].setName("Peter");
System.out.println("Modified List = " + pList);
System.out.println("Modified Array = " + Arrays.toString(pArray));
}
2.3 Deep Copy
private static void deepCopy() {
System.out.println("Deep copy example:");
Person p1 = new Person("Johnny");
Person p2 = new Person("Sean");
List<Person> pList = new ArrayList<>();
pList.add(p1);
pList.add(p2);
//convert ArrayList to Array using deep copy
Person[] pArray = new Person[pList.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < pList.size(); i++) {
Person p = pList.get(i);
Person temp = new Person(p.getName());
pArray[i] = temp;
}
System.out.println("Original List = " + pList);
System.out.println("Array from ArrayList = " + Arrays.toString(pArray));
//let's change the list and array
pList.get(0).setName("David");
pArray[1].setName("Peter");
System.out.println("Modified List = " + pList);
System.out.println("Modified Array = " + Arrays.toString(pArray));
}
2.4 Test
public static void main(String[] args) {
shallowCopy();
System.out.println();
deepCopy();
}
Output.
Shallow copy example:
Original List = [Johnny, Sean]
Array from ArrayList = [Johnny, Sean]
Modified List = [David, Peter]
Modified Array = [David, Peter]
Deep copy example:
Original List = [Johnny, Sean]
Array from ArrayList = [Johnny, Sean]
Modified List = [David, Sean]
Modified Array = [Johnny, Peter]
- In shallow copy, both the array and the list are changed by each other.
- In deep copy, the change to array or list doesn’t impact the other.